The significance fallacy in inferential statistics
- PMID: 25888971
- PMCID: PMC4377068
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-015-1020-4
The significance fallacy in inferential statistics
Abstract
Background: Statistical significance is an important concept in empirical science. However the meaning of the term varies widely. We investigate into the intuitive understanding of the notion of significance.
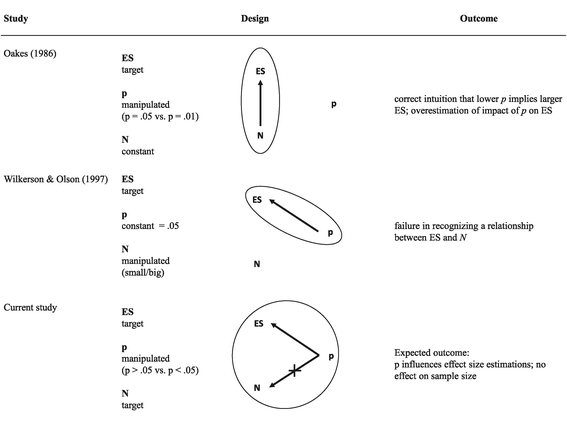
Methods: We described the results of two different experiments published in a major psychological journal to a sample of students of psychology, labeling the findings as 'significant' versus 'non-significant.' Participants were asked to estimate the effect sizes and sample sizes of the original studies.
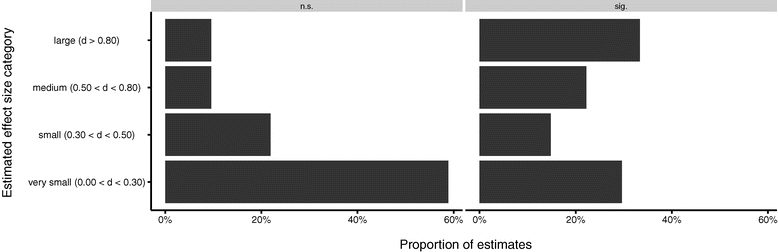
Results: Labeling the results of a study as significant was associated with estimations of a big effect, but was largely unrelated to sample size. Similarly, non-significant results were estimated as near zero in effect size.
Conclusions: After considerable training in statistics, students largely equate statistical significance with medium to large effect sizes, rather than with large sample sizes. The data show that students assume that statistical significance is due to real effects, rather than to 'statistical tricks' (e.g., increasing sample size).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Out with .05, in with Replication and Measurement: Isolating and Working with the Particular Effect Sizes that are Troublesome for Inferential Statistics.J Gen Psychol. 2017 Oct-Dec;144(4):309-316. doi: 10.1080/00221309.2017.1381496. Epub 2017 Oct 12. J Gen Psychol. 2017. PMID: 29023206
-
Power of mental health nursing research: a statistical analysis of studies in the International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2013 Feb;22(1):69-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0349.2012.00845.x. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2013. PMID: 22738423
-
The large sample size fallacy.Scand J Caring Sci. 2013 Jun;27(2):487-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2012.01052.x. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Scand J Caring Sci. 2013. PMID: 22862286
-
Redressing the power and effect of significance. A new approach to an old problem: teaching statistics to nursing students.Nurse Educ Today. 2000 Jul;20(5):358-64. doi: 10.1054/nedt.2000.0429. Nurse Educ Today. 2000. PMID: 10895117 Review.
-
[Significance, effect size, and confidence interval].Rehabilitation (Stuttg). 2004 Jun;43(3):174-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-814934. Rehabilitation (Stuttg). 2004. PMID: 15202042 Review. German.
Cited by
-
A Personalized Intervention to Increase Environmental Health Literacy and Readiness to Change in a Northern Nevada Population: Effects of Environmental Chemical Exposure Report-Back.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Jul 11;21(7):905. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21070905. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39063482 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate variable selection in N-of-1 observational studies via additive Bayesian networks.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 26;19(8):e0305225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305225. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39186511 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Daily-Use Products and Urinary Biomarkers of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Adults of Reproductive Age.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jan 13;22(1):99. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22010099. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39857552 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and predicting drug resistance rate and strength.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Aug;35(8):1259-67. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2659-z. Epub 2016 May 21. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27209288
-
What possibly affects nighttime heart rate? Conclusions from N-of-1 observational data.Digit Health. 2022 Aug 24;8:20552076221120725. doi: 10.1177/20552076221120725. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2022. PMID: 36046637 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

