Study of plants traditionally used in public and animal health management in Seharti Samre District, Southern Tigray, Ethiopia
- PMID: 25889411
- PMCID: PMC4371875
- DOI: 10.1186/s13002-015-0015-5
Study of plants traditionally used in public and animal health management in Seharti Samre District, Southern Tigray, Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: In Ethiopia, medicinal plants have continued to play vital role in fulfilling human and livestock healthcare needs of different communities. However, these valuable resources are being depleted mainly due to agricultural expansion and deforestation. Therefore, immediate action is required to conserve these resources and document the associated knowledge. The purpose of this study was, thus, to document and analyze information associated with medicinal plants that are used in managing public and animal health problems in Seharti Samre District, Southern Tigray, Ethiopia.
Methods: Ethnobotanical data were collected from July 1, 2011 to December 30, 201 mainly using semi-structured interviews with informants sampled using purposive sampling technique and through field observations.
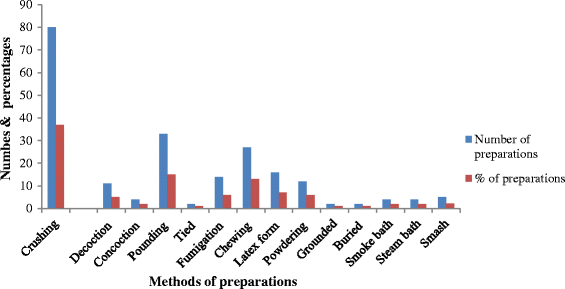
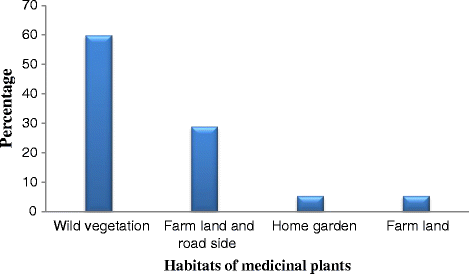
Results: The study revealed the use of 90 medicinal plant species in Seharti Samre District for the treatment of several human and livestock diseases. The plants belonged to 46 families and 82 genera. The majority of the medicinal plants were indicated to be harvested from the wild. Leaf was the most frequently harvested plant part accounting for 44% of the reported plants, followed by roots (16%), whole plants (10%) and seeds (8%). The most widely used method of preparation was crushing (37%), pounding (15%) and chewing (13%). Most medicinal plants were applied internally (64.6%), followed by external application on the skin (35.4%). Febrile illness is the disease group in the study area that scored the highest ICF value (0.97), followed by cardio-vascular problems (0.97) and evil eye (0.95). Different preference ranking exercises were also used to determine the most preferred and potential medicinal plants in the study area.
Conclusion: In Seharti Samre District, medicinal plants are still playing important role in the management of various human and livestock diseases, many of which are harvested for their leaf parts. However, activities of claimed medicinal plants need to be evaluated before recommending them for their wider use. Evaluation priority should be given to medicinal plants with the highest informant agreement as such plants are believed to have better activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional Arabic Palestinian ethnoveterinary practices in animal health care: A field survey in the West Bank (Palestine).J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 22;182:35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26869545
-
Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used to treat human and livestock ailments in Addi Arkay district, northwest Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025 May 9;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13002-025-00775-3. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025. PMID: 40346565 Free PMC article.
-
An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used in Kilte Awulaelo District, Tigray Region of Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013 Sep 8;9(1):65. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-9-65. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2013. PMID: 24011232 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of malaria and related symptoms using traditional herbal medicine in Ethiopia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;213:262-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.034. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29102764 Review.
-
A Systematic Review on Traditional Medicinal Plants Used for the Treatment of Viral and Fungal Infections in Ethiopia.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 16;13:807-815. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S316007. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34429665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In-vivo evaluation of immunomodulatory activity of crude extract and solvent fractions of Cyphostemma adenocaule (Steud. ex A.Rich).Heliyon. 2022 Dec 19;8(12):e12377. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12377. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36590494 Free PMC article.
-
Plants Used as Anticancer Agents in the Ethiopian Traditional Medical Practices: A Systematic Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Oct 3;2018:6274021. doi: 10.1155/2018/6274021. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30402131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rumex nervosus could alleviate streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats by activating Nrf2 signaling.Sci Prog. 2022 Apr-Jun;105(2):368504221102751. doi: 10.1177/00368504221102751. Sci Prog. 2022. PMID: 35619568 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial Activity of Meriandra dianthera Leaf Extracts in Plasmodium berghei-Infected Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 12;2020:8980212. doi: 10.1155/2020/8980212. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32104197 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Uses of Leguminosae among the Karen in Thailand.Plants (Basel). 2019 Dec 13;8(12):600. doi: 10.3390/plants8120600. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31847100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaur R, Kapoor K, Kaur H. Plants as a source of anticancer agents. J Nat Prod Plant Resour. 2011;1:119–24.
-
- Abebe D. Traditional medicine in Ethiopia. The attempt being made to promote it for effective and better utilization. SINET Ethiop J Sci. 1986;9:61–9.
-
- WHO . WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002–2005. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); 2002.
-
- Abebe D. The role of medicinal plants in health care coverage of Ethiopia, the possible benefits of integration. In: Zewdu M, Demissie A, editors. Proceedings of the National Workshop on Conservation and Sustainable use of Medicinal Plants in Ethiopia: 28 April - 01 May 1998. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Institute of Biodiversity Conservation and Research; 2001. pp. 6–21.
-
- Abebe D, Ayehu A. Medicinal plant and enigmatic health practices of north Ethiopia. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Berhanina Selam Printing Enterprise; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical