The absence of the leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 attenuates peripheral inflammation and spinal nociceptive processing following intraplantar formalin injury
- PMID: 25889478
- PMCID: PMC4363055
- DOI: 10.1186/s12990-015-0010-9
The absence of the leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 attenuates peripheral inflammation and spinal nociceptive processing following intraplantar formalin injury
Abstract
Background: Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a potent lipid mediator of inflammation, and its biological effects are mediated primarily through the high affinity LTB4 receptor BLT1. Although numerous studies have reported that LTB4-BLT1 signaling is involved in inflammatory diseases, the role of BLT1 signaling in pain remains undefined. To clarify the role of LTB4-BLT1 signaling in acute inflammatory pain induced by tissue injury, we performed pain behavioral analysis and assessment of local inflammation induced by peripheral formalin injections in BLT1 knockout mice. We examined the phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in the spinal cord both in wild-type and BLT1 knockout mice because phosphorylation of CREB in spinal cord neurons is important for nociceptive sensitization following peripheral injury. We also examined the effect of a BLT1 antagonist on formalin-induced pain responses in mice.
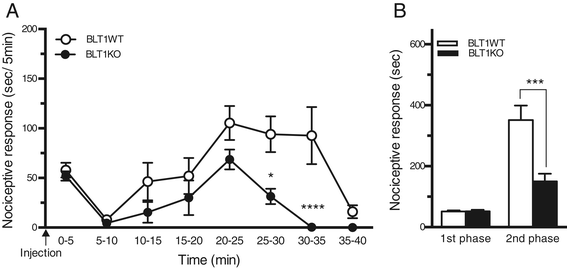
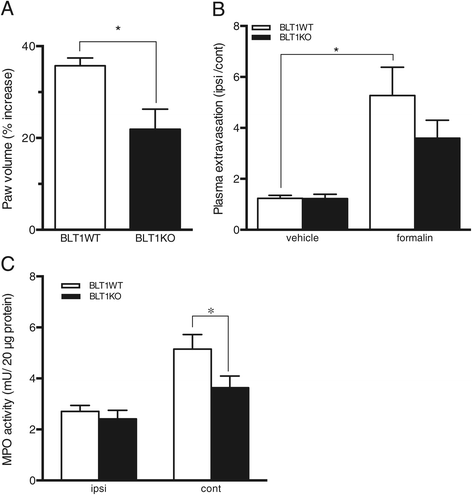
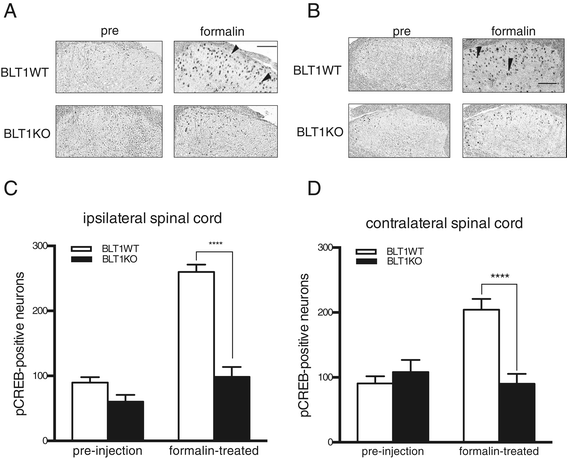
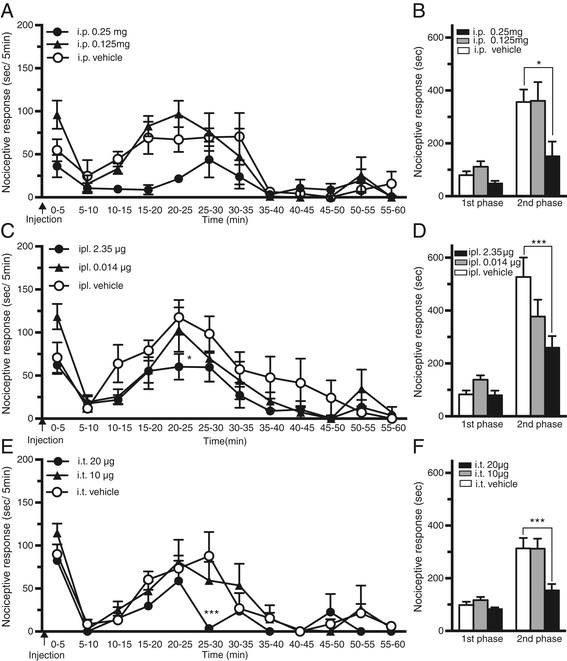
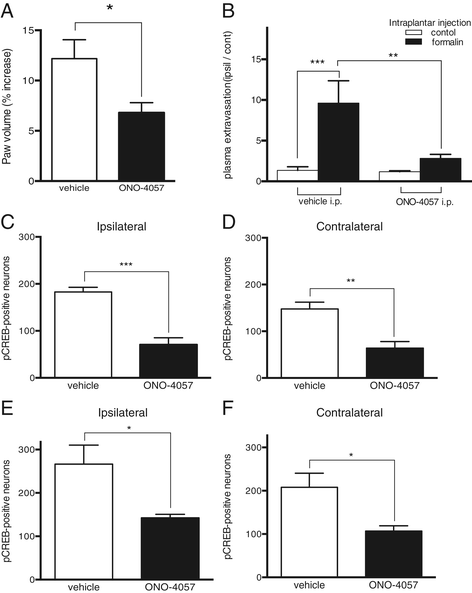
Results: BLT1 knockout mice exhibited markedly attenuated nociceptive responses induced by intraplantar formalin injections. Edema formation and neutrophil infiltration in the paw were significantly decreased in BLT1 knockout mice compared with wild-type mice. Phosphorylation of CREB in the spinal cord after the intraplantar formalin injection was decreased in BLT1 knockout mice. In addition, mice pretreated with a BLT1 antagonist showed reduced nociception and attenuated CREB phosphorylation in the spinal cord after the formalin injection.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that LTB4-BLT1 axis contributes not only to the peripheral inflammation but also to the neuronal activation in the spinal cord induced by intraplantar formalin injections. Thus, LTB4-BLT1 signaling is a potential target for therapeutic intervention of acute and persistent pain induced by tissue injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The leukotriene B4-leukotriene B4 receptor axis promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by modulating neutrophil recruitment.Kidney Int. 2017 Jul;92(1):89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28318626
-
Role of leukotriene B4 (LTB4)-LTB4 receptor 1 signaling in post-incisional nociceptive sensitization and local inflammation in mice.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 20;17(10):e0276135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276135. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36264904 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 signaling by receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE).FASEB J. 2016 May;30(5):1811-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500117. Epub 2016 Jan 26. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26813973
-
Identification, signaling, and functions of LTB4 receptors.Semin Immunol. 2017 Oct;33:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.07.010. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29042026 Review.
-
Role of the LTB4/BLT1 pathway in allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation.Allergol Int. 2006 Jun;55(2):91-7. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.55.91. Allergol Int. 2006. PMID: 17075244 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of conservative interventions for sickness and pain behaviors induced by a high repetition high force upper extremity task.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 29;18(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0354-3. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28356066 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Recombinant Crotamine in Mouse Models of Pain.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 6;13(10):707. doi: 10.3390/toxins13100707. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679000 Free PMC article.
-
The leukotriene B4 receptors BLT1 and BLT2 form an antagonistic sensitizing system in peripheral sensory neurons.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 14;292(15):6123-6134. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769125. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28242764 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvins: Potent Pain Inhibiting Lipid Mediators via Transient Receptor Potential Regulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 10;8:584206. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.584206. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33363143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Pain in Musculoskeletal Diseases: Do You Know Your Enemy?J Clin Med. 2022 May 6;11(9):2609. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092609. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

