Burden of bacterial resistance among neonatal infections in low income countries: how convincing is the epidemiological evidence?
- PMID: 25888320
- PMCID: PMC4364576
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-015-0843-x
Burden of bacterial resistance among neonatal infections in low income countries: how convincing is the epidemiological evidence?
Abstract
Background: Antibiotic resistance is a threat in developing countries (DCs) because of the high burden of bacterial disease and the presence of risk factors for its emergence and spread. This threat is of particular concern for neonates in DCs where over one-third of neonatal deaths may be attributable to severe infections and factors such as malnutrition and HIV infection may increase the risk of death. Additional, undocumented deaths due to severe infection may also occur due to the high frequency of at-home births in DCs.
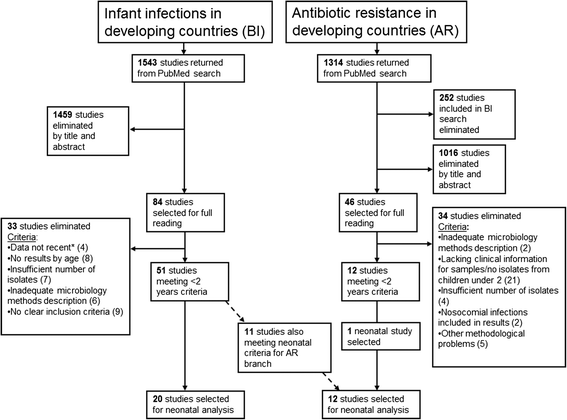
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of studies published after 2000 on community-acquired invasive bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance among neonates in DCs. Twenty-one articles met all inclusion criteria and were included in the final analysis.
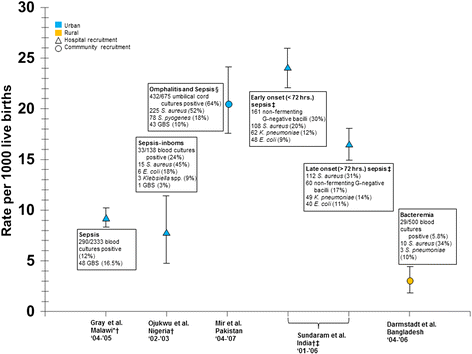
Results: Ninety percent of studies recruited participants at large or university hospitals. The majority of studies were conducted in Sub-Saharan Africa (n=10) and the Indian subcontinent (n=8). Neonatal infection incidence ranged from 2.9 (95% CI 1.9-4.2) to 24 (95% CI 21.8-25.7) for 1000 live births. The three most common bacterial isolates in neonatal sepsis were Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella. Information on antibiotic resistance was sparse and often relied on few isolates. The majority of resistance studies were conducted prior to 2008. No conclusions could be drawn on Enterobacteriaceae resistance to third generation cephalosporins or methicillin resistance among Staphylococcus aureus.
Conclusions: Available data were found insufficient to draw a true, recent, and accurate picture of antibiotic resistance in DCs among severe bacterial infection in neonates, particularly at the community level. Existing neonatal sepsis treatment guidelines may no longer be appropriate, and these data are needed as the basis for updated guidelines. Reliable microbiological and epidemiological data at the community level are needed in DCs to combat the global challenge of antibiotic resistance especially among neonates among whom the burden is greatest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, Perin J, Scott S, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Campbell H, Cibulskis R, Li M, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379(9832):2151–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60560-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumarasamy KK, Toleman MA, Walsh TR, Bagaria J, Butt F, Balakrishnan R, Chaudhary U, Doumith M, Giske CG, Irfan S, et al. Emergence of a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: a molecular, biological, and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10(9):597–602. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70143-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

