Advances in imaging technologies in the evaluation of high-grade bladder cancer
- PMID: 25882557
- PMCID: PMC4402158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ucl.2015.01.001
Advances in imaging technologies in the evaluation of high-grade bladder cancer
Abstract
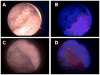
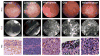
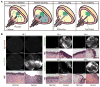
Bladder cancer ranges from a low-grade variant to high-grade disease. Assessment for treatment depends on white light cystoscopy, however because of its limitations there is a need for improved visualization of flat, multifocal, high-grade, and muscle-invasive lesions. Photodynamic diagnosis and narrow-band imaging provide additional contrast enhancement of bladder tumors and have been shown to improve detection rates. Confocal laser endomicroscopy and optical coherence tomography enable real-time, high-resolution, subsurface tissue characterization with spatial resolutions similar to histology. Molecular imaging offers the potential for the combination of optical imaging technologies with cancer-specific molecular agents to improve the specificity of disease detection.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Confocal laser endomicroscopy; Fluorescence cystoscopy; Molecular imaging; Narrow band imaging; Optical coherence tomography; Photodynamic diagnosis.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Dimitar Zlatev and Dr. Emanuela Altobelli declare no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article. Dr. Joseph C. Liao received a research grant from the National Institute of Health (NIH). Dr. Liao received travel support from Mauna Kea Technologies, including expenses covered or reimbursed.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9. - PubMed
-
- Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, et al. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology. 2005;66:4. - PubMed
-
- Morgan TM, Keegan KA, Clark PE. Bladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2011;23:275. - PubMed
-
- Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006;49:466. - PubMed
-
- Avritscher EB, Cooksley CD, Grossman HB, et al. Clinical model of lifetime cost of treating bladder cancer and associated complications. Urology. 2006;68:549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

