Genomics of Volvocine Algae
- PMID: 25883411
- PMCID: PMC4396658
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391499-6.00006-2
Genomics of Volvocine Algae
Abstract
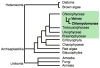
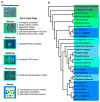
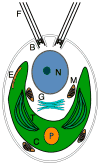
Volvocine algae are a group of chlorophytes that together comprise a unique model for evolutionary and developmental biology. The species Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Volvox carteri represent extremes in morphological diversity within the Volvocine clade. Chlamydomonas is unicellular and reflects the ancestral state of the group, while Volvox is multicellular and has evolved numerous innovations including germ-soma differentiation, sexual dimorphism, and complex morphogenetic patterning. The Chlamydomonas genome sequence has shed light on several areas of eukaryotic cell biology, metabolism and evolution, while the Volvox genome sequence has enabled a comparison with Chlamydomonas that reveals some of the underlying changes that enabled its transition to multicellularity, but also underscores the subtlety of this transition. Many of the tools and resources are in place to further develop Volvocine algae as a model for evolutionary genomics.
Figures
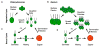



Similar articles
-
Volvox and volvocine green algae.Evodevo. 2020 Jul 1;11:13. doi: 10.1186/s13227-020-00158-7. eCollection 2020. Evodevo. 2020. PMID: 32626570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of cytokinesis-related protein localization during the emergence of multicellularity in volvocine green algae.BMC Evol Biol. 2017 Dec 6;17(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1091-z. BMC Evol Biol. 2017. PMID: 29212441 Free PMC article.
-
Fossil-calibrated molecular clock data enable reconstruction of steps leading to differentiated multicellularity and anisogamy in the Volvocine algae.BMC Biol. 2024 Apr 10;22(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01878-1. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38600528 Free PMC article.
-
Phylotranscriptomics points to multiple independent origins of multicellularity and cellular differentiation in the volvocine algae.BMC Biol. 2021 Aug 31;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01087-0. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 34465312 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of reproductive development in the volvocine algae.Sex Plant Reprod. 2011 Jun;24(2):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s00497-010-0158-4. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Sex Plant Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21174128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico and Cellular Differences Related to the Cell Division Process between the A and B Races of the Colonial Microalga Botryococcus braunii.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 5;11(10):1463. doi: 10.3390/biom11101463. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680096 Free PMC article.
-
Chitin oligosaccharide binding to the lysin motif of a novel type of chitinase from the multicellular green alga, Volvox carteri.Plant Mol Biol. 2017 Jan;93(1-2):97-108. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0549-5. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Plant Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27807643
-
The genome and phenome of the green alga Chloroidium sp. UTEX 3007 reveal adaptive traits for desert acclimatization.Elife. 2017 Jun 17;6:e25783. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25783. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28623667 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical principles of choanoflagellate self-organization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 21;117(3):1303-1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909447117. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31896587 Free PMC article.
-
Origins of multicellular complexity: Volvox and the volvocine algae.Mol Ecol. 2016 Mar;25(6):1213-23. doi: 10.1111/mec.13551. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Mol Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26822195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adair W. Organization and in vitro assembly of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell wall. Self-assembling architecture 1988
-
- Adams CR, Stamer KA, KMJ, McNally JG, Kirk MM, Kirk DL. Patterns of organellar and nuclear inheritance among progeny of two geographically isolated strains of Volvox carteri. Current Genetics. 1990;18:141–153. - PubMed
-
- Adams S, Maple J, Møller SG. Functional conservation of the MIN plastid division homologues of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta. 2008;227:1199–1211. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
