A basic review on the inferior alveolar nerve block techniques
- PMID: 25886095
- PMCID: PMC4173572
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.128891
A basic review on the inferior alveolar nerve block techniques
Abstract
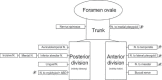
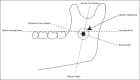
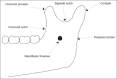
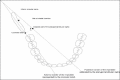
The inferior alveolar nerve block is the most common injection technique used in dentistry and many modifications of the conventional nerve block have been recently described in the literature. Selecting the best technique by the dentist or surgeon depends on many factors including the success rate and complications related to the selected technique. Dentists should be aware of the available current modifications of the inferior alveolar nerve block techniques in order to effectively choose between these modifications. Some operators may encounter difficulty in identifying the anatomical landmarks which are useful in applying the inferior alveolar nerve block and rely instead on assumptions as to where the needle should be positioned. Such assumptions can lead to failure and the failure rate of inferior alveolar nerve block has been reported to be 20-25% which is considered very high. In this basic review, the anatomical details of the inferior alveolar nerve will be given together with a description of its both conventional and modified blocking techniques; in addition, an overview of the complications which may result from the application of this important technique will be mentioned.
Keywords: Complications; inferior alveolar nerve block; techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stumbling block for inferior alveolar nerve block in predoctoral students: An analytical observational study and review of literature of mandibular nerve block techniques.J Family Med Prim Care. 2021 Apr;10(4):1633-1638. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_282_20. Epub 2021 Apr 29. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021. PMID: 34123904 Free PMC article.
-
The Incidence of Intravascular Needle Entrance during Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Injection.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2008 Winter;2(1):38-41. doi: 10.5681/joddd.2008.008. Epub 2008 May 15. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2008. PMID: 23285329 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of needle deflection in success of the inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis.J Endod. 2003 Oct;29(10):630-3. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200310000-00004. J Endod. 2003. PMID: 14606783 Clinical Trial.
-
Alternative techniques for failure of conventional inferior alveolar nerve block.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019 Jun;19(3):125-134. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.3.125. Epub 2019 Jun 30. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 31338418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applied anatomy of the pterygomandibular space: improving the success of inferior alveolar nerve blocks.Aust Dent J. 2011 Jun;56(2):112-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01312.x. Aust Dent J. 2011. PMID: 21623801 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation of efficacy of Halstead technique, Clark and Holmes technique, Gow Gates technique, and Sargenti technique for mandibular anesthesia.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Sep-Dec;14(3):466-470. doi: 10.4103/njms.njms_157_22. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 38273905 Free PMC article.
-
Dental students, interns, and junior dentists' awareness and attitude toward the inferior alveolar nerve block technique and related failure.J Dent Sci. 2024 Oct;19(4):2315-2322. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.02.008. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39347103 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed-release intraosseus anesthesia as an alternative to lower alveolar nerve block in lower third molar extraction: a randomized clinical trial.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2022 Jun;22(3):217-226. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2022.22.3.217. Epub 2022 May 27. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 35693356 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Exclusive Lingual Nerve Block versus Conventional Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block in Achieving Lingual Soft-tissue Anesthesia.Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Jul-Dec;7(2):250-255. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_65_17. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 29264294 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionising Third Molar Surgery: Unveiling the Superiority of Articaine and Lignocaine in Nerve Block Techniques. A Ground-breaking Triple-Blind, Randomised Clinical Trial.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025 Feb;24(1):286-292. doi: 10.1007/s12663-023-02107-y. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025. PMID: 39902435
References
-
- Malamed S. 6th ed. Maryland Heights: Mosby; 2012. Handbook of Local Anesthesia; pp. 157–253.
-
- Somayaji SK, Acharya SR, Mohandas KG, Venkataramana V. Anatomy and clinical applications of the mandibular nerve. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012;113:431–40. - PubMed
-
- Thotakura B, Rajendran SS, Gnanasundaram V, Subramaniam A. Variations in the posterior division branches of the mandibular nerve in human cadavers. Singapore Med J. 2013;54:149–51. - PubMed
-
- Siessere S, Hallak Regalo SC, Semprini M, De Oliveira Honorato R, Vitti M, Mizusaki Iyomasa M, et al. Anatomical variations of the mandibular nerve and its branches correlated to clinical situations. Minerva Stomatol. 2009;58:209–15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources