Therapeutic effect of Agaricus brasiliensis on phenylhydrazine-induced neonatal jaundice in rats
- PMID: 25883968
- PMCID: PMC4389989
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/651218
Therapeutic effect of Agaricus brasiliensis on phenylhydrazine-induced neonatal jaundice in rats
Abstract
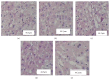
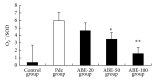
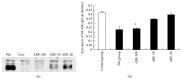
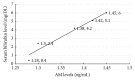
The present study was designed to investigate the effect of Agaricus brasiliensis extract (ABE) on phenylhydrazine-induced neonatal jaundice in rats. Administration of ABE dose-dependently reduced the elevated bilirubin level induced by phenylhydrazine. It can be somewhat supported from the results of in vitro bilirubin degradation experiment. ABE treatment also reduced the total antioxidant status (TAOS), cascade O2(-)/SOD, level of NF-κB protein, and adrenomedullin (AM). Overall, the results of this study demonstrated that Agaricus brasiliensis extract may be beneficial to reducing bilirubin level without causing hepatotoxicity in neonatal jaundice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Folic acid alleviates jaundice of phenylhydrazine (PHA)-induced neonatal rats by reducing Lys-homocysteinylation of albumin.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021 Oct;37(5):679-693. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09602-3. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33788065
-
Bilirubin clearance and antioxidant activities of ethanol extract of Phyllanthus amarus root in phenylhydrazine-induced neonatal jaundice in mice.J Physiol Biochem. 2013 Sep;69(3):467-76. doi: 10.1007/s13105-013-0234-y. Epub 2013 Jan 16. J Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23318962
-
Role of bilirubin as antioxidant in neonatal jaundice and effect of ethanolic extract of sweet lime peel on experimentally induced jaundice in rat.Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009 Feb;46(1):73-8. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009. PMID: 19374257
-
Characterization of chemical composition of Agaricus brasiliensis polysaccharides and its effect on myocardial SOD activity, MDA and caspase-3 level in ischemia-reperfusion rats.Int J Biol Macromol. 2010 Apr 1;46(3):363-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.01.008. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010. PMID: 20083132
-
[Agaritine and phenylhydrazine derivatives in Agaricus bisporus and Agaricus blazei Murrill].Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2007 Dec;48(6):J397-401. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 18203508 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Folic acid alleviates jaundice of phenylhydrazine (PHA)-induced neonatal rats by reducing Lys-homocysteinylation of albumin.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021 Oct;37(5):679-693. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09602-3. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33788065
-
Unconjugated Bilirubin exerts Pro-Apoptotic Effect on Platelets via p38-MAPK activation.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 13;5:15045. doi: 10.1038/srep15045. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26459859 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic effect of echinochrome on phenylhydrazine-induced hemolytic anemia in rats.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 8;11:e16576. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16576. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38089915 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effect of Faidherbia albida Against 2.4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine Induced Hyperbilirubinemia in Wistar Albino Rats.J Exp Pharmacol. 2024 May 28;16:211-219. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S457562. eCollection 2024. J Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38826848 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of phenylhydrazine induced hyperbilirubinemia in experimental rabbit.Exp Anim. 2016 Nov 1;65(4):363-372. doi: 10.1538/expanim.16-0011. Epub 2016 May 20. Exp Anim. 2016. PMID: 27210076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slusher T. M., Olusanya B. O. Care of the Jaundiced Neonate. chapter 13. 2012. Neonatal jaundice in low-and middle-income countries; pp. 263–273.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

