Renal angina: concept and development of pretest probability assessment in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 25887311
- PMCID: PMC4344798
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-015-0779-y
Renal angina: concept and development of pretest probability assessment in acute kidney injury
Abstract
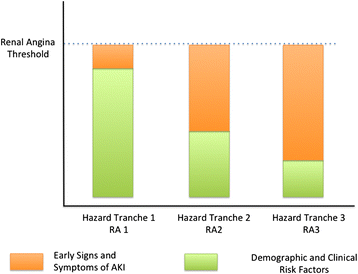
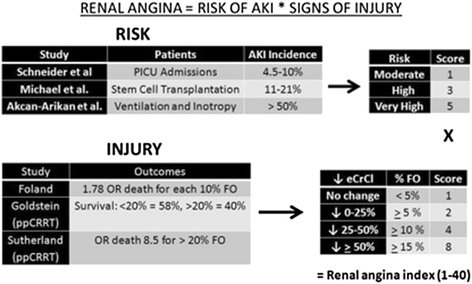
The context of a diagnostic test is a critical component for the interpretation of its result. This context defines the pretest probability of the diagnosis and forms the basis for the interpretation and value of adding the diagnostic test. In the field of acute kidney injury, a multitude of early diagnostic biomarkers have been developed, but utilization in the appropriate context is less well understood and has not been codified until recently. In order to better operationalize the context and pretest probability assessment for acute kidney injury diagnosis, the renal angina concept was proposed in 2010 for use in both children and adults. Renal angina has been assessed in approximately 1,000 subjects. However, renal angina as a concept is still unfamiliar to most clinicians and the rationale for introducing the term is not obvious. We therefore review the concept and development of renal angina, and the currently available data validating it. We discuss the various arguments for and against this construct. Future research testing the performance of renal angina with acute kidney injury biomarkers is warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary and serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury: an in-depth review of the literature.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Feb;28(2):254-73. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs380. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23115326 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for early diagnosis of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016 Mar;49(3):746-55. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezv199. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 26094017 Review.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin curve and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin extended-range assay: a new biomarker approach in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury and cardio-renal syndrome.Semin Nephrol. 2012 Jan;32(1):121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.11.015. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22365170
-
Biomarkers of renal function, which and when?Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25195004 Review.
-
Acute kidney injury: definition, diagnosis and epidemiology.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2016 Feb;68(1):49-57. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2016. PMID: 26364570 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 for acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 25;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1660-y. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28340605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index in predicting acute kidney injury in patients admitted to the intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure.Crit Care Sci. 2023 Dec 22;35(3):302-310. doi: 10.5935/2965-2774.20230141-en. eCollection 2023. Crit Care Sci. 2023. PMID: 38133160 Free PMC article.
-
Early Sequential Risk Stratification Assessment to Optimize Fluid Dosing, CRRT Initiation and Discontinuation in Critically Ill Children with Acute Kidney Injury: Taking Focus 2 Process Article.J Clin Trials. 2020;10(6):435. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Clin Trials. 2020. PMID: 34476130 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term outcomes after postsurgical acute kidney injury requiring dialysis.Clin Epidemiol. 2018 Oct 26;10:1583-1598. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S169302. eCollection 2018. Clin Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 30464638 Free PMC article.
-
Use of height-independent baseline creatinine imputation method with renal angina index.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Oct;34(10):1777-1784. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04294-8. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31286243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebell MH, White LL, Weismantel D. A systematic review of troponin T and I values as a prognostic tool for patients with chest pain. J Fam Pract. 2000;49:746–753. - PubMed
-
- Stein R, Gupta B, Agarwal S, Golub J, Bhutani D, Rosman A, et al. Prognostic implications of normal (<0.10 ng/ml) and borderline (0.10 to 1.49 ng/ml) troponin elevation levels in critically ill patients without acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102:509–512. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.04.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hammerer-Lercher A, Ploner T, Neururer S, Schratzberger P, Griesmacher A, Pachinger O, et al. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T compared with standard troponin T testing on emergency department admission: how much does it add in everyday clinical practice? J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000204. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012, 2:1–141.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

