Manipulation of prostate cancer metastasis by locus-specific modification of the CRMP4 promoter region using chimeric TALE DNA methyltransferase and demethylase
- PMID: 25888628
- PMCID: PMC4496338
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3192
Manipulation of prostate cancer metastasis by locus-specific modification of the CRMP4 promoter region using chimeric TALE DNA methyltransferase and demethylase
Abstract
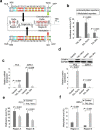
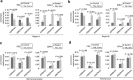
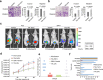
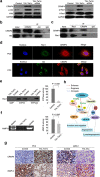
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed non-cutaneous cancer and one of the leading causes of cancer death for North American men. Whereas localized prostate cancer can be cured, there is currently no cure for metastatic prostate cancer. Here we report a novel approach that utilizes designed chimeric transcription activator-like effectors (dTALEs) to control prostate cancer metastasis. Transfection of dTALEs of DNA methyltransferase or demethylase induced artificial, yet active locus-specific CpG and subsequent histone modifications. These manipulations markedly altered expression of endogenous CRMP4, a metastasis suppressor gene. Remarkably, locus-specific CpG demethylation of the CRMP4 promoter in metastatic PC3 cells abolished metastasis, whereas locus-specific CpG methylation of the promoter in non-metastatic 22Rv1 cells induced metastasis. CRMP4-mediated metastasis suppression was found to require activation of Akt/Rac1 signaling and down-regulation of MMP-9 expression. This proof-of-concept study with dTALEs for locus-specific epigenomic manipulation validates the selected CpG methylation of CRMP4 gene as an independent biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer metastasis and opens up a novel avenue for mechanistic research on cancer biology.
Keywords: CRMP4; epigenetic manipulation; metastasis; prostate cancer; transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pound CR, Partin AW, Eisenberger MA, Chan DW, Pearson JD, Walsh PC. Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 1999;281:1591–1597. - PubMed
-
- Petrylak DP, Tangen CM, Hussain MH, Lara PN, Jr, Jones JA, Taplin ME, Burch PA, Berry D, Moinpour C, Kohli M, Benson MC, Small EJ, Raghavan D, et al. Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1513–1520. - PubMed
-
- Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN, Oudard S, Théodore C, James ND, Turesson I, Rosenthal MA. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1502–1512. - PubMed
-
- Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, Redfern CH, Ferrari AC, Dreicer R, Sims RB, Xu Y, Frohlich MW. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:411–422. - PubMed
-
- Yap TA, Pezaro CJ, de Bono JS. Cabazitaxel in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2012;12:1129–1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

