First rank symptoms for schizophrenia
- PMID: 25879096
- PMCID: PMC7079421
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010653.pub2
First rank symptoms for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Early and accurate diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia may have long-term advantages for the patient; the longer psychosis goes untreated the more severe the repercussions for relapse and recovery. If the correct diagnosis is not schizophrenia, but another psychotic disorder with some symptoms similar to schizophrenia, appropriate treatment might be delayed, with possible severe repercussions for the person involved and their family. There is widespread uncertainty about the diagnostic accuracy of First Rank Symptoms (FRS); we examined whether they are a useful diagnostic tool to differentiate schizophrenia from other psychotic disorders.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of one or multiple FRS for diagnosing schizophrenia, verified by clinical history and examination by a qualified professional (e.g. psychiatrists, nurses, social workers), with or without the use of operational criteria and checklists, in people thought to have non-organic psychotic symptoms.
Search methods: We conducted searches in MEDLINE, EMBASE, and PsycInfo using OvidSP in April, June, July 2011 and December 2012. We also searched MEDION in December 2013.
Selection criteria: We selected studies that consecutively enrolled or randomly selected adults and adolescents with symptoms of psychosis, and assessed the diagnostic accuracy of FRS for schizophrenia compared to history and clinical examination performed by a qualified professional, which may or may not involve the use of symptom checklists or based on operational criteria such as ICD and DSM.
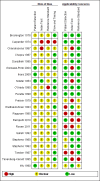
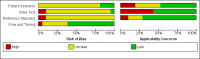
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently screened all references for inclusion. Risk of bias in included studies were assessed using the QUADAS-2 instrument. We recorded the number of true positives (TP), true negatives (TN), false positives (FP), and false negatives (FN) for constructing a 2 x 2 table for each study or derived 2 x 2 data from reported summary statistics such as sensitivity, specificity, and/or likelihood ratios.
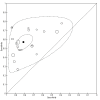
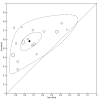
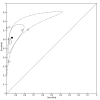
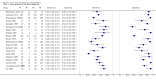
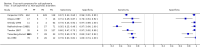
Main results: We included 21 studies with a total of 6253 participants (5515 were included in the analysis). Studies were conducted from 1974 to 2011, with 80% of the studies conducted in the 1970's, 1980's or 1990's. Most studies did not report study methods sufficiently and many had high applicability concerns. In 20 studies, FRS differentiated schizophrenia from all other diagnoses with a sensitivity of 57% (50.4% to 63.3%), and a specificity of 81.4% (74% to 87.1%) In seven studies, FRS differentiated schizophrenia from non-psychotic mental health disorders with a sensitivity of 61.8% (51.7% to 71%) and a specificity of 94.1% (88% to 97.2%). In sixteen studies, FRS differentiated schizophrenia from other types of psychosis with a sensitivity of 58% (50.3% to 65.3%) and a specificity of 74.7% (65.2% to 82.3%).
Authors' conclusions: The synthesis of old studies of limited quality in this review indicates that FRS correctly identifies people with schizophrenia 75% to 95% of the time. The use of FRS to diagnose schizophrenia in triage will incorrectly diagnose around five to 19 people in every 100 who have FRS as having schizophrenia and specialists will not agree with this diagnosis. These people will still merit specialist assessment and help due to the severity of disturbance in their behaviour and mental state. Again, with a sensitivity of FRS of 60%, reliance on FRS to diagnose schizophrenia in triage will not correctly diagnose around 40% of people that specialists will consider to have schizophrenia. Some of these people may experience a delay in getting appropriate treatment. Others, whom specialists will consider to have schizophrenia, could be prematurely discharged from care, if triage relies on the presence of FRS to diagnose schizophrenia. Empathetic, considerate use of FRS as a diagnostic aid - with known limitations - should avoid a good proportion of these errors.We hope that newer tests - to be included in future Cochrane reviews - will show better results. However, symptoms of first rank can still be helpful where newer tests are not available - a situation which applies to the initial screening of most people with suspected schizophrenia. FRS remain a simple, quick and useful clinical indicator for an illness of enormous clinical variability.
Conflict of interest statement
Karla Soares‐Weiser ‐ currently works for Enhance Reviews Ltd, a company that carries out systematic reviews mostly for the public sector, it currently does not provide services for the pharmaceutical industry.
Nicola Maayan ‐ currently works for Enhance Reviews Ltd, a company that carries out systematic reviews mostly for the public sector, it currently do not provide services for the pharmaceutical industry.
Hanna Bergman ‐ currently works for Enhance Reviews Ltd, a company that carries out systematic reviews mostly for the public sector, it currently does not provide services for the pharmaceutical industry.
Clare Davenport ‐ none known.
Sarah Grabowski ‐ none known.
Amanda Kirkham ‐ none known.
Clive E Adams ‐ none known.
Figures
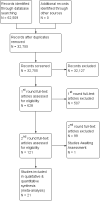

Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Brockington 1978 {published data only}
-
- Brockington IF, Kendell RE, Leff JP. Definitions of schizophrenia: concordance and prediction of outcome. Psychological Medicine 1978; Vol. 8, issue 3:387‐98. [0033‐2917: (Print).] - PubMed
-
- Kendell RE, Brockington IF, Leff JP. Prognostic implications of six alternative definitions of schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1979;36(1):25‐31. - PubMed
Carpenter 1974 {published data only}
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Strauss JS, Muleh S. Are there pathognomonic symptoms in schizophrenia? An empiric investigation of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms. Archives of General Psychiatry 1973;28(6):847‐52. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Strauss JS. Cross‐cultural evaluation of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms of schizophrenia: a report from the International Pilot Study of Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1974; Vol. 131, issue 6:682‐7. [0002‐953X] - PubMed
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Strauss JS, Bartko JJ. The diagnosis and understanding of schizophrenia. Part I. Use of signs and symptoms for the identification of schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1974;11:37‐49. [0586‐7614: (Print)]. - PubMed
Chandrasena 1987 {published data only}
-
- Chandrasena R. Schneider's First Rank Symptoms: An international and interethnic comparative study. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1987; Vol. 76, issue 5:574‐8. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
Chopra 1987 {published data only}
-
- Chopra H, Gunter M. Diagnostic value of Schneider's first rank symptoms in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987; Vol. 150:132. [0007‐1250] - PubMed
Daradkeh 1995 {published data only}
-
- Daradkeh TK, El‐Rufaie OEF, Younis YO, Ghubash R. The diagnostic stability of ICD‐10 psychiatric diagnoses in clinical practice. European Psychiatry 1997;12:136‐9. - PubMed
-
- Daradkeh TK, Hamdi E, Amin Y. Schneider's first‐rank symptoms of schizophrenia in an Arab patient population: Their prevalence and diagnostic validity. Arab Journal of Psychiatry 1995;6:39‐50.
Gonzalez‐Pinto 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez‐Pinto A, Os J, Peralta V, Perez de Heredia JL, Mosquera F, Aldama A, et al. The role of age in the development of Schneiderian symptoms in patients with a first psychotic episode. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2004; Vol. 109, issue 4:264‐8. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
Ihara 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ihara K, Morgan C, Fearon P, Dazzan P, Demjaha A, Lloyd T, et al. The prevalence, diagnostic significance and demographic characteristics of Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms in an epidemiological sample of first‐episode psychoses. Psychopathology 2009; Vol. 42, issue 2:81‐91. [0254‐4962] - PubMed
Ndetei 1983 {published data only}
-
- Ndetei DM, Singh A. Schneider's first rank symptoms of schizophrenia in Kenyan patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983; Vol. 67, issue 3:148‐53. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
O'Grady 1990 {published data only}
-
- O'Grady JC. The prevalence and diagnostic significance of Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms in a random sample of acute psychiatric in‐patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1990; Vol. 156:496‐500. [0007‐1250] - PubMed
Peralta 1999 {published data only}
-
- Peralta V, Cuesta MJ. Diagnostic significance of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms in schizophrenia. Comparative study between schizophrenic and non‐schizophrenic psychotic disorders. British Journal of Psychiatry 1999; Vol. 174:243‐8. [0007‐1250] - PubMed
Preiser 1979 {published data only}
-
- Preiser M, Jeffrey W. Schizophrenic patients and Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms. American Journal of Psychiatry 1979; Vol. 136, issue 3:323‐6. [0002‐953X] - PubMed
Radhakrishnan 1983 {published data only}
-
- Radhakrishnan J, Mathew K, Richard J, Verghese A. Schneider's first rank symptoms‐‐prevalence, diagnostic use and prognostic implications. British Journal of Psychiatry 1983; Vol. 142:557‐9. [0007‐1250] - PubMed
Raguram 1985 {published data only}
Ramperti 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ramperti N, Anwar M, Renwick L, Jackson D, Foley S, McWilliams S, et al. First rank symptoms in first episode psychosis and their relationship to the duration of untreated illness. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease 2010; Vol. 198, issue 11:820‐3. [1539‐736X] - PubMed
Rosen 2011 {published data only}
Salleh 1992 {published data only}
-
- Salleh MR. Specificity of Schneider's first rank symptoms for schizophrenia in Malay patients. Psychopathology 1992; Vol. 25, issue 4:199‐203. [0254‐4962] - PubMed
Stephens 1980 {published data only}
-
- Stephens JH, Ota KY, Carpenter WT Jr, Shaffer JW. Diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia: prognostic implications and diagnostic overlap. Psychiatry Research 1980; Vol. 2, issue 1:1‐12. [0165‐1781] - PubMed
Stephens 1982 {published data only}
-
- Stephens JH, Astrup C, Carpenter WT Jr, Shaffer JW, Goldberg J. A comparison of nine systems to diagnose schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research 1982; Vol. 6, issue 2:127‐43. [0165‐1781] - PubMed
Tandon 1987 {published data only}
-
- Tandon R, Greden JF. Schneiderian first rank symptoms: reconfirmation of high specificity for schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1987; Vol. 75, issue 4:392‐6. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
Tanenberg‐Karant 1995 {published data only}
-
- Tanenberg‐Karant M, Fennig S, Ram R, Krishna J, Jandorf L, Bromet EJ. Bizarre delusions and first‐rank symptoms in a first‐admission sample: a preliminary analysis of prevalence and correlates. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1995; Vol. 36, issue 6:428‐34. [0010‐440X] - PubMed
Wu 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y. Study of the diagnostic specificity by Schneider's first rank symptoms. [Chinese]. Zhonghua shen jing jing shen ke za zhi = Chinese Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 1990; Vol. 23, issue 2:79‐80, 126. [0412‐4057] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abrams 1973 {published data only}
-
- Abrams R, Taylor M. First‐rank symptoms, severity of illness, and treatment response in schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1973;14:353‐5. - PubMed
Abrams 1981 {published data only}
-
- Abrams R, Taylor MA. Importance of schizophrenic symptoms in the diagnosis of mania. American Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:658‐61. - PubMed
Ahmed 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed S H, Naeem S. First rank symptoms and diagnosis of schizophrenia in developing countries. Psychopathology 1984;17:275‐9. - PubMed
Al‐Ansari 1989 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Ansari EA, Emara MM, Mirza IA, El‐Islam MF. Schizophrenia in ICD‐10: a field trial of suggested diagnostic guidelines. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1989;30:416‐9. - PubMed
Anselmetti 2007 {published data only}
-
- Anselmetti S, Cavallaro R, Bechi M, Angelone SM, Ermoli E, Cocchi F, et al. Psychopathological and neuropsychological correlates of source monitoring impairment in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research 2007;150:51‐9. - PubMed
Asnis 1982 {published data only}
-
- Asnis L C, Baron M, Gruen R. Diagnostic overlap in schizophrenia research: relation to outcome predictors and family history. Psychiatry Research 1982;6:345‐53. - PubMed
Basu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Basu D, Malhotra A, Bhagat A, Varma VK. Cannabis psychosis and acute schizophrenia. a case‐control study from India. European Addiction Research 1999;5(2):71‐3. - PubMed
Beckmann 1990 {published data only}
-
- Beckmann H, Fritze J, Lanczik M. Prognostic validity of the cycloid psychoses. A prospective follow‐up study. Psychopathology 1990;23:205‐11. - PubMed
Berner 1984 {published data only}
-
- Berner P, Gabriel E, Kronberger ML, Kufferle B, Schanda H, Trappl R. Course and outcome of delusional psychoses. Psychopathology 1984;17:28‐36. - PubMed
Berner 1986 {published data only}
-
- Berner P, Katschnig H, Lenz C. The polydiagnostic approach in research on schizophrenia. Issues in Psychiatric Classification: Science, Practice, and Social Policy. New York: Human Sciences Press, 1986:70‐91.
Berner 1986a {published data only}
-
- Berner P, Katschnig H, Lenz G. First‐rank symptoms and Bleuler's basic symptoms. New results in applying the polydiagnostic approach. Psychopathology 1986;19:244‐52. - PubMed
Bland 1978 {published data only}
-
- Bland RC. Diagnosis of schizophrenia. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal. 1978;23:291‐6. - PubMed
Bland 1979 {published data only}
-
- Bland RC, Orn H. Schizophrenia: diagnostic criteria and outcome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:34‐8. - PubMed
Botros 2006 {published data only}
-
- Botros MM, Atalla SF, El‐Islam M F. Schneiderian first rank symptoms in a sample of schizophrenic patients in Egypt. International Journal of Social Psychiatry 2006;52:424‐31. - PubMed
Burbach 1984 {published data only}
-
- Burbach DJ, Lewine RR, Meltzer HY. Diagnostic concordance for schizophrenia as a function of sex. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1984;52:478‐9. - PubMed
Cardno 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cardno AG, Sham PC, Farmer AE, Murray RM, McGuffin P. Heritability of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms. British Journal of Psychiatry 2002;180:35‐8. - PubMed
Ceccherini‐Nelli 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ceccherini‐Nelli A, Crow TJ. Disintegration of the components of language as the path to a revision of Bleuler's and Schneider's concepts of schizophrenia: Linguistic disturbances compared with first‐rank symptoms in acute psychosis. British Journal of Psychiatry 2003; Vol. 182, issue MAR.:233‐40. [0007‐1250] - PubMed
Cernovsky 1985 {published data only}
-
- Cernovsky Z, Landmark J, Leslie B. Social and anamnestic correlates of consensus in diagnosing schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1985;41:614‐9. - PubMed
Chandrasena 1979 {published data only}
-
- Chandrasena R, Rodrigo A. Schneider's First Rank Symptoms: their prevalence and diagnostic implications in an Asian population. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;135:348‐51. - PubMed
Coffey 1993 {published data only}
-
- Coffey GJ, Mackinnon A, Minas IH. Interethnic variations in the presence of Schneiderian first rank symptoms. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1993;27:219‐27. - PubMed
Compton 2008 {published data only}
-
- Compton MT, Leiner AS, Bergner E, Chien VH, Franz L, Goulding SM, et al. Prevalence, factorial structure, and clinical correlates of first rank symptoms in urban, African‐American patients with first‐episode nonaffective psychosis. Clinical Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses 2008; Vol. 2, issue 1:59‐69. [1935‐1232]
Conus 2004 {published data only}
-
- Conus P, Abdel‐Baki A, Harrigan S, Lambert M, McGorry PD. Schneiderian first rank symptoms predict poor outcome within first episode manic psychosis. Journal of Affective Disorders 2004;81:259‐68. - PubMed
Cowell 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cowell PE, Kostianovsky DJ, Gur RC, Turetsky BI, Gur RE. Sex differences in neuroanatomical and clinical correlations in schizophrenia. The American Journal of Psychiatry 1996;153(6):799‐805. - PubMed
Craddock 1996 {published data only}
-
- Craddock M, Asherson P, Owen MJ, Williams J, McGuffin P, Farmer AE. Concurrent validity of the OPCRIT diagnostic system. Comparison of OPCRIT diagnoses with consensus best‐estimate lifetime diagnoses. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;169:58‐63. - PubMed
Cuesta 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cuesta M J, Peralta V, Zarzuela A. Empirical validation of competing definitions of schizophrenia: a poly‐diagnostic study of cognitive impairment in non‐affective psychosis. Schizophrenia Research 2007;95:39‐47. - PubMed
Deister 1993 {published data only}
-
- Deister A, Marneros A. Subtypes in schizophrenic disorders: frequencies in long‐term course and premorbid features. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 1993;28:164‐71. - PubMed
Deister 1994 {published data only}
-
- Deister A, Marneros A. Prognostic value of initial subtype in schizophrenic disorders. Schizophrenia Research 1994;12:145‐57. - PubMed
Dollfus 1992 {published data only}
-
- Dollfus S, Petit M, Menard JF. The relationship between 'chronic hallucinatory psychosis' (CHP) and schizophrenia. European Psychiatry 1992; Vol. 7:271‐6.
Dollfus 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dollfus S, Petit M, Menard J, Lesieur P. Schizophrenia: Comparison of 13 diagnostic systems in a cross‐sectional study. European Psychiatry. 1993;8:7‐13.
Dollfus 1993a {published data only}
-
- Dollfus S, Petit M, Menard J F, Lesieur P. Symptomatic and diagnostic stability in schizophrenia: A one‐year follow‐up study. European Psychiatry. 1993;8:131‐7.
Endicott 1982 {published data only}
-
- Endicott J, Nee J, Fleiss, J, Cohen J, Williams JBW, Robert Simon R. Diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia: Reliabilities and agreement between systems. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39(8):884‐9. - PubMed
Endicott 1986 {published data only}
-
- Endicott J, Nee J, Cohen J, Fleiss JL, Simon R. Diagnosis of schizophrenia. Prediction of short‐term outcome. Archives of General Psychiatry 1986;43:13‐9. - PubMed
Eva 1984 {published data only}
-
- Eva P, Cabane J, Ruiz A. Schizophrenia: Diagnostic errors. Revista de Psiquiatria Clinica 1984;21:31‐7.
Evans 1981 {published data only}
-
- Evans JW, Elliott H. Screening criteria for the diagnosis of schizophrenia in deaf patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1981;38:787‐90. - PubMed
Fanous 2012 {published data only}
Fourneret 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fourneret P, Franck N, Slachevsky A, Jeannerod M. Self‐monitoring in schizophrenia revisited. NeuroReport 2001;12:1203‐8. - PubMed
Franck 2002 {published data only}
-
- Franck N, O'Leary DS, Flaum M, Hichwa RD, Andreasen NC. Cerebral blood flow changes associated with Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms in schizophrenia. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2002;14:277‐82. - PubMed
Ganesan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ganesan V, Hunter MD, Spence SA. Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms and right parietal hyperactivation: a replication using FMRI. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(8):154‐5. - PubMed
Gharagozlou 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gharagozlou H, Behin M. Diagnostic evaluation of Schneider first rank symptoms of schizophrenia among three groups of Iranians. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1979;20(3):242‐5. - PubMed
Gift 1980 {published data only}
-
- Gift TE, Strauss JS, Ritzler BA. How diagnostic concepts of schizophrenia differ. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1980;168:3‐8. - PubMed
Glazer 1987 {published data only}
-
- Glazer WM, Pino CD, Quinlan D. The reassessment of chronic patients previously diagnosed as schizophrenic. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1987;48:430‐4. - PubMed
Gur 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gur RE, Mozley PD, Shtasel DL, Cannon TD, Gallacher F, Turetsky B, et al. Clinical subtypes of schizophrenia: differences in brain and CSF volume. American Journal of Psychiatry 1994;151:343‐50. - PubMed
Gureje 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gureje O, Bamgboye EA. A study of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms of schizophrenia in Nigerian patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:867‐9. - PubMed
Hayashi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hayashi T, Hotta N, Fukastu N, Suga H. Clinical and socio‐demographic studies of atypical psychoses using ICD‐ 10 criteria. Neurology Psychiatry and Brain Research. 1998;6:147‐54.
Helmes 1983 {published data only}
-
- Helmes E, Landmark J, Kazarian SS. Inter‐rater reliability of twelve diagnostic systems of schizophrenia. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1983;171:307‐11. - PubMed
Hill 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hill C, Keks N, Roberts S, Opeskin K, Dean B, MacKinnon A, et al. Problem of diagnosis in postmortem brain studies of schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1996;153:533‐7. - PubMed
Idrees 2010 {published data only}
-
- Idrees M, Khan I, Irfan M, Sarwar R. First rank symptoms in the diagnosis of schizophrenia. JPMI ‐ Journal of Postgraduate Medical Institute 2010;24:323‐8.
Jakobsen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jakobsen K, Frederiksen J, Parnas J, Werge T. Diagnostic agreement of schizophrenia spectrum disorders among chronic patients with functional psychoses. Psychopathology 2006;39(6):269‐76. - PubMed
Kendell 1979 {published data only}
-
- Kendell RE, Brockington IF, Leff JP. Prognostic implications of six alternative definitions of schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1979;36:25‐31. - PubMed
Klosterkotter 1992 {published data only}
-
- Klosterkotter J. The meaning of basic symptoms for the development of schizophrenic psychoses. Neurology Psychiatry and Brain Research. 1992;1:30‐41.
Koehler 1976 {published data only}
-
- Koehler K, Guth W. Schneider‐oriented versus Conrad‐oriented psychiatric diagnosis in the same German clinic. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;129:446‐51. - PubMed
Koehler 1978 {published data only}
-
- Koehler K, Seminario I. First rank schizophrenia and research diagnosable schizophrenic and affective illness. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1978;19(5):401‐6. - PubMed
Kulhara 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kulhara P, Chandiramani K. Outcome of schizophrenia in India using various diagnostic systems. Schizophrenia Research. 1988;1:339‐49. - PubMed
Kulhara 1989 {published data only}
Landmark 1986 {published data only}
-
- Landmark J, Cernovsky ZZ, Merskey H, Leslie B. Interrelationships of systems for diagnosing schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1986;27:343‐50. - PubMed
Landmark 1990 {published data only}
-
- Landmark J, Merskey H, Cernovsky Z, Helmes E. The positive triad of schizophrenic symptoms. Its statistical properties and its relationship to 13 traditional diagnostic systems. British Journal of Psychiatry 1990;156:388‐94. - PubMed
Lenz 1986 {published data only}
-
- Lenz G, Katschnig H, David H. Symptoms, diagnosis and time in hospital. A polydiagnostic study of schizophrenia. Psychopathology 1986;19:253‐8. - PubMed
Lewine 1982 {published data only}
-
- Lewine R, Renders R, Kirchhofer M, Monsour A, Watt N. The empirical heterogeneity of first rank symptoms in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1982;140:498‐502. - PubMed
Lewine 1984 {published data only}
-
- Lewine R, Burbach D, Meltzer HY. Effect of diagnostic criteria on the ratio of male to female schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1984;141:84‐7. - PubMed
Littlewood 1981 {published data only}
-
- Littlewood R, Lipsedge M. Acute psychotic reactions in Caribbean‐born patients. Psychological Medicine 1981;11:303‐18. - PubMed
Loftus 2000 {published data only}
-
- Loftus J, Delisi LE, Crow TJ. Factor structure and familiality of first‐rank symptoms in sibling pairs with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;177:15‐9. - PubMed
Maier 1986 {published data only}
-
- Maier W, Philipp M, Schlegel S. Operational diagnoses for schizophrenic and schizoaffective disorders: I. Interrater reliability. Pharmacopsychiatry 1986;19:178‐9.
Makanjuola 1987 {published data only}
-
- Makanjuola RO, Adedapo SA. The DSM‐III concepts of schizophrenic disorder and schizophreniform disorder. A clinical and prognostic evaluation. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;151:611‐8. - PubMed
Malik 1990 {published data only}
-
- Malik S, Ahmed M, Bashir A, Choudhry T. Schneider's first‐rank symptoms of schizophrenia: Prevalence and diagnostic use: A study from Pakistan. British Journal of Psychiatry 1990;156:109‐11. - PubMed
Marneros 1984 {published data only}
-
- Marneros A. The pathognomonic value of K. Schneider's First Rank symptoms. Psychiatria Fennica. 1984;15:99‐105.
Mason 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mason P, Harrison G, Croudace T, Glazebrook C, Medley I. The predictive validity of a diagnosis of schizophrenia. A report from the International Study of Schizophrenia (ISoS) coordinated by the World Health Organization and the Department of Psychiatry, University of Nottingham. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;170:321‐7. - PubMed
Matsuura 2004 {published data only}
-
- Matsuura M, Adachi N, Oana Y, Okubo Y, Kato M, Nakano T, et al. A polydiagnostic and dimensional comparison of epileptic psychoses and schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophrenia Research 2004;69:189‐201. - PubMed
Mauri 1992 {published data only}
-
- Mauri M, Borri C, Giannotti D, Zambotto S, Cassano G B, Akiskal HS. Psychotic symptom patterns and the diagnosis of schizophrenia. Psychopathology 1992;25:5‐10. - PubMed
McGuffin 1984 {published data only}
-
- McGuffin P, Farmer AE, Gottesman II. Twin concordance for operationally defined schizophrenia. Confirmation of familiality and heritability. Archives of General Psychiatry 1984; Vol. 41, issue 6:541‐5. [0003‐990X] - PubMed
McGuffin 1991 {published data only}
-
- McGuffin P, Farmer A, Harvey I. A polydiagnostic application of operational criteria in studies of psychotic illness. Development and reliability of the OPCRIT system. Archives of General Psychiatry 1991;48:764‐70. - PubMed
Melges 1977 {published data only}
-
- Melges FT, Freeman AM 3rd. Temporal disorganization and inner‐outer confusion in acute mental illness. American Journal of Psychiatry 1977;134:874‐7. - PubMed
Mellor 1970 {published data only}
-
- Mellor CS. First rank symptoms of schizophrenia. I. The frequnncy in schizophrenics on admission to hospital. II. Differences between individual first rank symptoms. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1970;117:15‐23. - PubMed
Menezes 1993 {published data only}
-
- Menezes PR, Mann AH. Characteristics of hospital‐treated schizophrenia in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Social Psychiatry & Psychiatric Epidemiology 1993; Vol. 28, issue 6:267‐74. [0933‐7954] - PubMed
Modestin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Modestin J, Huber A, Satirli E, Malti T, Hell D. Long‐term course of schizophrenic illness: Bleuler's study reconsidered. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160:2202‐8. - PubMed
Munk‐Jorgensen 1989 {published data only}
-
- Munk‐Jorgensen P, Mortensen PB. Schizophrenia: a 13‐year follow‐up. Diagnostic and psychopathological aspects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1989; Vol. 79, issue 4:391‐9. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
Nakaya 2002 {published data only}
-
- Nakaya M, Kusumoto K, Okada T, Ohmori K. Bizarre delusions and DSM‐IV schizophrenia. Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2002;56:391‐5. - PubMed
Ndetei 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ndetei DM, Vadher A. A cross‐cultural study of the frequencies of Schneider's first rank symptoms of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1984; Vol. 70, issue 6:540‐4. [0001‐690X] - PubMed
Nordgaard 2008 {published data only}
Pela 1982 {published data only}
-
- Pela OA. Cultural relativety of first rank symptoms in schizophrenia. International Journal of Social Psychiatry 1982; Vol. 28, issue 2:91‐5. [0020‐7640] - PubMed
Peralta 1992 {published data only}
-
- Peralta V, Cuesta MJ. A polydiagnostic approach to self‐perceived cognitive disorders in schizophrenia. Psychopathology 1992;25:232‐8. - PubMed
Philipp 1986 {published data only}
-
- Philipp M, Maier W. The polydiagnostic interview: a structured interview for the polydiagnostic classification of psychiatric patients. Psychopathology 1986;19:175‐85. - PubMed
Philipp 1986a {published data only}
-
- Philipp M, Maier W, Frommberger U. Operational diagnoses for schizophrenic and schizoaffective disorders: II. Agreement between systems. Pharmacopsychiatry 1986;19:180‐1.
Pihlajamaa 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pihlajamaa J, Suvisaari J, Henriksson M, Heila H, Karjalainen E, Koskela J, et al. The validity of schizophrenia diagnosis in the Finnish Hospital Discharge Register: findings from a 10‐year birth cohort sample. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 2008;62:198‐203. - PubMed
Ross 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ross CA. Epidemiology of multiple personality disorder and dissociation. Psychiatric Clinics of North America 1991;14:503‐17. - PubMed
Salvatore 2011 {published data only}
Schanda 1984 {published data only}
-
- Schanda H, Thau K, Kufferle B, Kieffer W, Berner P. Heterogeneity of delusional syndromes: diagnostic criteria and course prognosis. Psychopathology 1984;17:280‐9. - PubMed
Schiopu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Schiopu B, Nel M, Hiemstra LA, Latecki B. Relevance of Schneider's first‐rank symptoms in Zulu patients with paranoid schizophrenia. South African Family Practice 2005;47:55‐60.
Serban 1979 {published data only}
-
- Serban G, Gidynski CB. Relationship between cognitive defect, affect response and community adjustment in chronic schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:602‐8. - PubMed
Silverstein 1978 {published data only}
-
- Silverstein ML, Harrow M. First‐rank symptoms in the postacute schizophrenic: a follow‐up study. American Journal of Psychiatry 1978; Vol. 135, issue 12:1481‐6. [0002‐953X] - PubMed
Silverstein 1981 {published data only}
-
- Silverstein M L, Harrow M. Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1981;38:288‐93. - PubMed
Sougey 1987 {published data only}
-
- Sougey EB, Carvalho TF, Bandin JM, Albuquerque JO. Frequency of Kurt Schneider's first rank symptoms in schizophrenics in Northeastern Brazil. Revista ABP APAL 1987;9:151‐6.
Taylor 1972 {published data only}
-
- Taylor MA. Schneiderian first‐rank symptoms and clinical prognostic features in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972; Vol. 26, issue 1:64‐7. [0003‐990X] - PubMed
Thorup 2007 {published data only}
-
- Thorup A, Petersen L, Jeppesen P, Nordentoft M. Frequency and predictive values of first rank symptoms at baseline among 362 young adult patients with first‐episode schizophrenia Results from the Danish OPUS study. Schizophrenia Research. 2007;97:60‐7. - PubMed
Vazquez‐Barquero 1995 {published data only}
-
- Vazquez‐Barquero JL, Cuesta Nunez MJ, Varga M, Herrera Castanedo S, Gaite L, Arenal A. The Cantabria first episode schizophrenia study: a summary of general findings. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1995;91:156‐62. - PubMed
Vega 2006 {published data only}
-
- Vega WA, Sribney WM, Miskimen TM, Escobar JI, Aguilar‐Gaxiola S. Putative psychotic symptoms in the Mexican American population: prevalence and co‐occurrence with psychiatric disorders. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2006;194:471‐7. - PubMed
Wciorka 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wciorka J, Anczewska M, Chojnowska A, Stanikowska I. Delusional psychoses during first hospitalization: Age of onset and diagnosis of schizophrenia by six diagnostic criteria. Psychiatria Polska 1995;29:133‐46. - PubMed
Wetterberg 1991 {published data only}
-
- Wetterberg L, Farmer AE. Clinical polydiagnostic studies in a large Swedish pedigree with schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 1991;240:188‐90. - PubMed
Young 1982 {published data only}
-
- Young MA, Tanner MA, Meltzer HY. Operational definitions of schizophrenia: What do they identify?. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1982;170:443‐7. - PubMed
Zarrouk 1978 {published data only}
-
- Zarrouk ET. The usefulness of first‐rank symptoms in the diagnosis of schizophrenia in a Saudi Arabian population. British Journal of Psychiatry 1978;132:571‐3. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Friedrich 1980 {published data only}
-
- Friedrich M, Leixnering W. Differential diagnosis of schizophrenia in children and adolescents. Acta Paedopsychiatrica: International Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 1980;46:21‐30. - PubMed
Additional references
Astrachan 1974
-
- Astrachan BM, Brauer L, Harrow M, Schwartz C. Symptomatic outcome in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31:155‐63. - PubMed
Bellak 1973
-
- Bellak L, Hurvich M, Gediman HK. Ego Functions in Schizophrenics, Neurotics, and Normals: A Systematic Study of Conceptual, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic Aspects. Wiley New York, 1973.
Bergman 2014
-
- Bergman H, Khodabakhsh A, Maayan N, Kirkham AJ, Adams CE, Soares‐Weiser K. Operational Criteria Checklist for Psychotic Illness and Affective Illness (OPCRIT+) for diagnosing schizophrenia in people with psychotic symptoms. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011104] - DOI
Bleuler 1950
-
- Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. New York: International Universities Press, 1950.
Bottlender 2003
-
- Bottlender R, Sato T, Jager M, Wegener U, Wittmann J, Strauss A, et al. The impact of the duration of untreated psychosis prior to first psychiatric admission on the 15‐year outcome in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;62(1‐2):37‐44. [PUBMED: 12765741] - PubMed
Bustillo 2001
-
- Bustillo J, Lauriello J, Horan W, Keith S. The psychosocial treatment of schizophrenia: an update. American Journal of Psychiatry 2001;158(2):163‐75. - PubMed
Carpenter 1973
-
- Carpenter WT, Strauss JS, Bartko JJ. Flexible system for the diagnosis of schizophrenia: a report from the WHO pilot study of schizophrenia. Science 1973;182:1275. - PubMed
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Biavariate meta‐analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized mixed linear model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331‐2. - PubMed
De Haan 2003
-
- Haan L, Linszen DH, Lenior ME, Win ED, Gorsira R. Duration of untreated psychosis and outcome of schizophrenia: delay in intensive psychosocial treatment versus delay in treatment with antipsychotic medication. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2003;29(2):341‐8. [PUBMED: 14552508] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58:882‐93. - PubMed
Feighner 1972
-
- Feighner JP, Robins E, Guze SB, Woodruff RA Jr, Winokur G, Munoz R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;26(1):57‐63. - PubMed
Hor 2010
Kane 2001
-
- Kane JM, Marder SR, Schooler NR, Wirshing WC, Umbricht D, Baker RW, et al. Clozapine and haloperidol in moderately refractory schizophrenia: a 6‐month randomized and double‐blind comparison. Archive of General Psychiatry 2001;58(10):965‐72. - PubMed
Koehler 1979
-
- Koehler K, Seminario I. Research diagnosable "schizo‐affective" disorder in Schneiderian "first rank" schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1979;60(4):347‐54. - PubMed
Lawrie 2004
-
- Lawrie SM, Johnstone EC. Schizophrenia and related disorders. Companion to Psychiatric Studies. London: Churchill Livingstone, 2004.
Macaskill 2004
-
- Macaskill P. Empirical Bayes estimates generated in a hierarchical summary ROC analysis agreed closely with those of a full Bayesian analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2004;57(9):925‐32. - PubMed
Marshall 2011
McGrath 2008
-
- McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiologic Reviews 2008;30:67‐76. - PubMed
McKenzie 2004
Palaniyappan 2014
-
- Palaniyappan L, Maayan N, Kirkham AJ, Davenport C, Khodabakhsh A, Adams CE, et al. Voxel‐based morphometry for separation of schizophrenia from other types of psychosis in first‐episode psychosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011021] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58:982‐990. - PubMed
Schneider 1959
-
- Schneider K. Clinical Psychopathology. New York: Grune & Stratton, 1959.
Spitzer 1978
-
- Spitzer RL, Endicott J, Robins E. Research diagnostic criteria: rationale and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35(6):773‐82. - PubMed
Takwoingi 2010
-
- Takwoingi Y, Deeks JJ. METADAS: A SAS macro for meta‐analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. User Guide Version 1.3. 2010 July. http://srdta.cochrane.org (accessed 7th June 2012).
Tandon 2013
Taylor 1978
-
- Taylor MA, Abrams R. The prevalence of schizophrenia: a reassessment of using modern diagnostic criteria. American Journal of Psychiatry 1978;135:945‐8. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. - PubMed
WHO 2007
-
- WHO. Nurses in mental health. http://www.who.int/mental_health/evidence/nursing_atlas_2007.pdf (accessed on 12/12/13).
WHO 2011
-
- WHO. WHO highlights global under investment in mental health care. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/notes/2011/mental_health_20111007/en... (accessed on 12/12/13).
WHO 2012
-
- WHO. World Health Statistics 2012. http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/EN_WHS2012_F... (accessed on 19/12/13.
Worster 2008
-
- Worster A, Carpenter C. Incorporation bias in studies of diagnostic tests: how to avoid being biased about bias. CJEM 2008 Mar;10(2):174‐5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

