Novel syndromes associated with JC virus infection of neurons and meningeal cells: no longer a gray area
- PMID: 25887767
- PMCID: PMC4414882
- DOI: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000201
Novel syndromes associated with JC virus infection of neurons and meningeal cells: no longer a gray area
Abstract
Purpose of review: The availability of a growing number of immunomodulatory medications over the past few years has been associated with various JC virus (JCV)-associated brain syndromes in patients with autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis, Crohn's disease, and psoriasis that had not been previously recognized as predisposing factors for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. This review covers the three novel syndromes discovered in the last decade that are caused by JCV infection of neurons and meningeal cells.
Recent findings: For more than 30 years, JCV was thought to exclusively infect oligodendrocytes and astrocytes in the white matter of the brain of immunosuppressed individuals. We now recognize that JCV-infected glial cells are frequently located at the gray-white matter junction or exclusively within the gray matter causing demyelination in the cortex. Mutations in JCV can trigger a change in tropism leading to involvement of other cell types, such as neurons and meningeal cells, causing clinically distinct entities. These new features of JCV infection provide challenges for clinicians taking care of affected patients and investigators studying the biology of this polyomavirus, its pathogenesis, and tropism.
Summary: We hope that increasing awareness of these syndromes will lead to early diagnosis, and pave the way for new avenues of research to better understand all aspects of JCV pathogenesis and develop efficient therapies for our patients. However, we need to remain vigilant and open to the possibility that additional JC variants or yet unknown polyomaviruses may also be associated with neurological diseases.
Figures
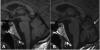
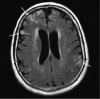
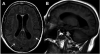

 = JC virion
= JC virionReferences
-
- Gheuens S, Wuthrich C, Koralnik IJ. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: why gray and white matter. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013;8:189–215. This review offers a more comprehensive overview of PML and other JC virus associated neurological conditions. - PubMed
-
- Astrom KE, Mancall EL, Richardson EP., Jr Progressive multifocal leuko-encephalopathy; a hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain. 1958;81:93–111. - PubMed
-
- Padgett BL, Walker DL, ZuRhein GM, et al. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971;1:1257–1260. - PubMed
-
- Messam CA, Hou J, Gronostajski RM, Major EO. Lineage pathway of human brain progenitor cells identified by JC virus susceptibility. Ann Neurol. 2003;53:636–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

