MeCP2 plays an analgesic role in pain transmission through regulating CREB / miR-132 pathway
- PMID: 25885346
- PMCID: PMC4404689
- DOI: 10.1186/s12990-015-0015-4
MeCP2 plays an analgesic role in pain transmission through regulating CREB / miR-132 pathway
Abstract
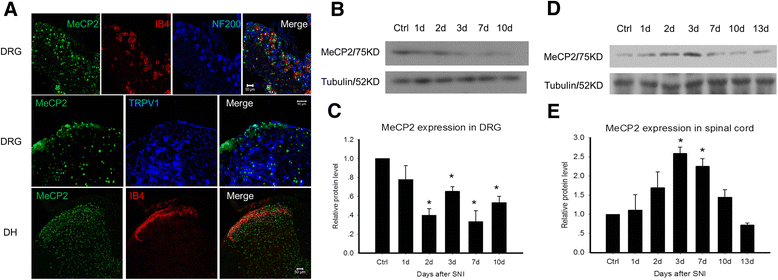
Background: The Methyl CpG binding protein 2 gene (MeCP2 gene) encodes a critical transcriptional repressor and is widely expressed in mammalian neurons. MeCP2 plays a critical role in neuronal differentiation, neural development, and synaptic plasticity. Mutations and duplications of the human MECP2 gene lead to severe neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Rett syndrome and autism. In this study we investigate the role of MeCP2 in the spinal cord and found that MeCP2 plays an important role as an analgesic mediator in pain circuitry.
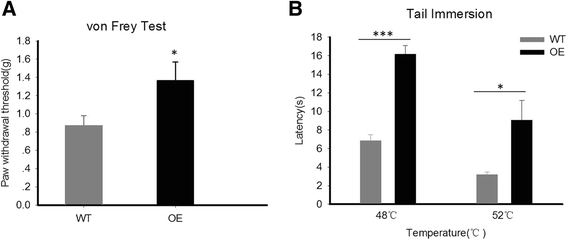
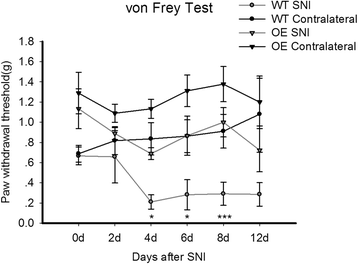
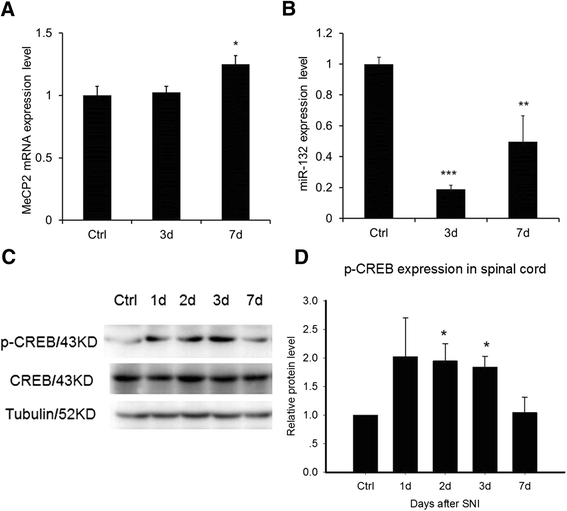
Findings: Experiments using MeCP2 transgenic mice showed that overexpression of MeCP2 weakens both acute mechanical pain and thermal pain, suggesting an analgesic role of MeCP2 in acute pain transduction. We found that through p-CREB/miR-132 signaling cascade is involved in MeCP2-mediated pain transduction. We also examined the role of MeCP2 in chronic pain formation using spared nerve injury (SNI) model. Strikingly, we found that development of neuropathic pain attenuates in MeCP2 transgenic mice comparing to wild type (WT) mice.
Conclusions: Our study shows that MeCP2 plays an analgesic role in both acute pain transduction and chronic pain formation through regulating CREB-miR-132 pathway. This work provides a potential therapeutic target for neural pathologic pain, and also sheds new lights on the abnormal sensory mechanisms associated with autism spectrum orders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MeCP2-regulated miRNAs control early human neurogenesis through differential effects on ERK and AKT signaling.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):1051-1065. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.86. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28439102 Free PMC article.
-
The role of MeCP2 in CNS development and function.Horm Behav. 2011 Mar;59(3):364-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.05.014. Epub 2010 May 31. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 20515694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal regulation of autism-related genes MeCP2 and PTEN via microRNAs.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 4;6:20392. doi: 10.1038/srep20392. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26843422 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal synaptic plasticity is impaired in the Mecp2-null mouse model of Rett syndrome.Neurobiol Dis. 2006 Jan;21(1):217-27. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.07.005. Epub 2005 Aug 8. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16087343
-
MeCP2 dysfunction in Rett syndrome and related disorders.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Jun;16(3):276-81. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.04.009. Epub 2006 May 2. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16647848 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide redistribution of MeCP2 in dorsal root ganglia after peripheral nerve injury.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016 Jun 7;9:23. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0073-5. eCollection 2016. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016. PMID: 27279901 Free PMC article.
-
Role of DNA Methyl-CpG-Binding Protein MeCP2 in Rett Syndrome Pathobiology and Mechanism of Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 8;11(1):75. doi: 10.3390/biom11010075. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33429932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances With Non-coding RNAs in Neuropathic Pain.Front Neurosci. 2021 Dec 23;15:760936. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.760936. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 35002601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE)-Induced Elevated Expression of the E1 Isoform of Methyl CpG Binding Protein 2 (MeCP2E1): Implications in Multiple Sclerosis (MS)-Induced Neurological Disability and Associated Myelin Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 12;18(6):1254. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061254. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28604632 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal astrocytic MeCP2 regulates Kir4.1 for the maintenance of chronic hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain.Prog Neurobiol. 2023 May;224:102436. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2023.102436. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Prog Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36931588 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

