Dynamic endothelial cell rearrangements drive developmental vessel regression
- PMID: 25884288
- PMCID: PMC4401640
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002125
Dynamic endothelial cell rearrangements drive developmental vessel regression
Erratum in
-
Correction: dynamic endothelial cell rearrangements drive developmental vessel regression.PLoS Biol. 2015 May 14;13(5):e1002163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002163. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 25974400 Free PMC article.
Abstract
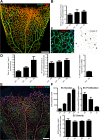
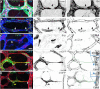
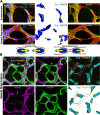
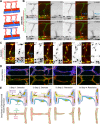
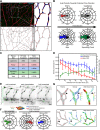
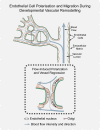
Patterning of functional blood vessel networks is achieved by pruning of superfluous connections. The cellular and molecular principles of vessel regression are poorly understood. Here we show that regression is mediated by dynamic and polarized migration of endothelial cells, representing anastomosis in reverse. Establishing and analyzing the first axial polarity map of all endothelial cells in a remodeling vascular network, we propose that balanced movement of cells maintains the primitive plexus under low shear conditions in a metastable dynamic state. We predict that flow-induced polarized migration of endothelial cells breaks symmetry and leads to stabilization of high flow/shear segments and regression of adjacent low flow/shear segments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438: 932–936. - PubMed
-
- Meeson AP, Argilla M, Ko K, Witte L, Lang RA (1999) VEGF deprivation-induced apoptosis is a component of programmed capillary regression. Development 126: 1407–1415. - PubMed
-
- Hughes S, Chang-Ling T (2000) Roles of endothelial cell migration and apoptosis in vascular remodeling during development of the central nervous system. Microcirculation 7: 317–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

