Study CAMBIMED: Effects of changes in medication appearance on safety of antihypertensive and hypolipidemic treatments in chronic patients older than 65 years in primary health care
- PMID: 25884988
- PMCID: PMC4361135
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-014-1342-5
Study CAMBIMED: Effects of changes in medication appearance on safety of antihypertensive and hypolipidemic treatments in chronic patients older than 65 years in primary health care
Abstract
Background: Different studies have investigated the effects that changes in drug appearance have on the control of chronic diseases and drug safety. The main objective of the proposed study is to evaluate if changes in the appearance of the packaging and presentation of drugs having the same active ingredient are related to a decrease in adherence and an increase in usage errors for chronic treatment using antihypertensive (enalapril and amlodipine) and hypolipidemic agents (simvastatin) in patients ≥65 years old, over a one-year follow-up period.
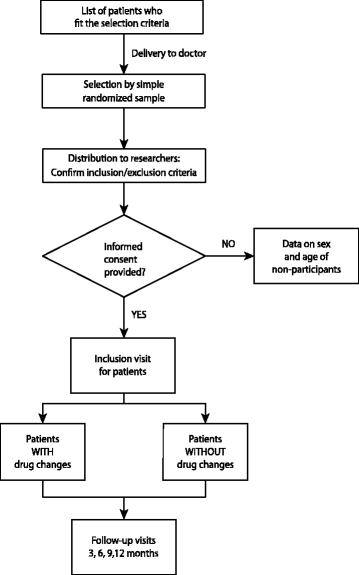
Methods/design: We propose a multicentric observational longitudinal cohort study with a one-year follow-up period in 8 primary health care centers (PHCC) in the Community of Madrid. 259 patients who are ≥65 years old, hypertensive and/or dyslipidemic, undergoing treatment with enalapril and/or amlodipine and/or simvastatin, and under formal follow-up of chronic patients in primary health care will be selected by simple random sampling. The main outcome variable will be a final combined variable (adherence and medication usage errors). Other included variables will be: sociodemographic and clinical variables of the patient, degree of disease control, drug taken, number of changes in the appearance of each drug by the pharmacy, and the type and frequency of both avoidable and non-avoidable adverse effects during the follow-up period. A descriptive and a multivariate analysis of the variables will be carried out by means of a logistic regression model, using the final combined variable as the dependent variable (error and/or inadequate usage of the drug), and variables shown to be related to it during the bivariate analysis as the independent variables.
Discussion: For drugs of the same active ingredient, the effect that different package appearances and presentation may have on the safety of patients undergoing chronic treatments is unknown under the new legislative framework. There are various initiatives that promote the iso-appearance of drugs: "If they are the same, make them look the same". It is to be expected that older, multi-medicated patients with chronic pathologies will be the ones under a greater risk of suffering from this problem.
Figures
References
-
- Real Decreto-ley 9/2011, De 19 De Agosto. Medidas Para La Mejora De La Calidad y Cohesión Del Sistema Nacional De Salud, De Contribución a La Consolidación Fiscal, y De Elevación Del Importe Máximo De Los Avales Del Estado Para 2011. Boletín Oficial del Estado no 200; 2011.
-
- Real Decreto-ley 16/2012, De 20 De Abril. Medidas Urgentes Para Garantizar La Sostenibilidad Del Sistema Nacional De Salud y Mejorar La Calidad y Seguridad De Sus Prestaciones. Boletín Oficial del Estado no 98; 2012.
-
- Ministerio de Sanidad . Estudio APEAS: Estudio Sobre La Seguridad De Los Pacientes En Atención Primaria De Salud. 2008.
-
- Grupo de seguridad del paciente [http://sano-y-salvo.blogspot.com/feeds/posts/default]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical