Trailing TRAIL Resistance: Novel Targets for TRAIL Sensitization in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 25883904
- PMCID: PMC4382980
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00069
Trailing TRAIL Resistance: Novel Targets for TRAIL Sensitization in Cancer Cells
Abstract
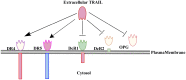
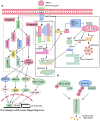
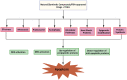
Resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs is the major hindrance in the successful cancer therapy. The tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of ligands, which initiates apoptosis in cancer cells through interaction with the death receptors DR4 and DR5. TRAIL is perceived as an attractive chemotherapeutic agent as it specifically targets cancer cells while sparing the normal cells. However, TRAIL therapy has a major limitation as a large number of the cancer develop resistance toward TRAIL and escape from the destruction by the immune system. Therefore, elucidation of the molecular targets and signaling pathways responsible for TRAIL resistance is imperative for devising effective therapeutic strategies for TRAIL resistant cancers. Although, various molecular targets leading to TRAIL resistance are well-studied, recent studies have implicated that the contribution of some key cellular processes toward TRAIL resistance need to be fully elucidated. These processes primarily include aberrant protein synthesis, protein misfolding, ubiquitin regulated death receptor expression, metabolic pathways, epigenetic deregulation, and metastasis. Novel synthetic/natural compounds that could inhibit these defective cellular processes may restore the TRAIL sensitivity and combination therapies with such compounds may resensitize TRAIL resistant cancer cells toward TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In this review, we have summarized the key cellular processes associated with TRAIL resistance and their status as therapeutic targets for novel TRAIL-sensitizing agents.
Keywords: DR4; DR5; TRAIL; TRAIL-resistance; apoptosis; cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ewing's sarcoma family tumors are sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and express death receptor 4 and death receptor 5.Cancer Res. 2001 Mar 15;61(6):2704-12. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11289151
-
Inhibition of euchromatin histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2 sensitizes breast cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand through reactive oxygen species-mediated activating transcription factor 4-C/EBP homologous protein-death receptor 5 pathway activation.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Nov;57(11):1492-1506. doi: 10.1002/mc.22872. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29964331
-
DR4-Ser424 O-GlcNAcylation Promotes Sensitization of TRAIL-Tolerant Persisters and TRAIL-Resistant Cancer Cells to Death.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;79(11):2839-2852. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1991. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30987996
-
Enhancement of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and irradiation: mechanisms and clinical implications.Drug Resist Updat. 2004 Apr;7(2):139-56. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2004.03.002. Drug Resist Updat. 2004. PMID: 15158769 Review.
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of TRAIL Signaling in Cancer: Searching for New Therapeutic Strategies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;13(7):521. doi: 10.3390/biology13070521. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAIL of Hope Meeting Resistance in Cancer.Trends Cancer. 2020 Dec;6(12):989-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32718904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the versatile role of OPG in bone oncology: counterbalancing RANKL and TRAIL signaling and beyond.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Feb;37(1):13-30. doi: 10.1007/s10585-019-09997-8. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 31578655 Review.
-
Downregulation of LOC441461 Promotes Cell Growth and Motility in Human Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;14(5):1149. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051149. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267457 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of combined treatment-induced cell death with recombinant TRAIL and bortezomib through TRAIL signaling in TRAIL-resistant cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4352-3. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29661248 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

