Application of long-acting VLHL PAI-1 during sutureless partial nephrectomy in mice reduces bleeding
- PMID: 25883959
- PMCID: PMC4391615
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/392862
Application of long-acting VLHL PAI-1 during sutureless partial nephrectomy in mice reduces bleeding
Abstract
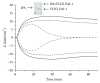
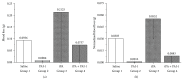
PAI-1 prevents lysis of blood clot by inhibiting the urokinase and tPA induced conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. VLHL PAI-1 protein mutant was created to extend half-life over 700 hours. The objective of this paper was to test VLHL PAI-1 effects on bleeding during partial nephrectomy in mice. All animals had a left partial nephrectomy after intravenous infusion of saline or tPA. The animals were divided into four groups. Group 1 was infused with saline and kidney was exposed to saline too; Group 2 was infused with saline and kidney was exposed to PAI-1. Group 3 was infused with tPA and kidney was exposed to saline, while Group 4 was infused with tPA and kidney was exposed to PAI-1. Preweighed gauze containing PAI-1 or saline was then applied to the kidney for 30 minutes. The gauze was afterward weighed and blood loss was measured by subtracting the preweight of gauze from the final weight. We have observed a statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05) reduction of bleeding in PAI-1-treated group in comparison to saline and tPA-treated groups. Based on these results we propose that VLHL PAI-1 can be used therapeutically in limiting the flow of blood from renal wounds.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemic or topical application of plasminogen activator inhibitor with extended half-life (VLHL PAI-1) reduces bleeding time and total blood loss.Int J Mol Med. 2010 Oct;26(4):501-4. doi: 10.3892/ijmm_00000491. Int J Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20818488
-
Very long half-life plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 reduces bleeding in a mouse model.BJU Int. 2010 May;105(10):1469-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08962.x. Epub 2009 Nov 13. BJU Int. 2010. PMID: 19912209
-
Highly stable plasminogen activator inhibitor type one (VLHL PAI-1) protects fibrin clots from tissue plasminogen activator-mediated fibrinolysis.Int J Mol Med. 2007 Nov;20(5):683-7. Int J Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17912461
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor with very long half-life (VLHL PAI-1) can reduce bleeding in PAI-1-deficient patients.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Aug;13(2):144-50. doi: 10.2174/1871529x11313020007. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23988002 Review.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in kidney pathology (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2013 Mar;31(3):503-10. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1234. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23314920 Review.
References
-
- Jorns J. J., Thiel D. D., Castle E. P. Update on contemporary management of clinically localized renal cell carcinoma. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica. 2012;64(4):261–272. - PubMed
-
- Allan E. H., Martin T. J. Prostaglandin E2 regulates production of plasminogen activator isoenzymes, urokinase receptor, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in primary cultures of rat calvarial osteoblasts. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 1995;165(3):521–529. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041650310. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

