Poor prognosis of single hormone receptor- positive breast cancer: similar outcome as triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 25880075
- PMCID: PMC4396721
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1121-4
Poor prognosis of single hormone receptor- positive breast cancer: similar outcome as triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Response to endocrine therapy in breast cancer correlates with estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) status. Generally, hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancers have favorable prognosis. In order to understand the exact clinical characteristics and prognosis of single HR-positive breast cancer (ER + PR- tumors and ER-PR+ tumors), we compared these tumors to double HR+ tumors as well as HR- negative tumors (ER-PR-).
Methods: We examined the clinical and biological features of 6,980 women with invasive ductal carcinoma, and these patients were stratified according to ER and PR expression as double HR+ (ER + PR+), single HR+ (ER + PR- and ER-PR+) and double HR-negative (HR-, ER-PR-) tumors.
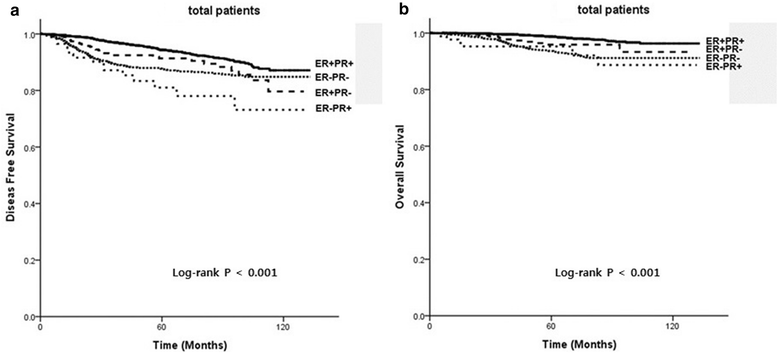
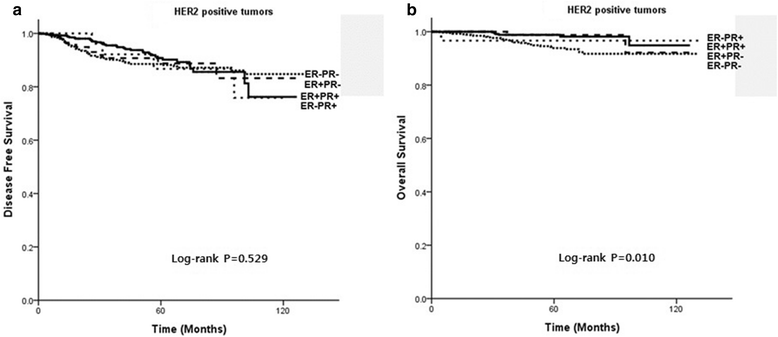
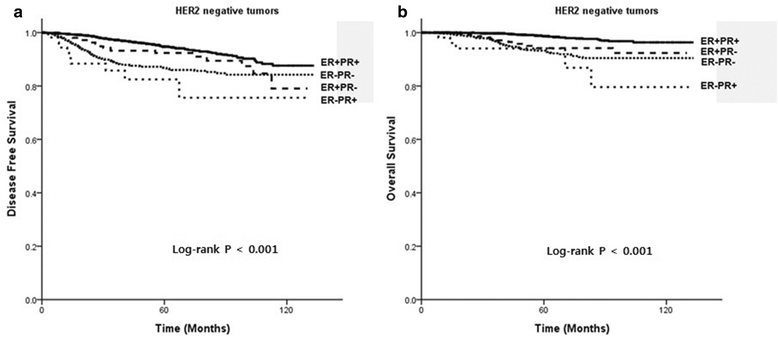
Results: In this study, 571 (8.2%) cases were single HR+ tumors, of which 90 (1.3%) were ER-PR+ tumors and 481 (6.9%) were ER + PR- tumors. Our multivariate analysis showed that in patients without HER2 overexpression ER + PR- tumors were associated with an increased risk of recurrence and death compared with ER + PR+ tumors, with a hazard ratio of 2.12 for disease-free survival (DFS) and 4.79 for overall survival (OS). In patients without HER2 overexpression ER-PR+ tumors had increased risk of recurrence and death compared with ER + PR+ tumor, with a hazard ratio of 4.19 for DFS and 7.22 for OS. In contrast, in patients with HER2 overexpression, the difference in survival between single HR+ tumors and double HR+ HR- tumors was not statistically significant. In patients without HER2 overexpression the DFS and OS of ER + PR- and ER-PR+ tumors were not significantly different from those of ER-PR- tumors.
Conclusion: We have identified clinically and biologically distinct features of single HR+ tumors (ER-PR+ and ER + PR-) through comparison with both ER + PR+ and ER-PR- tumors. These differences were only significant in HER2- tumors, not in HER2+ tumors. Single HR+ tumors without HER2 overexpression (ER + PR-HER2- or ER-PR + HER2-) were associated with poorer survival than ER + PR + HER2- tumors, and had comparable poor survival to ER-PR-HER2- tumors (triple-negative breast cancer).
Figures
References
-
- Bardou V-J, Arpino G, Elledge RM, Osborne CK, Clark GM. Progesterone Receptor Status Significantly Improves Outcome Prediction Over Estrogen Receptor Status Alone for Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy in Two Large Breast Cancer Databases. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(10):1973–1979. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.09.099. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elledge RM, Green S, Pugh R, Allred DC, Clark GM, Hill J, et al. Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PgR), by ligand-binding assay compared with ER, PgR and pS2, by immuno-histochemistry in predicting response to tamoxifen in metastatic breast cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group Study. Int J Cancer. 2000;89(2):111–7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000320)89:2<111::AID-IJC2>3.0.CO;2-W. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ravdin PM, Green S, Dorr TM, McGuire WL, Fabian C, Pugh RP, et al. Prognostic significance of progesterone receptor levels in estrogen receptor-positive patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with tamoxifen: results of a prospective Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10(8):1284–91. - PubMed
-
- Arpino G, Weiss H, Lee AV, Schiff R, De Placido S, Osborne CK, et al. Estrogen Receptor–Positive, Progesterone Receptor–Negative Breast Cancer: Association With Growth Factor Receptor Expression and Tamoxifen Resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(17):1254–1261. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji249. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

