Promoting improved utilization of laboratory testing through changes in an electronic medical record: experience at an academic medical center
- PMID: 25880934
- PMCID: PMC4344785
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-015-0137-7
Promoting improved utilization of laboratory testing through changes in an electronic medical record: experience at an academic medical center
Abstract
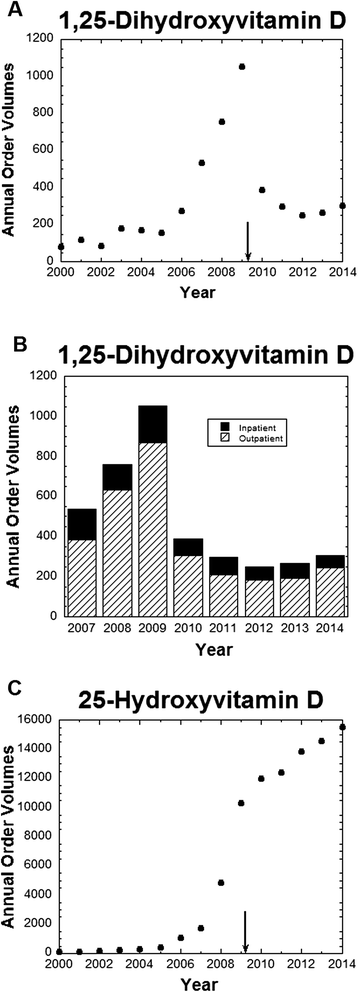
This case study over time describes five years of experience with interventions to improve laboratory test utilization at an academic medical center. The high-frequency laboratory tests showing the biggest declines in order volume post intervention were serum albumin (36%) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (17%). Introduction of restrictions for 170 high-cost send-out tests resulted in a 23% decline in order volume. Targeted interventions reduced mis-orders involving several "look-alike" tests: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; manganese, magnesium; beta-2-glycoprotein, beta-2-microglobulin. Lastly, targeted alerts reduced duplicate orders of germline genetic testing and orders of hepatitis B surface antigen within 2 weeks of hepatitis B vaccination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changing the electronic request form proves to be an effective tool for optimizing laboratory test utilization in the emergency department.Int J Med Inform. 2017 Jun;102:29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Int J Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 28495346
-
An effective utilization management strategy by dual approach of influencing physician ordering and gate keeping.Clin Biochem. 2016 Feb;49(3):208-12. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26554607
-
Reducing Unnecessary Laboratory Testing in the Medical ICU.Am J Med. 2017 Jun;130(6):648-651. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.02.014. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Am J Med. 2017. PMID: 28285068 Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Perceptual type error in everyday practice.Clin Radiol. 2016 Jun;71(6):593-601. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.11.024. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Clin Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26973044 Review.
-
[Quality assessment according to DIN EN ISO 9001:2000: certification in a university ENT department].HNO. 2006 Dec;54(12):922-8. doi: 10.1007/s00106-006-1467-7. HNO. 2006. PMID: 17041776 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Patterns and trends of potentially inappropriate high-density lipoprotein cholesterol testing in Australian adults at high risk of cardiovascular disease from 2008 to 2014: analysis of linked individual patient data from the Australian Medicare Benefits Schedule and Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme.BMJ Open. 2018 Mar 8;8(3):e019041. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019041. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29523561 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of nonintrusive clinical decision support systems on laboratory test utilization in a large academic centre.J Eval Clin Pract. 2018 Jun;24(3):474-479. doi: 10.1111/jep.12890. Epub 2018 Feb 15. J Eval Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 29446193 Free PMC article.
-
Current practices for lupus anticoagulant testing at a tertiary care hospital and impact on laboratory resources.Ann Saudi Med. 2015 Sep-Oct;35(5):383-6. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2015.383. Ann Saudi Med. 2015. PMID: 26506972 Free PMC article.
-
Review of interference indices in body fluid specimens submitted for clinical chemistry analyses.Pract Lab Med. 2020 Feb 8;19:e00155. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2020.e00155. eCollection 2020 Mar. Pract Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32099890 Free PMC article.
-
Results of a Quality Improvement Project Aimed at Eliminating Healthcare Waste by Changing Medical Resident Test Ordering Behavior.J Clin Med Res. 2017 Dec;9(12):965-969. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3210w. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Clin Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29163728 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

