Signaling by exosomal microRNAs in cancer
- PMID: 25886763
- PMCID: PMC4391656
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-015-0148-3
Signaling by exosomal microRNAs in cancer
Abstract
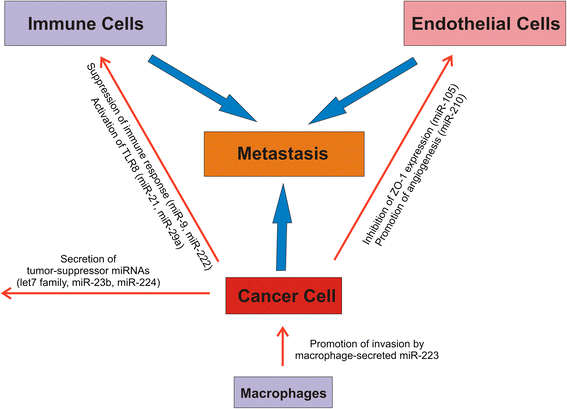
A class of small non-coding RNAs, the microRNAs (miRNAs), have recently attracted great attention in cancer research since they play a central role in regulation of gene-expression and miRNA aberrant expression is found in almost all types of human cancer. The discovery of circulating miRNAs in body fluids and the finding that they are often tumor specific and can be detected early in tumorigenesis has soon led to the evaluation of their possible use as cancer biomarkers and treatment-response predictors. The evidence that tumor cells communicate via the secretion and delivery of miRNAs packed into tumor-released microvesicles has prompted to investigate miRNA contribution as signaling molecules to the establishment and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment and the metastatic niche in cancer. In this review we highlight the recent advances on the role of exosomal miRNAs as mediators of cancer cell-to-cell communication.
Figures
References
-
- Ciesla M, Skrzypek K, Kozakowska M, Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J. MicroRNAs as biomarkers of disease onset. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;401:2051–2061. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources