DNA methylation and histone modifications regulate SOX11 expression in lymphoid and solid cancer cells
- PMID: 25880212
- PMCID: PMC4403777
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1208-y
DNA methylation and histone modifications regulate SOX11 expression in lymphoid and solid cancer cells
Abstract
Background: The neural transcription factor SOX11 is present at specific stages during embryo development with a very restricted expression in adult tissue, indicating precise regulation of transcription. SOX11 is strongly up-regulated in some malignancies and have a functional role in tumorgenesis. With the aim to explore differences in epigenetic regulation of SOX11 expression in normal versus neoplastic cells, we investigated methylation and histone modifications related to the SOX11 promoter and the possibility to induce re-expression using histone deacetylase (HDAC) or EZH2 inhibitors.
Methods: The epigenetic regulation of SOX11 was investigated in distinct non-malignant cell populations (n = 7) and neoplastic cell-lines (n = 42) of different cellular origins. DNA methylation was assessed using bisulfite sequencing, methylation-specific melting curve analysis, MethyLight and pyrosequencing. The presence of H3K27me3 was assessed using ChIP-qPCR. The HDAC inhibitors Vorinostat and trichostatin A were used to induce SOX11 in cell lines with no endogenous expression.
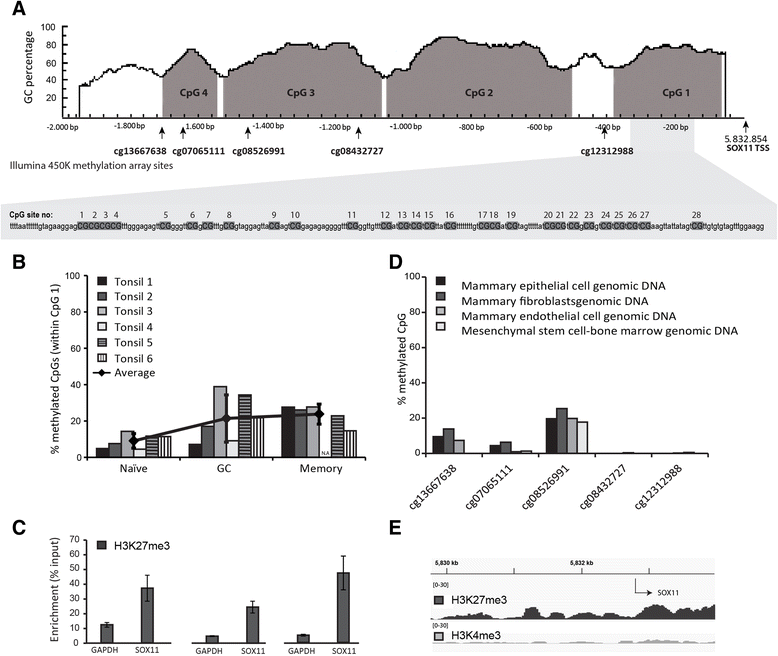
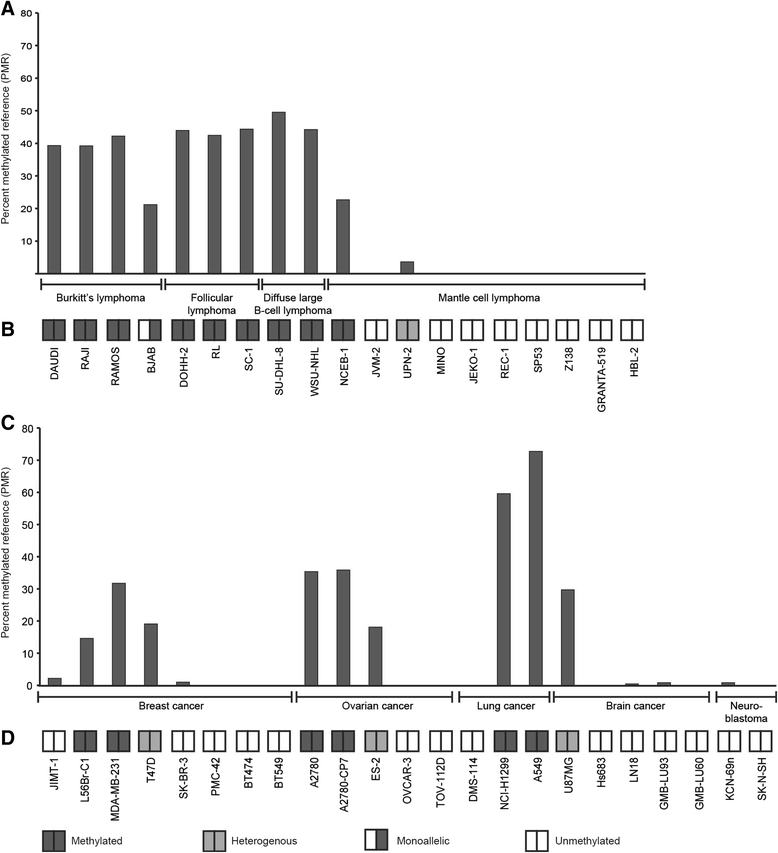
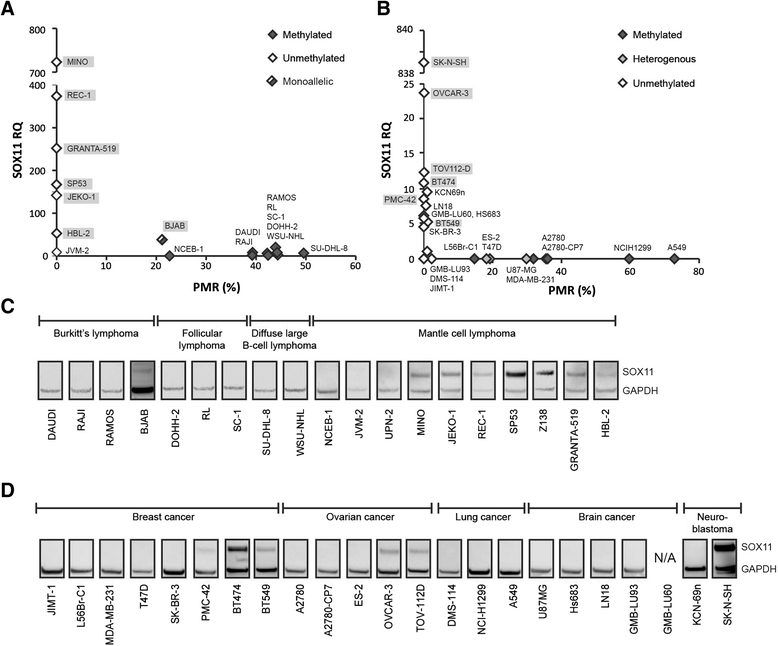
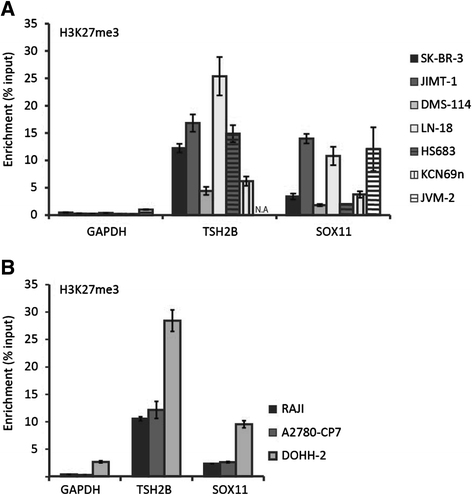
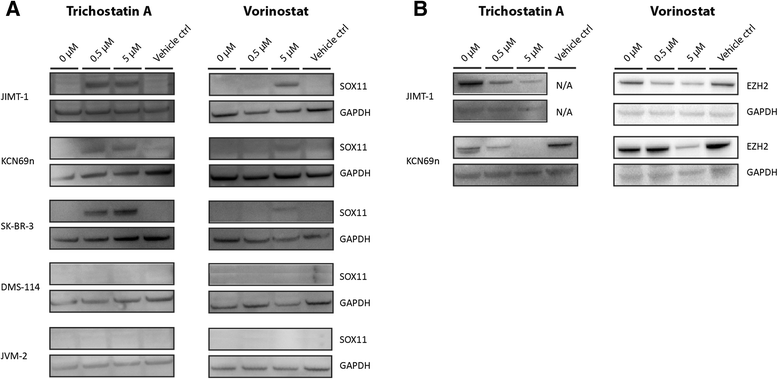
Results: The SOX11 promoter shows a low degree of methylation and strong enrichment of H3K27me3 in non-malignant differentiated cells, independent of cellular origin. Cancers of the B-cell lineage are strongly marked by de novo methylation at the SOX11 promoter in SOX11 non-expressing cells, while solid cancer entities display a more varying degree of SOX11 promoter methylation. The silencing mark H3K27me3 was generally present at the SOX11 promoter in non-expressing cells, and an increased enrichment was observed in cancer cells with a low degree of SOX11 methylation compared to cells with dense methylation. Finally, we demonstrate that the HDAC inhibitors (vorinostat and trichostatin A) induce SOX11 expression in cancer cells with low levels of SOX11 methylation.
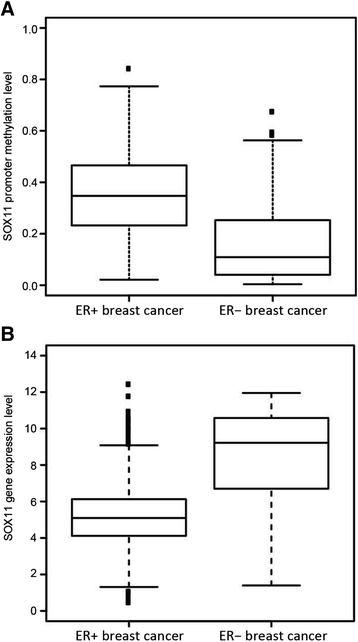
Conclusions: We show that SOX11 is strongly marked by repressive histone marks in non-malignant cells. In contrast, SOX11 regulation in neoplastic tissues is more complex involving both DNA methylation and histone modifications. The possibility to re-express SOX11 in non-methylated tissue is of clinical relevance, and was successfully achieved in cell lines with low levels of SOX11 methylation. In breast cancer patients, methylation of the SOX11 promoter was shown to correlate with estrogen receptor status, suggesting that SOX11 may be functionally re-expressed during treatment with HDAC inhibitors in specific patient subgroups.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic activation of SOX11 in lymphoid neoplasms by histone modifications.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021382. Epub 2011 Jun 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21738649 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant SOX11 promoter methylation is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015 Jun;38(3):183-94. doi: 10.1007/s13402-015-0219-7. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015. PMID: 25801783
-
The tumour suppressor SOX11 is associated with improved survival among high grade epithelial ovarian cancers and is regulated by reversible promoter methylation.BMC Cancer. 2011 Sep 24;11:405. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-405. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21943380 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic therapy of cancer with histone deacetylase inhibitors.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Jul-Sep;10(3):469-78. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.137937. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25313724 Review.
-
Human DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferases: a functional and structural perspective for epigenetic cancer therapy.Biochimie. 2017 Aug;139:137-147. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28600135 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression level comparison of marker genes related to early embryonic development and tumor growth.Oncol Lett. 2022 Oct 26;24(6):444. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13564. eCollection 2022 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36420077 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation-associated Sox11 upregulation promotes oncogenesis via the PI3K/AKT pathway in OLP-associated OSCC.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(14):e18556. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18556. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39039706 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of V-ATPase as a molecular sensor of SOX11-levels and potential therapeutic target for mantle cell lymphoma.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 18;16:493. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2550-4. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27430213 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Inheritance From Normal Origin Cells Can Determine the Aggressive Biology of Tumor-Initiating Cells and Tumor Heterogeneity.Cancer Control. 2022 Jan-Dec;29:10732748221078160. doi: 10.1177/10732748221078160. Cancer Control. 2022. PMID: 35213254 Free PMC article.
-
The SOX11 transcription factor is a critical regulator of basal-like breast cancer growth, invasion, and basal-like gene expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 15;7(11):13106-21. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7437. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26894864 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

