Psychopathic traits among a consecutive sample of Finnish pretrial fire-setting offenders
- PMID: 25886305
- PMCID: PMC4382829
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-015-0425-x
Psychopathic traits among a consecutive sample of Finnish pretrial fire-setting offenders
Abstract
Background: Psychopathy, a severe disorder of personality, is well represented in the criminal and forensic psychiatric population and is significantly associated with increased risk of violence and crime. Fire-setting is a major source of property damage, injury, and death in many Western countries. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate psychopathic traits in a consecutive sample of Finnish male pretrial fire-setting offenders. Further, we wanted to investigate whether fire-setting recidivists show higher traits of psychopathy than one-time firesetters and whether exclusive firesetters show lower traits of psychopathy than those with criminal versatility.
Methods: The forensic psychiatric examination statements for male firesetters who underwent a pretrial forensic psychiatric evaluation during a 10-year period (1989 -1998) were reviewed. The sample comprised 129 firesetters with normal IQ, 41 of whom were fire-setting recidivists. Fifty men were exclusive firesetters. Assessment of psychopathy-like personality character was performed using the 20-item Hare Psychopathy Checklist-Revised.
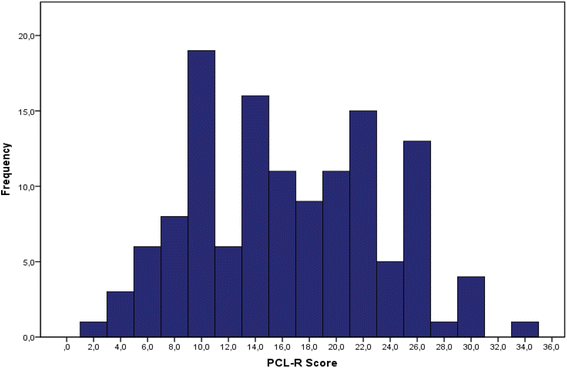
Results: Two individuals (1.6%, 95% Cl: 0.0-3.7) scored ≥30 points and 19 (14.7%, 95% Cl: 8.6-20.8) ≥ 25 points on the PCL-R. The mean PCL-R total score was 16.1 (SD 6.88), the mean Factor 1 score 5.0 (SD 3.41), and the mean Factor 2 score 9.9 (SD 3.86). No significant differences emerged between the recidivists and the one-time firesetters. The versatile firesetters exhibited significantly higher mean total and factor scores than the exclusive ones.
Conclusion: Among firesetters, there is a subgroup of persons with significant psychopathic traits, which should be recognized in legal and health care organizations. Although psychopathy was associated with greater criminal versatility, it bore no relationship to fire-setting recidivism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Firesetting and general criminal recidivism among a consecutive sample of Finnish pretrial male firesetters: A register-based follow-up study.Psychiatry Res. 2018 Jan;259:377-384. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Nov 5. Psychiatry Res. 2018. PMID: 29120846
-
Psychopathic traits and offender characteristics - a nationwide consecutive sample of homicidal male adolescents.BMC Psychiatry. 2009 May 6;9:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-9-18. BMC Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19419577 Free PMC article.
-
Personality traits and violent behavior: a comparison between psychopathic and non-psychopathic male murderers.Psychiatry Res. 2014 Nov 30;219(3):604-8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.06.026. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Psychiatry Res. 2014. PMID: 25023368
-
[From conduct disorder in childhood to psychopathy in adult life].Psychiatriki. 2012 Jun;23 Suppl 1:107-16. Psychiatriki. 2012. PMID: 22796980 Review. Greek, Modern.
-
Psychopathic Personality Traits and the Successful Criminal.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2018 Nov;62(15):4834-4853. doi: 10.1177/0306624X18787304. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2018. PMID: 30066592 Review.
Cited by
-
Do seriously offending girls differ from their age- and offence type-matched male counterparts on psychopathic traits or psychopathy-related background variables?Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2016 Nov 1;10:38. doi: 10.1186/s13034-016-0128-1. eCollection 2016. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2016. PMID: 27822299 Free PMC article.
-
Suicide risk of male State patients with antisocial personality traits.S Afr J Psychiatr. 2020 Oct 23;26:1543. doi: 10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v26i0.1543. eCollection 2020. S Afr J Psychiatr. 2020. PMID: 33240553 Free PMC article.
-
Bringing Light Into the Dark: Associations of Fire Interest and Fire Setting With the Dark Tetrad.Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 27;13:876575. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.876575. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35832918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cleckley H. The Mask of Sanity 5th edition. St. Louis: MO; 1976.
-
- Hare RD. The Hare Psychopathy Checklist – Revised. Toronto: Multi-Health Systems; 1991.
-
- Hare RD. Psychopaths and their nature: Implications for the mental health and criminal justice systems. In: Millon T, Simonson E, Burket-Smith M, Davis R, editors. Psychopathy: Antisocial, Criminal, and Violent Behaviour. New York: Guilford Press; 1998. pp. 188–212.
-
- Forth AE, Burke HC. Psychopathy in adolescence: assessment, violence, and developmental precursors. In: Cooke DJ, Forth AE, Hare RD, editors. Psychopathy: Theory, Research, and Implications for Society. Dordrecht: Kluwer; 1998. pp. 205–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous