Diffusion-weighted MRI for imaging cell death after cytotoxic or apoptosis-inducing therapy
- PMID: 25880014
- PMCID: PMC4453679
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.134
Diffusion-weighted MRI for imaging cell death after cytotoxic or apoptosis-inducing therapy
Abstract
Background: Non-invasive serial imaging is desirable to detect processes such as necrotic and apoptotic cell death in cancer patients undergoing treatment. This study investigated the use of diffusion-weighted (DW-) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for imaging cell death induced by either a cytotoxic drug (irinotecan), or the apoptosis-inducing agent birinapant, in human tumour xenografts in vivo.
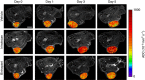
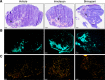
Methods: Nude mice bearing human SW620 colon carcinoma xenografts were treated with vehicle, irinotecan (50 mg kg(-1)) or birinapant (30 mg kg(-1)) for up to 5 days. DW-MRI was performed prior to and on days 1, 3 and 5 during treatment. Assessment of tumour apoptosis and necrosis ex vivo was used to validate the imaging findings.
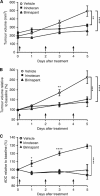
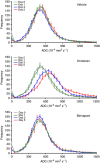
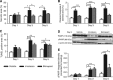
Results: Both irinotecan and birinapant induced significant tumour growth delay. Irinotecan induced a small increase in the tumour apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) after 1 day, with a 20 and 30% increase at days 3 and 5 respectively. ADC was unchanged in the vehicle- and birinapant-treated tumours despite a growth delay in the latter. Histological analysis showed that irinotecan increased necrosis at days 3 and 5, and induced apoptosis after 1 day, compared with vehicle. Birinapant induced apoptosis after day 3, but had no effect on tumour necrosis.
Conclusions: Tumour ADC changes after irinotecan treatment were associated with the induction of a mixture of necrotic and apoptotic cell death, whereas induction of apoptosis alone with birinapant was not sufficient to induce changes in tissue microstructure that were detectable with DW-MRI. ADC is a useful non-invasive biomarker for early detection of response to cytotoxic drugs, but false negatives may arise while detecting apoptotic response to birinapant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute tumour response to the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) evaluated by non-invasive diffusion-weighted MRI.Br J Cancer. 2013 Sep 17;109(6):1562-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.456. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23942066 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic and anticolorectal cancer effects of metronomic irinotecan chemotherapy alone and in combination with semaxinib.Br J Cancer. 2008 May 20;98(10):1619-29. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604352. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Br J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18443598 Free PMC article.
-
Combination effects of SMAC mimetic birinapant with TNFα, TRAIL, and docetaxel in preclinical models of HNSCC.Laryngoscope. 2015 Mar;125(3):E118-24. doi: 10.1002/lary.25056. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Laryngoscope. 2015. PMID: 25431358 Free PMC article.
-
SMAC mimetic birinapant inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating the cIAP1/TRAF3 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):1251-1257. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10908. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31922244 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody IMC-C225 in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) against human colorectal tumor xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 May;8(5):994-1003. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12006511
Cited by
-
Multi-parametric MRI for radiotherapy simulation.Med Phys. 2023 Aug;50(8):5273-5293. doi: 10.1002/mp.16256. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36710376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uveal melanoma: quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the response assessment after proton-beam therapy, long-term follow-up.Radiol Med. 2017 Feb;122(2):131-139. doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0697-3. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Radiol Med. 2017. PMID: 27752969
-
Predict Treatment Response by Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Weighted Imaging: A Preliminary Study on 46 Meningiomas Treated with Proton-Therapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Sep 15;11(9):1684. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091684. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34574025 Free PMC article.
-
Use of non-invasive imaging to monitor response to aflibercept treatment in murine models of colorectal cancer liver metastases.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2017 Jan;34(1):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s10585-016-9829-3. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2017. PMID: 27812769
-
ENETS standardized (synoptic) reporting for radiological imaging in neuroendocrine tumours.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 Mar;34(3):e13044. doi: 10.1111/jne.13044. Epub 2021 Oct 25. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 34693574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allensworth JL, Sauer SJ, Lyerly HK, Morse MA, Devi GR. Smac mimetic Birinapant induces apoptosis and enhances TRAIL potency in inflammatory breast cancer cells in an IAP-dependent and TNF-alpha-independent mechanism. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;137:359–371. - PubMed
-
- Beloueche-Babari M, Jamin Y, Arunan V, Walker-Samuel S, Revill M, Smith PD, Halliday J, Waterton JC, Barjat H, Workman P, Leach MO, Robinson SP. Acute tumour response to the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) evaluated by non-invasive diffusion-weighted MRI. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:1562–1569. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benetatos CA, Mitsuuchi Y, Burns JM, Neiman EM, Condon SM, Yu G, Seipel ME, Kapoor GS, Laporte MG, Rippin SR, Deng Y, Hendi MS, Tirunahari PK, Lee YH, Haimowitz T, Alexander MD, Graham MA, Weng D, Shi Y, McKinlay MA, Chunduru SK. Birinapant (TL32711), a bivalent SMAC mimetic, targets TRAF2-associated cIAPs, abrogates TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation, and is active in patient-derived xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:867–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

