The effectiveness of a web-based Dutch parenting program to prevent overweight in children 9-13 years of age: study protocol for a two-armed cluster randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25884190
- PMCID: PMC4335372
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1394-1
The effectiveness of a web-based Dutch parenting program to prevent overweight in children 9-13 years of age: study protocol for a two-armed cluster randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Although parental support is an important component in overweight prevention programs for children, current programs pay remarkably little attention to the role of parenting. To close this gap, we developed a web-based parenting program for parents entitled "Making a healthy deal with your child". This e-learning program can be incorporated into existing prevention programs, thereby improving these interventions by reinforcing the role of parenting and providing parents with practical tools for use in everyday situations in order to stimulate a healthy lifestyle. Here, we report the research design of a study to determine the effectiveness of our e-learning program.
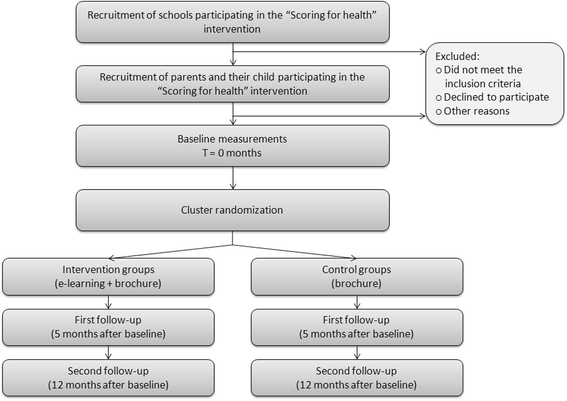
Methods/design: The effectiveness of an e-learning program was studied in a two-armed cluster randomized controlled trial. Parents of children 9-13 years of age who live in the Nijmegen region, the Netherlands, and who participated in the existing school-based overweight prevention program "Scoring for Health" were invited to participate in this study. Our goal was to recruit 322 parent-child dyads. At the school grade level, parents were randomly assigned to either the intervention group (which received e-learning and a brochure) or the control group (which received only the brochure); the participants were stratified by ethnicity. Measurements were taken from both the parents and the children at baseline, and then 5 and 12 months after baseline. Primary outcomes included the child's dietary and sedentary behavior, and level of physical activity. Secondary outcomes included general parenting style, specific parenting practices (e.g., set of rules, modeling, and monitoring), and parental self-efficacy.
Discussion: We hypothesize that children of parents who follow the e-learning program will have a healthier diet, will be less sedentary, and will have a higher level of physical activity compared to the children in the control group. If the e-learning program is found to be effective, it can be incorporated into existing overweight prevention programs for children (e.g., "Scoring for Health"), as well as activities regarding Youth Health Care.
Trial registration: Dutch Trial Register: NTR3938 . Date of registration: April 7(th), 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Childhood overweight and obesity. [http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood/en/]
-
- Schonbeck Y, Talma H, van Dommelen P, Bakker B, Buitendijk SE, Hirasing RA, et al. Increase in prevalence of overweight in Dutch children and adolescents: a comparison of nationwide growth studies in 1980, 1997 and 2009. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027608. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schönbeck Y, Buuren S, van. Factsheet: Resultaten Vijfde Landelijke Groeistudie [Results of Fifth Dutch Growth Study]. In.: TNO; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous