Alpha-2 agonists for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients
- PMID: 25879090
- PMCID: PMC6353054
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010269.pub2
Alpha-2 agonists for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients
Abstract
Background: Sedation reduces patient levels of anxiety and stress, facilitates the delivery of care and ensures safety. Alpha-2 agonists have a range of effects including sedation, analgesia and antianxiety. They sedate, but allow staff to interact with patients and do not suppress respiration. They are attractive alternatives for long-term sedation during mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients.
Objectives: To assess the safety and efficacy of alpha-2 agonists for sedation of more than 24 hours, compared with traditional sedatives, in mechanically-ventilated critically ill patients.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, Issue 10, 2014), MEDLINE (1946 to 9 October 2014), EMBASE (1980 to 9 October 2014), CINAHL (1982 to 9 October 2014), Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (1982 to 9 October 2014), ISI Web of Science (1987 to 9 October 2014), Chinese Biological Medical Database (1978 to 9 October 2014) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (1979 to 9 October 2014), the World Health Organization international clinical trials registry platform (to 9 October 2014), Current Controlled Trials metaRegister of controlled trials active registers (to 9 October 2014), the ClinicalTrials.gov database (to 9 October 2014), the conference proceedings citation index (to 9 October 2014) and the reference lists of included studies and previously published meta-analyses and systematic reviews for relevant studies. We imposed no language restriction.
Selection criteria: We included all randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials comparing alpha-2 agonists (clonidine or dexmedetomidine) versus alternative sedatives for long-term sedation (more than 24 hours) during mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed study quality and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information. We performed meta-analyses when more than three studies were included, and selected a random-effects model due to expected clinical heterogeneity. We calculated the geometric mean difference for continuous outcomes and the risk ratio for dichotomous outcomes. We described the effects by values and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We considered two-sided P < 0.05 to be statistically significant.
Main results: Seven studies, covering 1624 participants, met the inclusion criteria. All included studies investigated adults and compared dexmedetomidine with traditional sedatives, including propofol, midazolam and lorazepam. Compared with traditional sedatives, dexmedetomidine reduced the geometric mean duration of mechanical ventilation by 22% (95% CI 10% to 33%; four studies, 1120 participants, low quality evidence), and consequently the length of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU) by 14% (95% CI 1% to 24%; five studies, 1223 participants, very low quality evidence). There was no evidence that dexmedetomidine decreased the risk of delirium (RR 0.85; 95% CI 0.63 to 1.14; seven studies, 1624 participants, very low quality evidence) as results were consistent with both no effect and appreciable benefit. Only one study assessed the risk of coma, but lacked methodological reliability (RR 0.69; 95% CI 0.55 to 0.86, very low quality evidence). Of all the adverse events included, the most commonly reported one was bradycardia, and we observed a doubled (111%) increase in the incidence of bradycardia (RR 2.11; 95% CI 1.39 to 3.20; six studies, 1587 participants, very low quality evidence). Our meta-analysis provided no evidence that dexmedetomidine had any impact on mortality (RR 0.99; 95% CI 0.79 to 1.24; six studies, 1584 participants, very low quality evidence). We observed high levels of heterogeneity in risk of delirium (I² = 70%), but due to the limited number of studies we were unable to determine the source of heterogeneity through subgroup analyses or meta-regression. We judged six of the seven studies to be at high risk of bias.
Authors' conclusions: In this review, we found no eligible studies for children or for clonidine. Compared with traditional sedatives, long-term sedation using dexmedetomidine in critically ill adults reduced the duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU length of stay. There was no evidence for a beneficial effect on risk of delirium and the heterogeneity was high. The evidence for risk of coma was inadequate. The most common adverse event was bradycardia. No evidence indicated that dexmedetomidine changed mortality. The general quality of evidence ranged from very low to low, due to high risks of bias, serious inconsistency and imprecision, and strongly suspected publication bias. Future studies could pay more attention to children and to using clonidine
Conflict of interest statement
Ken Chen: none known Zhijun Lu: none known Yi Chun Xin: none known Yong Cai: none known Yi Chen: none known Shu Ming Pan: none known
Figures

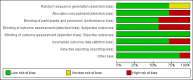
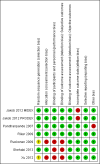







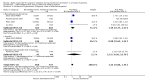



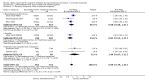

Comment in
-
Alpha-2 Agonists for Long-Term Sedation During Mechanical Ventilation in Critically Ill Patients.Am J Nurs. 2016 Feb;116(2):21. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000480489.10481.df. Am J Nurs. 2016. PMID: 26817548 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Jakob 2012 MIDEX {published data only}
-
- Jakob SM, Ruokonen E, Grounds RM, Sarapohja T, Garratt C, Pocock SJ, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2012;307(11):1151‐60. [PUBMED: 22436955] - PubMed
Jakob 2012 PRODEX {published data only}
-
- Jakob SM, Ruokonen E, Grounds RM, Sarapohja T, Garratt C, Pocock SJ, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation: two randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2012;307(11):1151‐60. [PUBMED: 22436955] - PubMed
Pandharipande 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;298(22):2644‐53. [PUBMED: 18073360] - PubMed
Riker 2009 {published data only}
-
- Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA 2009;301(5):489‐99. [PUBMED: 19188334] - PubMed
Ruokonen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ruokonen E, Parviainen I, Jakob SM, Nunes S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd ST, et al. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol/midazolam for long‐term sedation during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Medicine 2009;35(2):282‐90. [PUBMED: 18795253] - PubMed
Shehabi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early goal‐directed sedation versus standard sedation in mechanically ventilated critically III patients: A pilot study. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41(8):1983‐91. [PUBMED: 23863230] - PubMed
Xu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Xu JB, Wang YZ, Shi QS. A combined protocol for dexmedetomidine used in prolonged sedation in intensive care unit [右美托咪啶联合用药新方案用于重症医学科长时间镇静的研究]. Modern Medicine Journal of China 2012;14(12):20‐2.
References to studies excluded from this review
Arenas 2004 {published data only}
-
- Arenas‐Lopéz S, Riphagen S, Tibby SM, Durward A, Tomlin S, Davies G, et al. Use of oral clonidine for sedation in ventilated paediatric intensive care patients. Intensive Care Medicine 2004;30(8):1625‐9. [PUBMED: 15197439] - PubMed
Corbett 2005 {published data only}
-
- Corbett SM, Rebuck JA, Greene CM, Callas PW, Neale BW, Healey MA, et al. Dexmedetomidine does not improve patient satisfaction when compared with propofol during mechanical ventilation. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33(5):940‐5. [PUBMED: 15891317] - PubMed
Fang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fang SD, Zhu YS, Xu H, Jiang H. Dexmedetomidine for sedation during intubation period in postoperative patients receiving orthognathic surgery in intensive care unit [右美托咪定用于重症监护病房正颌外科术后留置气管插管患者的镇静]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies 2012;31(8):454‐7.
Feng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Feng JH, Li KP, Deng ZB. Comparison of dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation of flail chest complicated with acute pulmonary contusion patients in intensive care unit [右美托咪定与丙泊酚用于ICU连枷胸合并急性肺损伤患者镇静的效果比较]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease 2012;20(11):1772‐3.
Guo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Guo JY, Deng Q, Guo XS, Liu SQ, Zhang YH, He ZJ. Study of sedation with dexmedetomidine in postoperative patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome [右美托咪定对重症睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者术后镇静作用的研究]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army 2012;37(6):649‐52.
Herr 2003 {published data only}
-
- Herr DL, Sum‐Ping ST, England M. ICU sedation after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: dexmedetomidine‐based versus propofol‐based sedation regimens. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2003;17(5):576‐84. [PUBMED: 14579210] - PubMed
Hu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hu MJ. The sedative effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam in mechanical ventilated patients [右美托咪啶与咪达唑仑在机械通气患者中镇静作用的研究]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal 2013;25:3.
Jiang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jiang L, Ding S, Zhang YH, Zhang LP, Chen X, Zhang JB. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam/fentanyl for sedation of children with pulmonary artery hypertension after congenital cardiac surgery [右旋美托咪啶和咪达唑仑联合芬太尼镇静治疗在先心病肺动脉高压患儿术后的对比研究]. Chinese Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2012;28(8):485‐7.
Kadoi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kadoi Y, Saito S, Kawauchi C, Hinohara H, Kunimoto F. Comparative effects of propofol vs dexmedetomidine on cerebrovascular carbon dioxide reactivity in patients with septic shock. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008;100(2):224‐9. [PUBMED: 18178608] - PubMed
Kaneko 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kaneko T. Postoperative management of carotid endarterectomy with dexmedetomidine ‐ a comparison with propofol [デクスメデトミジンを用いた頸動脈内膜剥離術後管理 一プロポフォールとの比較一]. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2008;57:696‐703. [PUBMED: 18546896] - PubMed
Li 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li HQ, Hou DP, Jiang CH, Han CH. Use of dexmedetomidine in the postoperative patients with mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定在术后机械通气患者中的应用]. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2011;31(8):697‐700.
Li 2012 {published data only}
-
- Li JQ, Xiong XM, Chen XW, Chen SL, Zhou HF, Chen HW, et al. A study of dexmedetomidine in treatment of mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome [右美托咪定在急性呼吸窘迫综合征机械通气患者中的应用]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine in Intensive and Critical Care 2012;19(2):79‐82.
Li 2013 {published data only}
-
- Li ZY. The influence of dexmedetomidine on patients' renal function [右美托咪定用于计划镇静时对病人肾脏功能的影响]. Chinese Selected Doctoral Dissertations and Master's Theses Full‐Text Databases 2013; Vol. 2.
Linj 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lin JP, Wen JS, Yang JP, Lin F, Chen Y. The use of dexmedetomidine in postoperative elder patients with mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定和咪达唑仑用于术后老年患者机械通气镇静的临床观察]. Fujian Medical Journal 2012;34:76‐7.
Liu 2013a {published data only}
-
- Liu P, Xiu GH, Gu YF, Ling B. Right dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam mechanical ventilation sedative efficacy analysis [咪达唑仑对比右美托咪啶用于机械通气镇静临床疗效分析]. National Medical Frontiers of China 2013;12:31.
Liu 2013b {published data only}
-
- Liu P, Guo XC, WangD. Observation of sedative effect for ICU patients sedation using dexmedetomidine and midazolam [右美托咪定与咪达唑仑对ICU危重患者镇静效果观察]. Jilin Medical Journal 2013;32:6708‐9.
Luo 2012a {published data only}
-
- Luo J, Tan XF, Deng XK, Wu HB. The use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride in mechanical ventilated patients [盐酸右美托咪定在机械通气患者中的应用]. Hebei Medical Journal 2012;34:989‐90.
Luo 2012b {published data only}
-
- Luo L, Zeng M, Kuan KP. Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine with midazolam on the respiration and circulation of mechanically ventilated patients [右美托咪啶和咪达唑仑对机械通气患者呼吸和循环影响的比较]. Chinese Journal of Emergency Medicine 2012;21(3):295‐8.
Luo 2012c {published data only}
-
- Luo ZZ, Xiao YF. The sedative effect research of dexmedetomidine in the ICU patients [右美托咪啶对重症治疗室患者镇静效果研究]. China Modern Medicine 2012;19(279):74‐5.
Peng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Peng M, Fang WQ, Yu XT, Cai JY. Clinical application of dexmedetomidine in intensive care unit [右美托咪定在重症监护病房镇静中的临床应用]. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2011;31(3):197‐9.
Pu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pu N, Wu Y, Cao QT. Clinical observation of sedate treatment of dexmedetomidine on ICU patients [右美托咪定在重症监护患者镇静中的临床观察]. Guide of China Medicine 2012;10:24‐5.
Qu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Qu G. The clinical observation of dexmedetomidine for sedation of the patients after CABG in the ICU [右美托咪啶用于CABG术后患者ICU镇静的临床观察]. Chinese Selected Doctoral Dissertations and Master's Theses Full‐Text Databases 2011; Vol. 10.
Su 2014 {published data only}
-
- Su J, Li Y. Observation of the sedative effects and adverse reactions of dexmedetomidine on the patients with craniocerebral injury [右美托咪定对颅脑损伤患者的镇静效果及不良反应观察]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacoepidemiology 2014;6:348‐50.
Tasdogan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N, Yuksel M. Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal pressure in severe sepsis. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2009;21(6):394‐400. [PUBMED: 19833271] - PubMed
Tian 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tian ST, Huang H. The clinical effect of dexmedetomidine in ventilated patients sedation [盐酸右美托咪定用于机械通气患者镇静的临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacovigilance 2010;7(45):515‐7.
Tobias 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tobias JD, Berkenbosch JW. Sedation during mechanical ventilation in infants and children: dexmedetomidine versus midazolam. Southern Medical Journal 2004;97(5):451‐5. [PUBMED: 15180019] - PubMed
Venn 2001 {published data only}
-
- Venn RM, Grounds RM. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation in the intensive care unit: patient and clinician perceptions. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2001;87(5):684‐90. [PUBMED: 11878517] - PubMed
Wan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wan LJ, Huang QQ, Yue JX, Lin L, Li SH. Comparison of sedative effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for post‐operative patients undergoing mechanical ventilation in surgical intensive care unit [右美托咪啶与咪达唑仑用于外科重症监护病房术后机械通气患者镇静的比较研究]. Chinese Critical Care Medicine 2011;23:543‐6. [PUBMED: 21944176] - PubMed
Wang 2011a {published data only}
-
- Wang CY, Shang M, Cheng L, Zhou QS. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation in critically ill patients [右美托咪啶和咪达唑仑用于危重症患者镇静效应的比较]. Journal of Hainan Medical University 2011;17(96):695‐7.
Wang 2011b {published data only}
-
- Wang HL, Liu HT, Yu KJ. Comparison of dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation of eclampsia patients in intensive care unit [右美托咪定与丙泊酚用于重症监护病房子痫患者镇静的效果比较]. Shanghai Medical Journal 2011;34(8):613‐5.
Wang 2011c {published data only}
-
- Wang KM, Sun YH, Hou YQ. Clinical observation of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride on sedation and analgesia of ICU patients [盐酸右美托咪定用于重症监护患者镇静及镇痛的临床观察]. Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology (Medical Science) 2011;29(4):267‐8, 271.
Wang 2012a {published data only}
-
- Wang HB, Li KP, Deng ZB. The sedation effect comparison of dexmedetomidine and midazolam to treat patients with flail chest complicated with pulmonary injury in ICU [右美托咪定与咪达唑仑用于重症监护病房连枷胸并肺损伤患者镇静的效果比较]. Journal of Heze Medical College 2012;24(90):4‐5, 60.
Wang 2012b {published data only}
-
- Wang H. Curative effect observation of dexmedetomidine in ICU sedation [右美托嘧啶在ICU中镇静的疗效观察]. Guide of China Medicine 2012;10:153‐4.
Wang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wang S, Zhu L. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine and midazolam combined with fentanyl on sedation of postoperative and mechanically ventilated ICU patients [右美托咪定和咪达唑仑复合芬太尼对ICU术后机械通气患者镇静的影响]. Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies 2014;3:308‐10.
Xiao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Xiao Y, Wang Y, Wu Y. Evaluation on sedation effect of dexmedetomidine used in ICU [右美托咪啶用于重症监护病房镇静的效果评价]. China Pharmaceuticals 2013;20:37‐9.
Yang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Yang S, Xie J, Huo K, Xu F, Chen L. Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for sedation of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease underwent mechanical ventilation [右美托咪啶与咪达唑仑对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期机械通气患者镇静的比较研究]. Chinese Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2013;5:481‐4.
Yao 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yao L, Zhou XM, Zhao JJ. The role of dexmedetomidine in treatment of serious patients in intensive care unit [右美托咪啶在重症监护病房应用的研究]. Chinese Critical Care Medicine 2010;22(10):632‐4. [PUBMED: 20977851] - PubMed
Yuan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yuan L, Ma HY. Comparasion of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for ICU patients with mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定与咪达唑仑用于ICU机械通气患者镇静疗效比较]. Jilin Medical Journal 2014;12:2555.
Zhang 2012a {published data only}
-
- Zhang BC, Zhong ZY, Li HZ, Liang XJ, Li J, Shen J. Comparison of the sedative effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for critically Ill patients [右美托咪定与咪达唑仑对危重病患者镇静效果的比较]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Medicine 2012;19(97):290‐2.
Zhang 2012b {published data only}
-
- Zhang J, Lou TZ, Zhang N, Xu JL, Jiu H, Qiu ZL, et al. Feasibility of dexmedetomidine in sedation for chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases patients undergoing mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定在慢性阻塞性肺疾病需机械通气患者镇静中的应用]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies 2012;31:451‐4.
Zhang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhang C, Wang Y, Du Z, Zhang S, Chang X, Zhang W. Clinical study of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol for post‐operative patients in intensive care unit [右美托咪定联合丙泊酚在ICU中的应用]. Medical Journal of Wuhan University 2013;3:395‐8.
Zhang 2014a {published data only}
-
- Zhang W, Zhang B, Liu N. Analysis of curative effect of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride in tube drawing from patients with mechanical ventilation [盐酸右美托咪定用于机械通气患者撤机拔管的疗效分析]. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine 2014;5:828‐30.
Zhang 2014b {published data only}
-
- Zhang W, Tan J, Guan R, Xie S. Clinical study of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride in mechanical ventilation for critical patients [盐酸右美托咪定在危重症患者机械通气的临床研究]. China Medicine and Pharmacy 2014;12:82‐3.
Zheng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zheng M, Tian G, Li HN, Liu Y, Wang Q. Effect evaluation of dexmedetomidine and midazolam in infants in mechanical ventilation [婴幼儿机械通气时使用右旋美托咪定和咪达唑仑的效果评价]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine 2012;12:2342‐4, 2348.
Zhou 2012a {published data only}
-
- Zhou J. Clinical research of sedation with dexmedetomidine for surgical patients requiring mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定用于外科手术后需机械通气患者镇静治疗的临床观察]. Chinese Selected Doctoral Dissertations and Master's Theses Full‐Text Databases 2012; Vol. 11.
Zhou 2012b {published data only}
-
- Zhou LX, Yang TF. The sedative effect of dexmedetomidine in ICU patients receiving mechanical ventilation [右美托咪定用于ICU机械通气患者的镇静效果及护理]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal 2012;24(150):187‐8.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Tao 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tao SY, Li WX, Qi XF. Sedative effects of dexmedetomidine on patients in intensive care unit [右美托咪定在ICU患者镇静中的疗效分析]. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2011;31(12):1103‐5.
References to ongoing studies
NCT01059929 {published data only}
-
- NCT01059929. Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol in the Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01059929 accessed 10 December 2014.
NCT01760967 {published data only}
-
- NCT01760967. Dexmedetomidine for Sepsis in ICU Randomized Evaluation Trial (DESIRE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01760967 accessed 10 December 2014.
Additional references
Agarwal 2010
Aho 1991
-
- Aho MS, Erkola OA, Scheinin H, Lehtinen AM, Korttila KT. Effect of intravenously administered dexmedetomidine on pain after laparoscopic tubal ligation. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1991;73(2):112‐8. [PUBMED: 1854025] - PubMed
Aitken 2012
-
- Aitken LM, Bucknall T, Kent B, Mitchell M, Burmeister E, Keogh SJ. Protocol directed sedation versus non‐protocol directed sedation to reduce duration of mechanical ventilation in mechanically ventilated intensive care patients. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009771] - DOI - PubMed
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical
-
- Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System. WHO collaborating centre for drugs statistics methodology. International language for drug utilization research. www.whocc.no/ (Accessed 31st October 2012).
Bailey 1991
-
- Bailey PL, Sperry RJ, Johnson GK, Eldredge SJ, East KA, East TD, et al. Respiratory effects of clonidine alone and combined with morphine, in humans. Anesthesiology 1991;74(1):43‐8. [PUBMED: 1898841] - PubMed
Barr 2013
-
- Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gélinas C, Dasta JF, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41(1):263‐306. [PUBMED: 23269131] - PubMed
Blaudszun 2012
-
- Blaudszun G, Lysakowski C, Elia N, Tramèr MR. Effect of perioperative systemic α2 agonists on postoperative morphine consumption and pain intensity: systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 2012 Jun;116(6):1312‐22. [PUBMED: 22546966] - PubMed
Bohrer 1990
-
- Bohrer H, Bach A, Layer M, Werning P. Clonidine as a sedative adjunct in intensive care. Intensive Care Medicine 1990;16(4):265‐6. [PUBMED: 2358560] - PubMed
Breen 2005
-
- Breen D, Karabinis A, Malbrain M, Morais R, Albrecht S, Jarnvig IL, et al. Decreased duration of mechanical ventilation when comparing analgesia‐based sedation using remifentanil with standard hypnotic‐based sedation for up to 10 days in intensive care unit patients: a randomised trial. Critical Care 2005;9(3):R200‐10. [PUBMED: 15987391] - PMC - PubMed
Brook 1999
-
- Brook AD, Ahrens TS, Schaiff R, Prentice D, Sherman G, Shannon W, et al. Effect of a nursing‐implemented sedation protocol on the duration of mechanical ventilation. Critical Care Medicine 1999;27(12):2609‐15. [PUBMED: 10628598] - PubMed
Burry 2014
-
- Burry L, Rose L, McCullagh I, Ferguson ND, Ferguson D, Mehta S. Daily sedation interruption versus no daily sedation interruption for critically ill adult patients requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009176.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Carney 2013
Carson 2006
-
- Carson SS, Kress JP, Rodgers JE, Vinayak A, Campbell‐Bright S, Levitt J, et al. A randomized trial of intermittent lorazepam versus propofol with daily interruption in mechanically ventilated patients. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34(5):1326‐32. [PUBMED: 16540958] - PubMed
Czaja 2009
-
- Czaja AS, Zimmerman JJ. The use of dexmedetomidine in critically ill children. Paediatric Critical Care Medicine 2009;10(3):381‐6. [PUBMED: 19325505] - PubMed
Dahmani 2010
-
- Dahmani S, Brasher C, Stany I, Golmard J, Skhiri A, Bruneau B, et al. Premedication with clonidine is superior to benzodiazepines. A meta analysis of published studies. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2010;54(4):397‐402. [PUBMED: 20085541] - PubMed
Dasta 2010
-
- Dasta JF, Kane‐Gill SL, Pencina M, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Wisemandle W, et al. A cost‐minimization analysis of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for long‐term sedation in the intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(2):497‐503. [PUBMED: 19789442] - PubMed
De Wit 2006
-
- Wit M, Best AM, Epstein SK, Greenblatt DJ. Lorazepam concentrations, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in a cohort of mechanically ventilated ICU patients. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;44(10):466‐73. [PUBMED: 17063976] - PubMed
Dubois 2001
-
- Dubois MJ, Bergeron N, Dumont M, Dial S, Skrobik Y. Delirium in an intensive care unit: a study of risk factors. Intensive Care Medicine 2001;27(8):1297‐304. [PUBMED: 11511942] - PubMed
Ely 2004
-
- Ely EW, Shintani A, Truman B, Speroff T, Gordon SM, Harrell FEJ, et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA 2004;291(14):1753‐62. [PUBMED: 15082703] - PubMed
Fraser 2007
-
- Fraser GL, Riker RR. Sedation and analgesia in the critically ill adult. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology 2007;20(2):119‐23. [PUBMED: 17413394] - PubMed
Friedrich 2012
-
- Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, Beyene J. Ratio of geometric means to analyze continuous outcomes in meta‐analysis: comparison to mean differences and ratio of arithmetic means using empiric data and simulation. Statistic in Medicine 2012;31(17):1857‐86. [PUBMED: 22438170] - PubMed
Gehlbach 2002
-
- Gehlbach BK, Kress JP. Sedation in the intensive care unit. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2002;8(4):290‐8. [PUBMED: 12386488] - PubMed
Girard 2008
-
- Girard TD, Kress JP, Fuchs BD, Thomason JW, Schweickert WD, Pun BT, et al. Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled trial): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 2008;371(9607):126–34. [PUBMED: 18191684] - PubMed
Gregoretti 2009
-
- Gregoretti C, Moglia B, Pelosi P, Navalesi P. Clonidine in perioperative medicine and intensive care unit: more than an anti‐hypertensive drug. Current Drug Targets 2009;10(8):799‐814. [PUBMED: 19702526] - PubMed
Gupta 2012
-
- Gupta P, Whiteside W, Sabati A, Tesoro TM, Gossett JM, Tobias JD, et al. Safety and efficacy of prolonged dexmedetomidine use in critically ill children with heart disease. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2012;13(6):660‐6. [PUBMED: 22791093] - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Hall 2000
-
- Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Barney JA, Arain SR, Ebert TJ. Sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties of small‐dose dexmedetomidine infusions. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2000;90(3):699‐705. [PUBMED: 10702460] - PubMed
Hall 2001
-
- Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Ebert TJ. Sedative, analgesic and cognitive effects of clonidine infusions in humans. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2001;86(1):5‐11. [PUBMED: 11575409] - PubMed
Hashiba 2003
-
- Hashiba E, Hirota K, Suzuki K, Matsuki A. Effects of propofol on bronchoconstriction and bradycardia induced by vagal nerve stimulation. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2003;47(9):1059‐63. [PUBMED: 12969095] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2008
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboratio, 2011. available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hozo 2005
Hsu 2004
-
- Hsu YW, Cortinez LI, Robertson KM, Keifer J‐C, Sum‐Ping ST, Moretti EW, et al. Dexmedetomidine pharmacodynamics: part I: crossover comparison of the respiratory effects of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology 2004;101(5):1066‐76. [PUBMED: 15505441] - PubMed
Huupponen 2008
-
- Huupponen E, Maksimow A, Lapinlampi P, Särkelä M, Saastamoinen A, Snapir A, et al. Electroencephalogram spindle activity during dexmedetomidine sedation and physiological sleep. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2008; Vol. 52, issue 2:289‐94. [PUBMED: 18005372] - PubMed
Ise 2002
-
- Ise T, Yamashiro M, Furuya H. Clonidine as a drug for intravenous conscious sedation. Odontology/the Society of the Nippon Dental University 2002;90(1):57‐63. [PUBMED: 12955567] - PubMed
Jaakola 1991
-
- Jaakola ML, Salonen M, Lehtinen R, Scheinin H. The analgesic action of dexmedetomidine‐‐a novel alpha 2‐adrenoceptor agonist‐‐in healthy volunteers. Pain 1991 Sep;46(3):281‐5. [PUBMED: 1684653] - PubMed
Jamadarkhana 2010
Jessen 2013
Kam 2007
-
- Kam PC, Cardone D. Propofol infusion syndrome. Anaesthesia 2007;62(7):690‐701. [PUBMED: 17567345] - PubMed
Lambert 2014
Lin 2012
Machado 2011
-
- Machado FO, Moritz RD, Berbigier EJ, Berbigier RJ. Comparison between clonidine and dexmedetomidine for sedation and analgesia in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Medicine. 2011; Vol. Conference: 24th Annual Congress of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, ESICM LIVES 2011 Berlin Germany.
Maclaren 2013
-
- Maclaren R, Preslaski CR, Mueller SW, Kiser TH, Fish DN, Lavelle JC, et al. A randomized, double‐blind pilot study of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for intensive care unit sedation: patient recall of their experiences and short‐term psychological outcomes. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine 2013 [Epub ahead of print]. [PUBMED: 24227448] - PubMed
Mantz 2011
-
- Mantz J, Josserand J, Hamada S. Dexmedetomidine: new insights. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(1):3‐6. [PUBMED: 20881501] - PubMed
Martin 2003
-
- Martin E, Ramsay G, Mantz J, Sum‐Ping ST. The role of the alpha2‐adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in postsurgical sedation in the intensive care unit. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine 2003;18(1):29‐41. [PUBMED: 15189665] - PubMed
Mason 2009
-
- Mason KP, O'Mahony E, Zurakowski D, Libenson MH. Effects of dexmedetomidine sedation on the EEG in children. Paediatric Anaesthesia 2009;19(12):1175‐83. [PUBMED: 20017865] - PubMed
Meert 1994
-
- Meert TF, Kock M. Potentiation of the analgesic properties of fentanyl‐like opioids with alpha 2‐adrenoceptor agonists in rats. Anesthesiology 1994 Sep;81(3):677‐88. [PUBMED: 7916547] - PubMed
Mehta 2011
-
- Mehta S, McCullagh I, Burry L. Current sedation practices: lessons learned from international surveys. Critical Care Clinics 2011;29(4):607‐24. [PUBMED: 19576525] - PubMed
Miller 1998
-
- Miller LJ, Wiles‐Pfeifler R. Propofol for the long‐term sedation of a critically ill patient. American Journal of Critical Care 1998;7(1):73‐6. [PUBMED: 9429686] - PubMed
Oto 2012
-
- Oto J, Yamamoto K, Koike S, Onodera M, Imanaka H, Nishimura M. Sleep quality of mechanically ventilated patients sedated with dexmedetomidine. Intensive Care Medicine 2012;38(12):1982‐9. [PUBMED: 22961436] - PubMed
Pandharipande 2006
-
- Pandharipande P, Shintani A, Peterson J, Pun BT, Wilkinson GR, Dittus RS, et al. Lorazepam is an independent risk factor for transitioning to delirium in intensive care unit patients. Anesthesiology 2006;104(1):21‐6. [PUBMED: 16394685] - PubMed
Pandharipande 2008
Pandharipande 2010
Pichot 2012
-
- Pichot C, Ghignone M, Quintin L. Dexmedetomidine and clonidine: from second‐to‐first‐line sedative agents in the critical care setting?. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine 2012;27(4):219‐37. [PUBMED: 21525113] - PubMed
Precedex Prescribing Information
-
- Precedex prescribing information. www.precedex.com/safety/full‐prescribing‐information (Accessed 31st October 2012).
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rubino 2010
-
- Rubino AS, Onorati F, Caroleo S, Galato E, Nucera S, Amantea B, et al. Impact of clonidine administration on delirium and related respiratory weaning after surgical correction of acute type‐A aortic dissection: results of a pilot study. Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 2010;10(1):58‐62. [PUBMED: 19854793] - PubMed
Schnabel 2013
-
- Schnabel A, Meyer‐Frießem CH, Reichl SU, Zahn PK, Pogatzki‐Zahn EM. Is intraoperative dexmedetomidine a new option for postoperative pain treatment? A meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain 2013 Jul;154(7):1140‐9. [PUBMED: 23706726] - PubMed
Shehabi 2012
-
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early intensive care sedation predicts long‐term mortality in ventilated critically ill patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2012;186(8):724‐31. [PUBMED: 22859526] - PubMed
Shelly 1991
-
- Shelly MP, Sultan MA, Bodenham A, Park GR. Midazolam infusions in critically ill patients. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 1991;8(1):21‐7. [PUBMED: 1678701] - PubMed
Spies 2003
-
- Spies CD, Otter HE, Huske B, Sinha P, Neumann T, Rettig J, et al. Alcohol withdrawal severity is decreased by symptom‐orientated adjusted bolus therapy in the ICU. Intensive Care Medicine 2003;29(12):2230‐8. [PUBMED: 14557857] - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. [PUBMED: 21784880] - PubMed
Strom 2010
-
- Strom T, Martinussen T, Toft P. A protocol of no sedation for critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomised trial. Lancet 2010;375(9713):475‐80. [PUBMED: 20116824] - PubMed
Tan 2010
-
- Tan JA, Ho KM. Use of dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic agent in critically ill adult patients: a meta‐analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2010;36(6):926‐39. [PUBMED: 20376429] - PubMed
Tanios 2009
-
- Tanios MA, Wit M, Epstein SK, Devlin JW. Perceived barriers to the use of sedation protocols and daily sedation interruption: a multidisciplinary survey. Journal of Critical Care 2009;24(1):66‐73. [PUBMED: 19272541] - PubMed
Tejani 2010
-
- Tejani AM, Schwenger E. Comment on dexmedetomidine systematic review and meta‐analysis methodology. Intensive Care Medicine 2010;36(11):1974; author reply 1975. [PUBMED: 20689913] - PubMed
Tham 2005
Thompson 2002
-
- Thompson SG, Higgins JP. How should meta‐regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted?. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1559‐73. [PUBMED: 12111920] - PubMed
Treggiari 2009
-
- Treggiari MM, Romand JA, Yanez ND, Deem SA, Goldberg J, Hudson L, et al. Randomized trial of light versus deep sedation on mental health after critical illness. Critical Care Medicine 2009;37(9):2527‐34. [PUBMED: 19602975] - PubMed
Van Eijk 2011
-
- Eijk MM, Boogaard M, Marum RJ, Benner P, Eikelenboom P, Honing ML, et al. Routine use of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit: a multicenter study. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2011;184(3):340‐4. [PUBMED: 21562131] - PubMed
Viechtbauer 2010
-
- Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta‐analyses in R with the metafor package.. Journal of Statistical Software 2010;36(3):1‐48.
Virtanen 1988
-
- Virtanen R, Savola JM, Saano V, Nyman L. Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of medetomidine as an alpha 2‐adrenoceptor agonist. European Journal of Pharmacology 1988;150(1‐2):9‐14. [PUBMED: 2900154] - PubMed
Watling 1996
-
- Watling SM, Johnson M, Yanos J. A method to produce sedation in critically ill patients. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 1996;30(11):1227‐31. [PUBMED: 8913400] - PubMed
Watson 2008
Wunsch 2009
-
- Wunsch H, Kahn JM, Kramer AA, Rubenfeld GD. Use of intravenous infusion sedation among mechanically ventilated patients in the United States. Critical Care Medicine 2009;37(12):3031‐9. [PUBMED: 19633543] - PubMed
Wunsch 2012
Xia 2013
-
- Xia ZQ, Chen SQ, Yao X, Xie CB, Wen SH, Liu KX. Clinical benefits of dexmedetomidine versus propofol in adult intensive care unit patients: a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of Surgical Research 2013;185(2):833‐43. [PUBMED: 23910886] - PubMed
Zhuo 2012
-
- Zhuo S, Zheng J, Llu B. Sedative effect of dexmedetomidine versus propofol on postoperative patients in ICU: a systematic review. Chinese Journal of Evidence‐Based Medicine 2012;12(6):686‐93. [EMBASE: 2012409765]
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

