Potential complications when developing gene deletion clones in Xylella fastidiosa
- PMID: 25880211
- PMCID: PMC4403849
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-015-1117-9
Potential complications when developing gene deletion clones in Xylella fastidiosa
Abstract
Background: The Gram-negative xylem-limited bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa, is an important plant pathogen that infects a number of high value crops. The Temecula 1 strain infects grapevines and induces Pierce's disease, which causes symptoms such as scorching on leaves, cluster collapse, and eventual plant death. In order to understand the pathogenesis of X. fastidiosa, researchers routinely perform gene deletion studies and select mutants via antibiotic markers.
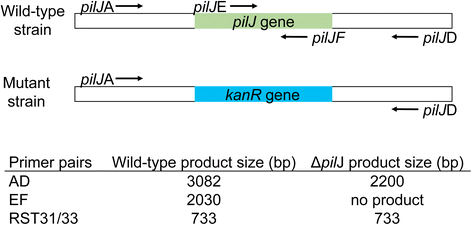
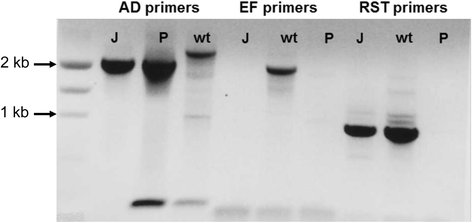
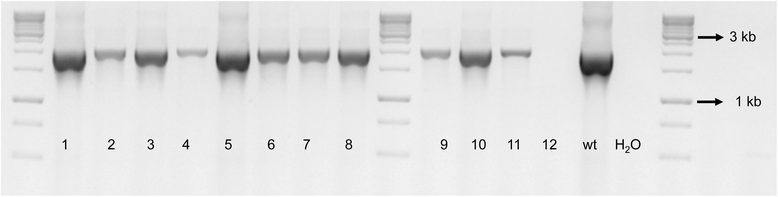
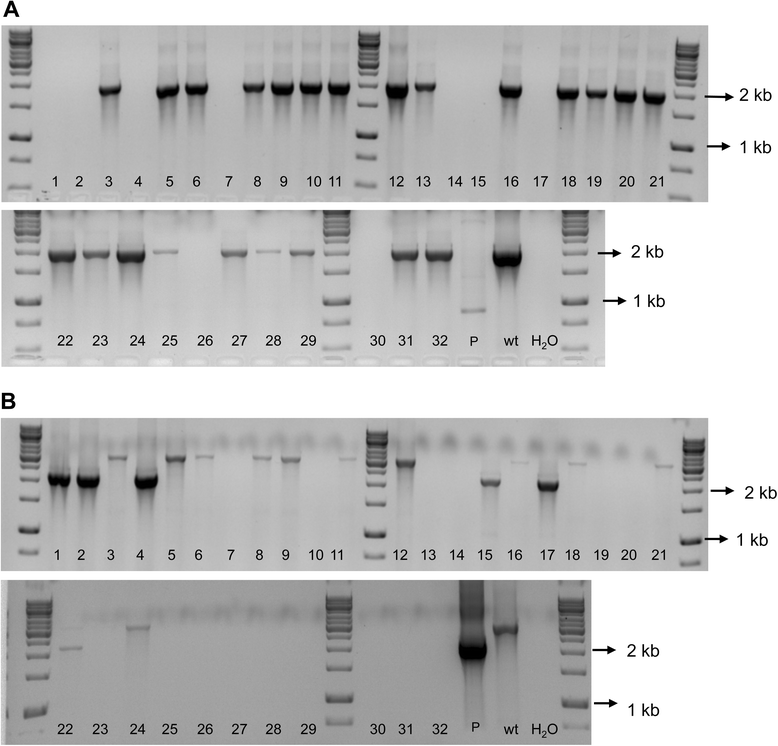
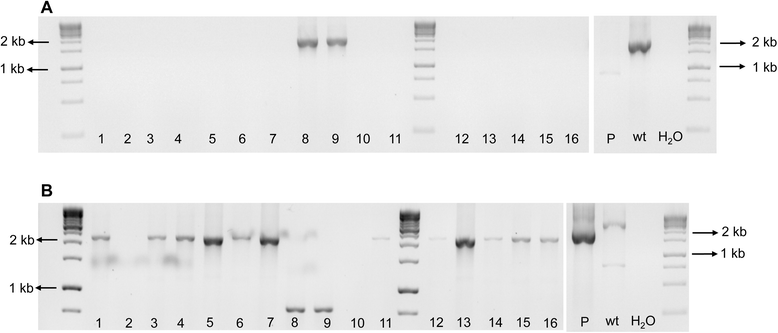
Methods: Site-directed pilJ mutant of X. fastidiosa were generated and selected on antibiotic media. Mutant cultures were assessed by PCR to determine if they were composed of purely transformant cells or included mixtures of non-transformants cells. Then pure pilJ mutant and wildtype cells were mixed in PD2 medium and following incubation and exposure to kanamycin were assessed by PCR for presence of mutant and wildtype populations.
Results: We have discovered that when creating clones of targeted mutants of X. fastidiosa Temecula 1 with selection on antibiotic plates, X. fastidiosa lacking the gene deletion often persist in association with targeted mutant cells. We believe this phenomenon is due to spontaneous antibiotic resistance and/or X. fastidiosa characteristically forming aggregates that can be comprised of transformed and non-transformed cells. A combined population was confirmed by PCR, which showed that targeted mutant clones were mixed with non-transformed cells. After repeated transfer and storage the non-transformed cells became the dominant clone present.
Conclusions: We have discovered that special precautions are warranted when developing a targeted gene mutation in X. fastidiosa because colonies that arise following transformation and selection are often comprised of transformed and non-transformed cells. Following transfer and storage the cells can consist primarily of the non-transformed strain. As a result, careful monitoring of targeted mutant strains must be performed to avoid mixed populations and confounding results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TolC is required for pathogenicity of Xylella fastidiosa in Vitis vinifera grapevines.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007 Apr;20(4):403-10. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-4-0403. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007. PMID: 17427810
-
Characterization of the Xylella fastidiosa PD1311 gene mutant and its suppression of Pierce's disease on grapevines.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Jun;18(5):684-694. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12428. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27388152 Free PMC article.
-
Xylella fastidiosa: an examination of a re-emerging plant pathogen.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Apr;19(4):786-800. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12585. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28742234 Free PMC article.
-
Paradigms: examples from the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013;51:339-56. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102325. Epub 2013 May 17. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013. PMID: 23682911 Review.
-
The biology of xylem fluid-feeding insect vectors of Xylella fastidiosa and their relation to disease epidemiology.Annu Rev Entomol. 2004;49:243-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.49.061802.123403. Annu Rev Entomol. 2004. PMID: 14651464 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

