Optimizing mean arterial pressure in septic shock: a critical reappraisal of the literature
- PMID: 25888071
- PMCID: PMC4355573
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-015-0794-z
Optimizing mean arterial pressure in septic shock: a critical reappraisal of the literature
Abstract
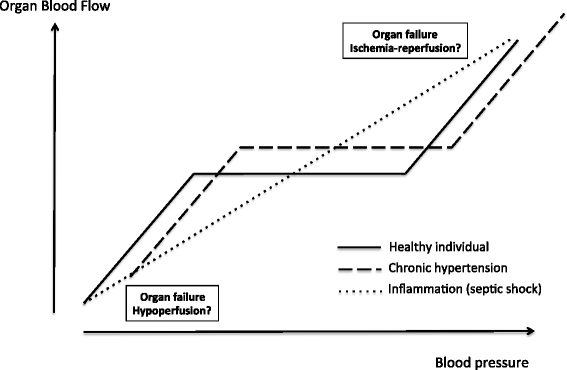
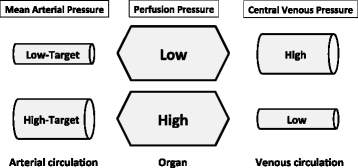
Guidelines recommend that a mean arterial pressure (MAP) value greater than 65 mm Hg should be the initial blood pressure target in septic shock, but what evidence is there to support this statement? We searched Pubmed and Google Scholar by using the key words 'arterial pressure', 'septic shock', and 'norepinephrine' and retrieved human studies published between 1 January 2000 and 31 July 2014. We identified seven comparative studies: two randomized clinical trials and five observational studies. The results of the literature review suggest that a MAP target of 65 mm Hg is usually sufficient in patients with septic shock. However, a MAP of around 75 to 85 mm Hg may reduce the development of acute kidney injury in patients with chronic arterial hypertension. Because of the high prevalence of chronic arterial hypertension in patients who develop septic shock, this finding is of considerable importance. Future studies should assess interactions between time, fluid volumes administered, and doses of vasopressors.
Figures
Comment in
-
One-size MAP does not fit all.Crit Care. 2015 May 7;19(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0939-0. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25947571 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb SA, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R, Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including the Pediatric Subgroup Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López A, Lorente JA, Steingrub J, Bakker J, McLuckie A, Willatts S, Brockway M, Anzueto A, Holzapfel L, Breen D, Silverman MS, Takala J, Donaldson J, Arneson C, Grove G, Grossman S, Grover R. Multiple-center, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor 546C88: effect on survival in patients with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:21–30. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000105581.01815.C6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

