Pullulan: a new cytoadhesive for cell-mediated cartilage repair
- PMID: 25889571
- PMCID: PMC4414433
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-015-0011-7
Pullulan: a new cytoadhesive for cell-mediated cartilage repair
Abstract
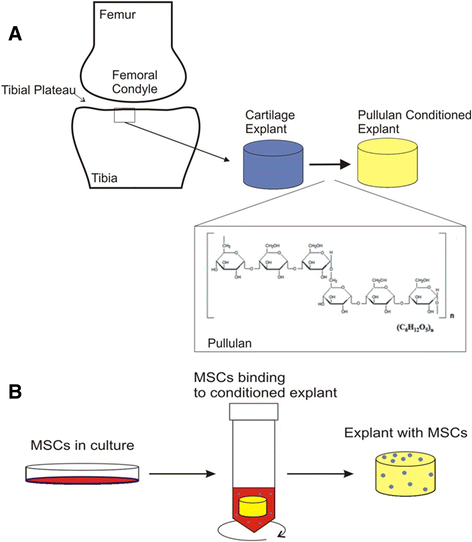
Introduction: Local delivery of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to the acutely injured or osteoarthritic joint retards cartilage destruction. However, in the absence of assistive materials the efficiency of engraftment of MSCs to either intact or fibrillated cartilage is low and localization is further reduced by natural movement of the joint surfaces. It is hypothesised that enhanced engraftment of the delivered MSCs at the cartilage surface will increase their reparative effect and that the application of a bioadhesive to the degraded cartilage surface will provide improved cell retention. Pullulan is a structurally flexible, non-immunogenic exopolysaccharide with wet-stick adhesive properties and has previously been used for drug delivery via the wet surfaces of the buccal cavity. In this study, the adhesive character of pullulan was exploited to enhance MSC retention on the damaged cartilage surface.
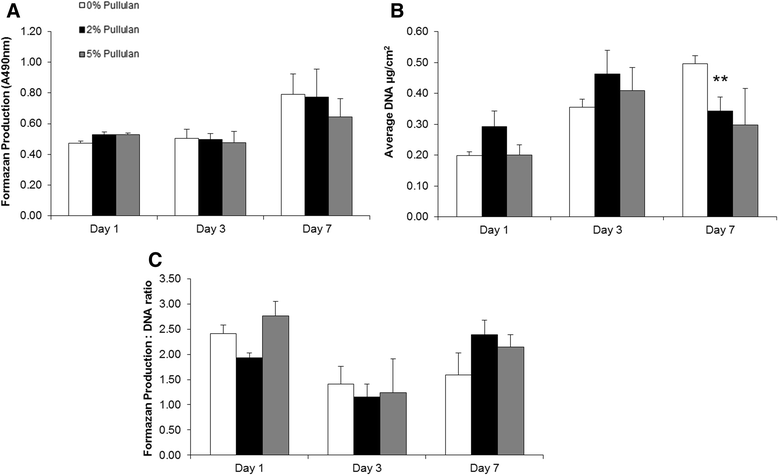
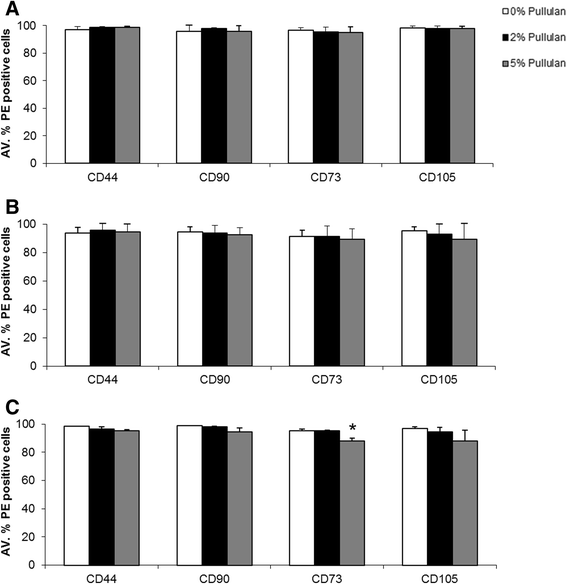
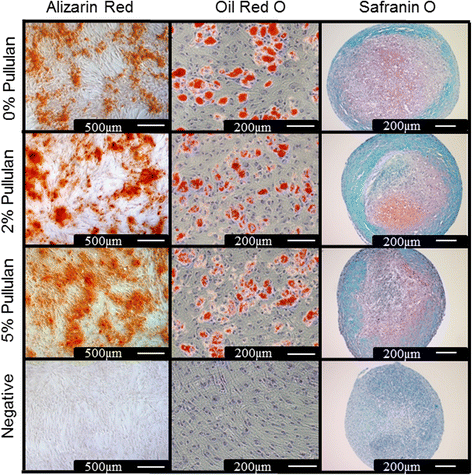
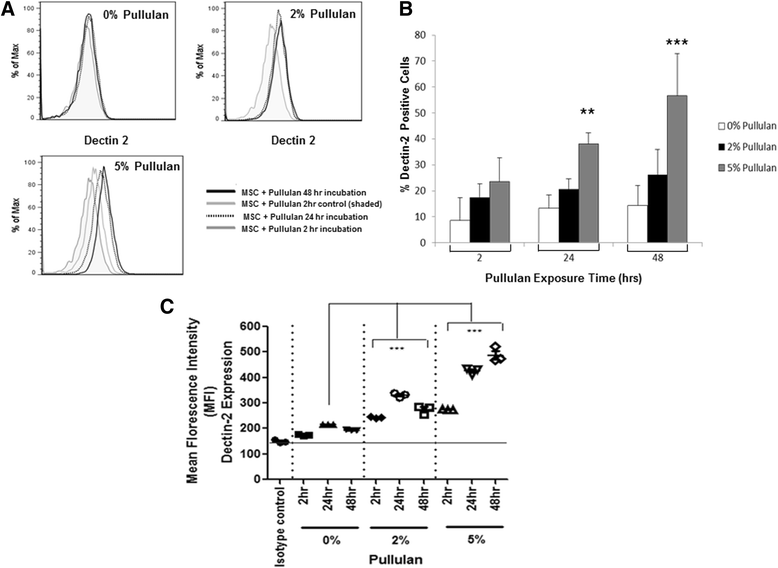
Methods: MSCs labeled with PKH26 were applied to pullulan-coated osteoarthritic cartilage explants to measure cell retention. Cytocompatability was assessed by measuring the effects of prolonged exposure to the bioadhesive on MSC viability and proliferation. The surface phenotype of the cells was assessed by flow cytometry and their multipotent nature by measuring osteogenic, adipogenic and chrondrogenic differentiation. Experiments were also carried out to determine expression of the C-type lectin Dectin-2 receptor.
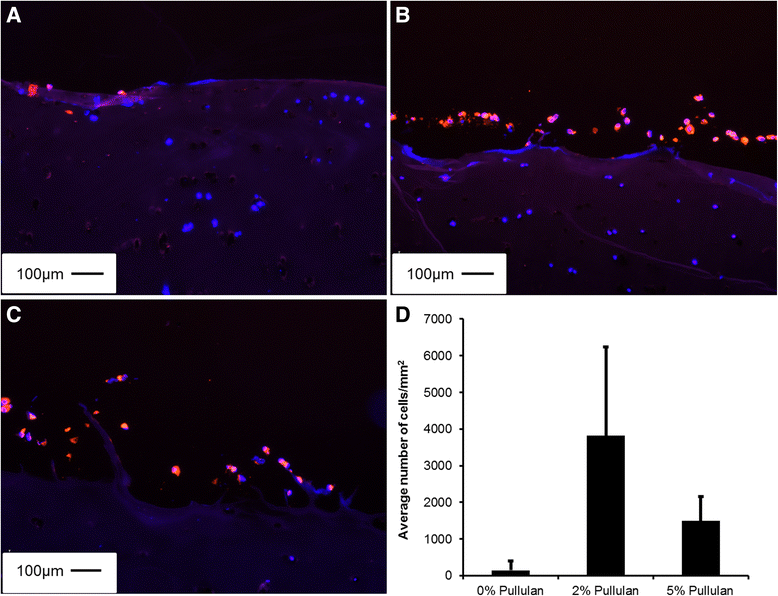
Results: MSCs maintained a stable phenotype following exposure to pullulan in terms of metabolic activity, proliferation, differentiation and surface antigen expression. An increase in osteogenic activity and Dectin-2 receptor expression was seen in MSCs treated with pullulan. Markedly enhanced retention of MSCs was observed in explant culture of osteoarthritic cartilage.
Conclusions: Pullulan is a biocompatible and effective cytoadhesive material for tissue engraftment of MSCs. Prolonged exposure to pullulan has no negative impact on the phenotype, viability and differentiation potential of the cells. Pullulan dramatically improves the retention of MSCs at the fibrillated surface of osteoarthritic articular cartilage. Pullulan causes an upregulation in expression of the Dectin-2 C-type lectin transmembrane complex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro cartilage tissue engineering with 3D porous aqueous-derived silk scaffolds and mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials. 2005 Dec;26(34):7082-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.05.022. Biomaterials. 2005. PMID: 15985292
-
Spontaneous Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Poly-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid Nano-Fiber Scaffold.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 7;11(4):e0153231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153231. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27055270 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells secrete factors that inhibit inflammatory processes in short-term osteoarthritic synovium and cartilage explant culture.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012 Oct;20(10):1186-96. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012. PMID: 22771777
-
The use of mesenchymal stem cells for chondrogenesis.Injury. 2008 Apr;39 Suppl 1:S58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2008.01.038. Injury. 2008. PMID: 18313473 Review.
-
Chondrocytes or adult stem cells for cartilage repair: the indisputable role of growth factors.Injury. 2012 Mar;43(3):259-65. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2011.05.035. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Injury. 2012. PMID: 21696723 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioadhesives for musculoskeletal tissue regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2020 Nov;117:77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.050. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 33031966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospinning Live Cells Using Gelatin and Pullulan.Bioengineering (Basel). 2020 Feb 22;7(1):21. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7010021. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32098366 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Particle Hydrophobicity, Surface Charge, Media pH Value and Complexation with Human Serum Albumin on Drug Release Behavior of Mitoxantrone-Loaded Pullulan Nanoparticles.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2015 Dec 25;6(1):2. doi: 10.3390/nano6010002. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2015. PMID: 28344259 Free PMC article.
-
ARTP mutagenesis of Aureobasidium pullulans RM1603 for high pullulan production and transcriptome analysis of mutants.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Aug 14;206(9):375. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04094-1. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39141138
-
Delivery of streptomycin to the rat colon by use of electrospun nanofibers.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 13;12(1):21503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25769-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36513721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

