The 15kDa selenoprotein and thioredoxin reductase 1 promote colon cancer by different pathways
- PMID: 25886253
- PMCID: PMC4401539
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124487
The 15kDa selenoprotein and thioredoxin reductase 1 promote colon cancer by different pathways
Abstract
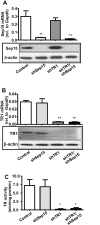
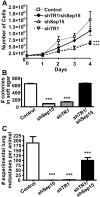
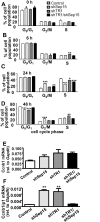
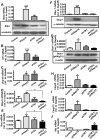
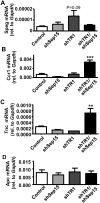
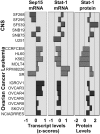
Selenoproteins mediate much of the cancer-preventive properties of the essential nutrient selenium, but some of these proteins have been shown to also have cancer-promoting effects. We examined the contributions of the 15kDa selenoprotein (Sep15) and thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1) to cancer development. Targeted down-regulation of either gene inhibited anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent growth and formation of experimental metastases of mouse colon carcinoma CT26 cells. Surprisingly, combined deficiency of Sep15 and TR1 reversed the anti-cancer effects observed with down-regulation of each single gene. We found that inflammation-related genes regulated by Stat-1, especially interferon-γ-regulated guanylate-binding proteins, were highly elevated in Sep15-deficient, but not in TR1-deficient cells. Interestingly, components of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were up-regulated in cells lacking both TR1 and Sep15. These results suggest that Sep15 and TR1 participate in interfering regulatory pathways in colon cancer cells. Considering the variable expression levels of Sep15 and TR1 found within the human population, our results provide insights into new roles of selenoproteins in cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2013. Atlanta: American Cancer Society, 2013.
-
- Duffield-Lillico AJ, Dalkin BL, Reid ME, Turnbull BW, Slate EH, Jacobs ET, et al. Selenium supplementation, baseline plasma selenium status and incidence of prostate cancer: an analysis of the complete treatment period of the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Trial. BJU Int. 2003;91: 608–612. - PubMed
-
- Jao SW, Shen KL, Lee WP, Ho YS. Effect of selenium on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced intestinal cancer in rats. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996;39: 628–631. - PubMed
-
- Almondes KG, Leal GV, Cozzolino SM, Philippi ST, Rondó PH. The role of selenoproteins in cancer. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2010;56: 484–488. - PubMed
-
- Apostolou S, Klein JO, Mitsuuchi Y, Shetler JN, Poulikakos PL, Jhanwar SC, et al. Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in mesothelioma cells by selenium and dependence on selenoprotein SEP15 genotype. Oncogene. 2004;23: 5032–5040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

