Molecular basis for mid-region amyloid-β capture by leading Alzheimer's disease immunotherapies
- PMID: 25880481
- PMCID: PMC4549621
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09649
Molecular basis for mid-region amyloid-β capture by leading Alzheimer's disease immunotherapies
Abstract
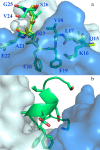
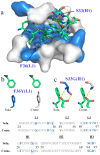
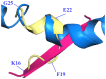
Solanezumab (Eli Lilly) and crenezumab (Genentech) are the leading clinical antibodies targeting Amyloid-β (Aβ) to be tested in multiple Phase III clinical trials for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease in at-risk individuals. Aβ capture by these clinical antibodies is explained here with the first reported mid-region Aβ-anti-Aβ complex crystal structure. Solanezumab accommodates a large Aβ epitope (960 Å(2) buried interface over residues 16 to 26) that forms extensive contacts and hydrogen bonds to the antibody, largely via main-chain Aβ atoms and a deeply buried Phe19-Phe20 dipeptide core. The conformation of Aβ captured is an intermediate between observed sheet and helical forms with intramolecular hydrogen bonds stabilising residues 20-26 in a helical conformation. Remarkably, Aβ-binding residues are almost perfectly conserved in crenezumab. The structure explains the observed shared cross reactivity of solanezumab and crenezumab with proteins abundant in plasma that exhibit this Phe-Phe dipeptide.
Figures
References
-
- Herrmann A. & Spires-Jones T. Clearing the way for tau immunotherapy in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 132, 1–4 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Hardy J. et al. Pathways to Alzheimer's disease. J. Intern. Med. 275, 296–303 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Legleiter J. et al. Effect of different anti-Abeta antibodies on Abeta fibrillogenesis as assessed by atomic force microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 335, 997–1006 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

