Characteristics of de novo structural changes in the human genome
- PMID: 25883321
- PMCID: PMC4448676
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.185041.114
Characteristics of de novo structural changes in the human genome
Abstract
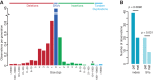
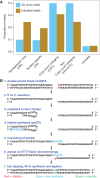
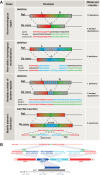
Small insertions and deletions (indels) and large structural variations (SVs) are major contributors to human genetic diversity and disease. However, mutation rates and characteristics of de novo indels and SVs in the general population have remained largely unexplored. We report 332 validated de novo structural changes identified in whole genomes of 250 families, including complex indels, retrotransposon insertions, and interchromosomal events. These data indicate a mutation rate of 2.94 indels (1-20 bp) and 0.16 SVs (>20 bp) per generation. De novo structural changes affect on average 4.1 kbp of genomic sequence and 29 coding bases per generation, which is 91 and 52 times more nucleotides than de novo substitutions, respectively. This contrasts with the equal genomic footprint of inherited SVs and substitutions. An excess of structural changes originated on paternal haplotypes. Additionally, we observed a nonuniform distribution of de novo SVs across offspring. These results reveal the importance of different mutational mechanisms to changes in human genome structure across generations.
© 2015 Kloosterman et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
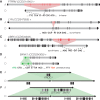

References
-
- Batista DAS, Pai GS, Stetten G. 1994. Molecular analysis of a complex chromosomal rearrangement and a review of familial cases. Am J Med Genet 53: 255–263. - PubMed
-
- Belancio VP, Hedges DJ, Deininger P. 2008. Mammalian non-LTR retrotransposons: for better or worse, in sickness and in health. Genome Res 18: 343–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
