Rhipicephalus microplus and Ixodes ovatus cystatins in tick blood digestion and evasion of host immune response
- PMID: 25889092
- PMCID: PMC4340882
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-015-0743-3
Rhipicephalus microplus and Ixodes ovatus cystatins in tick blood digestion and evasion of host immune response
Abstract
Background: Cystatins are a group of cysteine protease inhibitors responsible for physiological proteolysis regulation and present in a wide range of organisms. Studies about this class of inhibitors in parasites have contributed to clarify their roles in important physiological processes, like blood digestion and modulation of host immune response during blood feeding. Thus, cystatins are a subject of research on the development of new parasite control methods. Additionally, the characterization of proteins shared by different parasite species represents a valuable strategy to find potential targets in multi-species control methods. However, cystatin functions in ticks remain undetermined, especially in Rhipicephalus microplus and Ixodes ovatus, two species that affect livestock and human health, respectively.
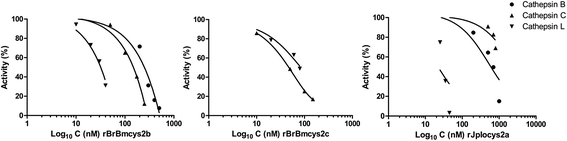
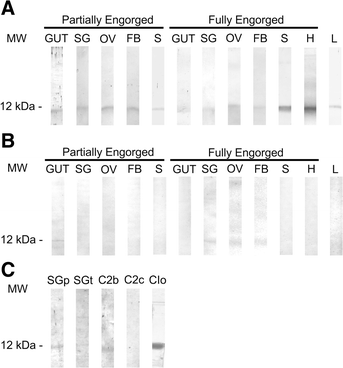
Methods: Here we report the inhibitory profile of two R. microplus (BrBmcys2b and BrBmcys2c) and one I. ovatus (JpIocys2a) cystatins to commercial cathepsins B, C, and L. The presence of native cystatins in R. microplus tissues was analyzed using sera against recombinant BrBmcys2b and BrBmcys2c. Also, a peptide from JpIocys2a was synthesized for rabbit immunization, and this serum was used to analyze the cross antigenicity between R. microplus and I. ovatus cystatins.
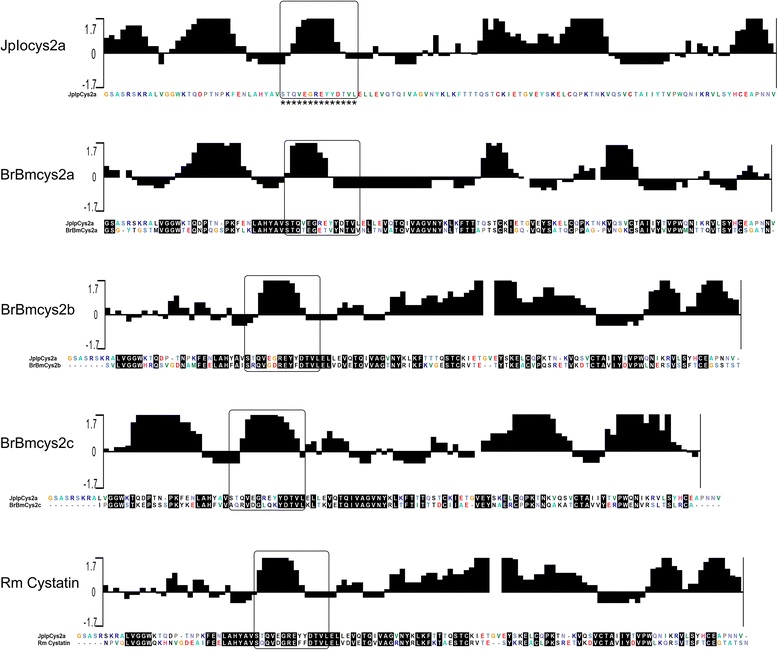
Results: Enzymatic inhibition profile of tick cystatins shows a distinct modulation for cathepsins related to tick blood digestion and evasion of host immune response. Furthermore, BrBmcys2b was detected in saliva and different tissues along tick stages, while BrBmcys2c was detected mainly in gut from partially engorged R. microplus females, demonstrating a distinct pattern of cystatin expression, secretion and traffic between tick tissues. Moreover, phylogenetic analysis suggests that JpIocys2a belongs to the group of tick gut secreted cystatins. Finally, cross-antigenicity assays revealed that antibodies against the JpIocys2a peptide recognize native and recombinant R. microplus cystatins.
Conclusion: The presence of these proteins in different tissues and their ability to differentially inhibit cathepsins suggest distinct roles for JpIocys2a, BrBmcys2b, and BrBmcys2c in blood digestion, egg and larvae development, and modulation of host immune response in tick physiology. The cross-antigenicity between native and recombinant cystatins supports further experiments using JpIocys2a, BrBmcys2b, and BrBmcys2c as vaccine antigens.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sequence characterization and immunogenicity of cystatins from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013 Dec;4(6):492-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.06.005. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013. PMID: 24035585
-
Molecular and structural characterization of novel cystatins from the taiga tick Ixodes persulcatus.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017 Mar;8(3):432-441. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017. PMID: 28174118
-
Rhipicephalus microplus cystatin as a potential cross-protective tick vaccine against Rhipicephalus appendiculatus.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020 May;11(3):101378. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101378. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020. PMID: 31982372
-
Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus embryo proteins as target for tick vaccine.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Jul 15;148(1-2):149-56. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 7. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 21620488 Review.
-
Ticks and antibodies: May parasite density and tick evasion influence the outcomes following immunization protocols?Vet Parasitol. 2021 Dec;300:109610. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109610. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Vet Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34735848 Review.
Cited by
-
Mialostatin, a Novel Midgut Cystatin from Ixodes ricinus Ticks: Crystal Structure and Regulation of Host Blood Digestion.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 20;22(10):5371. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105371. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34065290 Free PMC article.
-
Host Immune Responses to Salivary Components - A Critical Facet of Tick-Host Interactions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 16;12:809052. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.809052. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35372098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low Genetic Polymorphism in the Immunogenic Sequences of Rhipicephalus microplus Clade C.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;10(11):1909. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111909. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423005 Free PMC article.
-
A longitudinal transcriptomic analysis of Rhipicephalus microplus midgut upon feeding.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024 Mar;15(2):102304. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2023.102304. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024. PMID: 38159432 Free PMC article.
-
Amblyostatin-1, the first salivary cystatin with host immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties from the Neotropical tick Amblyomma sculptum, vector of Brazilian spotted fever.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 17;16:1585703. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1585703. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40746554 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

