Penile and generalised calciphylaxis in peritoneal dialysis
- PMID: 25883256
- PMCID: PMC4401979
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-209153
Penile and generalised calciphylaxis in peritoneal dialysis
Abstract
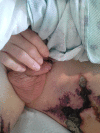
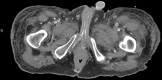
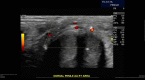
This is a rare case of penile and generalised calciphylaxis. We describe the case of a patient admitted to our hospital for septic shock and necrotic skin findings, end-stage renal disease on peritoneal dialysis. Skin findings turned out to be calciphyactic lesions. The patient was taken to the operating room for penile debridement and started on antibiotics. He was treated with sodium thiosulfate and switched to haemodialysis. Calciphylaxis is a rare disease in which the treatment is basically supportive. Further studies are needed to identify the risk factors, mechanisms of disease and treatment modalities.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
