Impact of nucleos(t)ide analogue combination therapy on the estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 25881837
- PMCID: PMC4602512
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000646
Impact of nucleos(t)ide analogue combination therapy on the estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
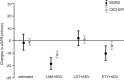
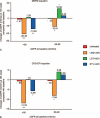
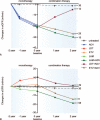
Monotherapy with telbivudine or adefovir can affect estimated the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). However, only a few studies have assessed changes in eGFR in patients who have chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and are receiving nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA) combination therapy. In our study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of long-term NA combination therapy on eGFR in Chinese CHB patients. This retrospective study included 195 CHB patients. Patient subgroups included those treated with lamivudine plus adefovir (n = 73), telbivudine plus adefovir (n = 51), and entecavir plus adefovir (n = 35); untreated patients (n = 36) served as a control group. After an average follow-up duration of 24 months with combination therapy, analysis of changes in eGFR from baseline values, calculated by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formulas, showed decrease by 11.08 and 18.34 mL/min (P < .001), respectively, in the lamivudine plus adefovir group; decrease by 3.73 and 10.04 mL/min (P = .012), respectively, in the entecavir plus adefovir group; and increase by 0.91 and 2.12 mL/min (P = .46), respectively, in the telbivudine plus adefovir group. The eGFR in the telbivudine plus adefovir group was similar to that for the untreated group. The eGFR decreases due to adefovir therapy could be rescued by adding telbivudine, and the eGFR increase due to telbivudine could be compromised by adding adefovir. Adefovir in combination with lamivudine or entecavir therapy was significantly associated with decreased eGFR, but telbivudine could rescue the eGFR decrease that results from adefovir treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of nucleos(t)ide analogues on the estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a prospective cohort study in China.J Viral Hepat. 2015 Jan;22(1):46-54. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12229. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Viral Hepat. 2015. PMID: 25402626
-
[Compare the effect of combined therapy between telbivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil and lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil corresponding to renal function in patients with hepatitis B virus infection].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 20;26(4):288-293. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.011. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29996341 Chinese.
-
Telbivudine protects renal function in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection in conjunction with adefovir-based combination therapy.J Viral Hepat. 2014 Dec;21(12):873-81. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12217. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Viral Hepat. 2014. PMID: 24351112
-
Review article: nucleos(t)ide analogues in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and chronic kidney disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jan;39(1):35-46. doi: 10.1111/apt.12538. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24299322 Review.
-
Mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis evaluating the relative efficacy of nucleos(t)ides for treatment of nucleos(t)ide-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B.Value Health. 2010 Dec;13(8):934-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2010.00777.x. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Value Health. 2010. PMID: 20825624
Cited by
-
Early renal injury indicators can help evaluate renal injury in patients with chronic hepatitis B with long-term nucleos(t)ide therapy.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Dec 26;8(24):6306-6314. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6306. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33392311 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil induced hypophosphatemic osteomalacia in chronic hepatitis B: a comparative study of Chinese and foreign case series.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 May 16;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0212-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29769119 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 48-week pegylated interferon α-2a or nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy on renal function in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B.Virol J. 2017 Mar 9;14(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0712-x. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28274240 Free PMC article.
-
Fanconi syndrome induced by adefovir dipivoxil: a case report and clinical review.J Int Med Res. 2020 Oct;48(10):300060520954713. doi: 10.1177/0300060520954713. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33100076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telbivudine and adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy improves renal function in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A STROBE-compliant article.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(48):e13430. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013430. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30508954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuen M-F, Lai C-L. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: evolution over two decades. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 26 Suppl 1:138–181. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2012; 57:167–185. - PubMed
-
- Hongthanakorn C, Chotiyaputta W, Oberhelman K, et al. Virological breakthrough and resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving nucleos(t)ide analogues in clinical practice. Hepatology 2011; 53:1854–1863. - PubMed
-
- Zoulim F, Locarnini S. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology 2009; 137:1593–1608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

