The non-coding RNAs of the H19-IGF2 imprinted loci: a focus on biological roles and therapeutic potential in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 25884481
- PMCID: PMC4397711
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-015-0467-3
The non-coding RNAs of the H19-IGF2 imprinted loci: a focus on biological roles and therapeutic potential in Lung Cancer
Abstract
Since it was first described, the imprinted cluster 11p15.5 has been reported to be deregulated in a variety of pediatric and adult cancers including that of the lung. Both protein coding and non-coding genes functioning as oncogenes or as tumor suppressor genes reside within this cluster. Oncomirs that can function as oncogenes or as tumor suppressors have also been reported. While a complete account of the role played by the 11p15.5 imprinted cluster in lung cancer is beyond the scope of this review, we will focus on the role of the non-coding RNAs processed from the H19-IGF2 loci. A special emphasis will be given to the H19/miR-675 gene locus. Their potential diagnostic and therapeutic use in lung cancer will be described.
Figures
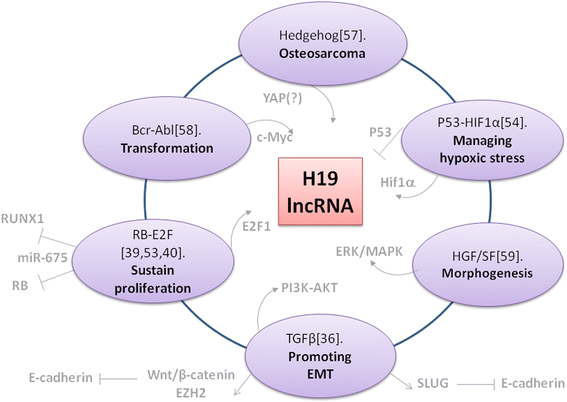
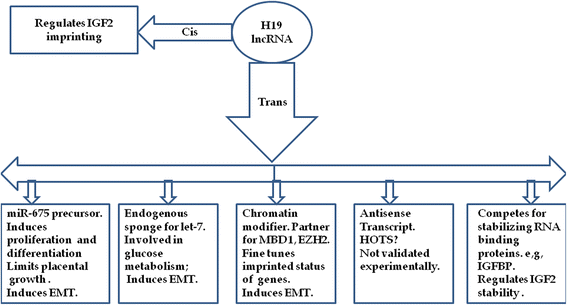
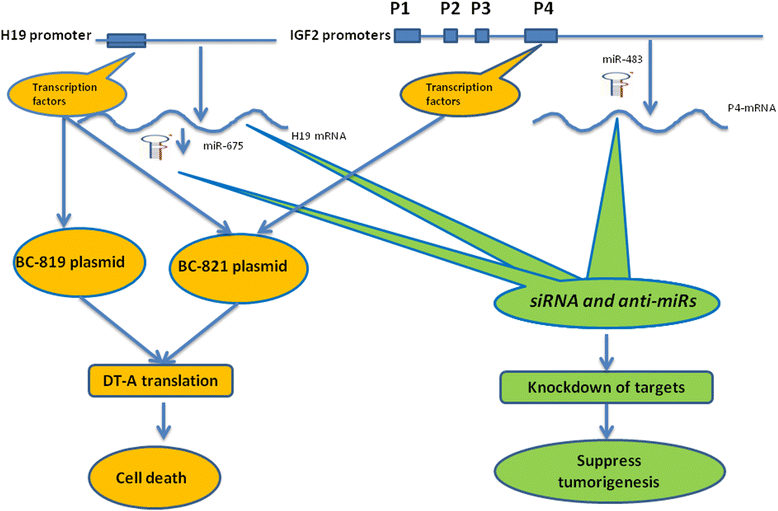
References
-
- Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:391–407. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

