Anticholinesterase and antioxidant investigations of crude extracts, subsequent fractions, saponins and flavonoids of atriplex laciniata L.: potential effectiveness in Alzheimer's and other neurological disorders
- PMID: 25889712
- PMCID: PMC4393635
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-015-0011-1
Anticholinesterase and antioxidant investigations of crude extracts, subsequent fractions, saponins and flavonoids of atriplex laciniata L.: potential effectiveness in Alzheimer's and other neurological disorders
Abstract
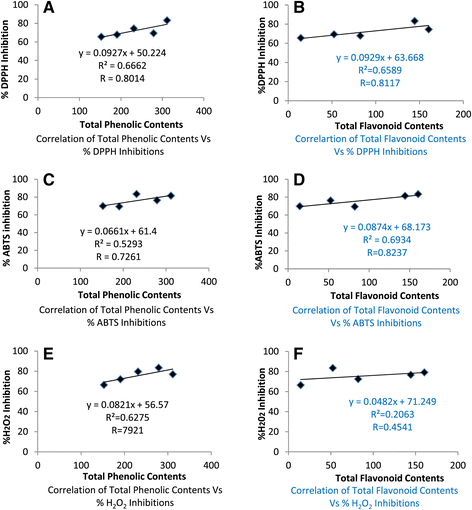
Background: Atriplex laciniata L. was investigated for phenolic, flavonoid contents, antioxidant, anticholinesterase activities, in an attempt to explore its effectiveness in Alzheimer's and other neurological disorders. Plant crude methanolic extract (Al.MeF), subsequent fractions; n-hexane (Al.HxF), chloroform (Al.CfF), ethyl acetate (Al.EaF), aqueous (Al.WtF), Saponins (Al.SPF) and Flavonoids (Al.FLVF) were investigated for DPPH, ABTS and H2O2 free radical scavenging activities. Further these extracts were subjected to acetylcholinesterase (AChE) & butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities using Ellman's assay. Phenolic and Flavonoid contents were determined and expressed in mg Gallic acid GAE/g and Rutin RTE/g of samples respectively.
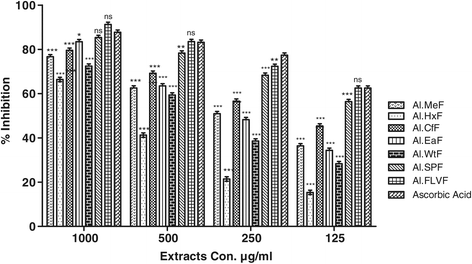
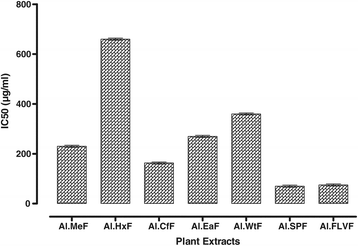
Results: In DPPH free radicals scavenging assay, Al.FLVF, Al.SPF and Al.MeF showed highest activity causing 89.41 ± 0.55, 83.37 ± 0.34 and 83.37 ± 0.34% inhibition of free radicals respectively at 1 mg/mL concentration. IC50 for these fractions were 33, 83 and 82 μg/mL respectively. Similarly, plant extracts showed high ABTS scavenging potential, i.e. Al.FLVF (90.34 ± 0.55), Al.CfF (83.42 ± 0.57), Al.MeF (81.49 ± 0.60) with IC50 of 30, 190 and 70 μg/ml respectively. further, H2O2 percent scavenging was highly appraised in Al.FLVF (91.29 ± 0.53, IC50 75), Al.SPF (85.35 ± 0.61, IC50 70) and Al.EaF (83.48 ± 0.67, IC50 270 μg/mL). All fractions exhibited concentration dependent AChE inhibitory activity as; Al.FLVF, 88.31 ± 0.57 (IC50 70 μg/mL), Al.SPF, 84.36 ± 0.64 (IC50 90 μg/mL), Al.MeF, 78.65 ± 0.70 (IC50 280 μg/mL), Al.EaF, 77.45 ± 0.46 (IC50 270 μg/mL) and Al.WtF 72.44 ± 0.58 (IC50 263 μg/mL) at 1 mg/mL. Likewise the percent BChE inhibitory activity was most obvious in Al.FLVF 85.46 ± 0.62 (IC50 100 μg/mL), Al.CfF 83.49 ± 0.46 (IC50 160 μg/mL), Al.MeF 82.68 ± 0.60 (IC50 220 μg/mL) and Al.SPF 80.37 ± 0.54 (IC50 120 μg/mL).
Conclusions: These results stipulate that A. laciniata is enriched with phenolic and flavonoid contents that possess significant antioxidant and anticholinestrase effects. This provide pharmacological basis for the presence of compounds that may be effective in Alzheimer's and other neurological disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and anticholinesterase investigations of Rumex hastatus D. Don: potential effectiveness in oxidative stress and neurological disorders.Biol Res. 2015 Mar 26;48(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40659-015-0010-2. Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 25857346 Free PMC article.
-
Investigations of anticholinestrase and antioxidant potentials of methanolic extract, subsequent fractions, crude saponins and flavonoids isolated from Isodon rugosus.Biol Res. 2014 Dec 26;47(1):76. doi: 10.1186/0717-6287-47-76. Biol Res. 2014. PMID: 25723481 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic contents, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of crude extract, subsequent fractions and crude saponins from Polygonum hydropiper L.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 May 3;14:145. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-145. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24884823 Free PMC article.
-
Management of oxidative stress and other pathologies in Alzheimer's disease.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Sep;93(9):2491-2513. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02538-y. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31440798 Review.
-
Exploring Antioxidant Properties of Standardized Extracts from Medicinal Plants Approved by the Thai FDA for Dietary Supplementation.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 4;17(5):898. doi: 10.3390/nu17050898. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40077768 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Ameliorative Potential of 3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazinane-2-thione against Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9104. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169104. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201791 Free PMC article.
-
Phytoecdysteroids and Anabolic Effect of Atriplex dimorphostegia: UPLC-PDA-MS/MS Profiling, In Silico and In Vivo Models.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;12(1):206. doi: 10.3390/plants12010206. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36616335 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of an Herbal Formulation of Boswellia sacra Flueck. In Improving Cognitive and Behavioral Symptoms in Patients with Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease.J Res Pharm Pract. 2023 Mar 24;11(3):91-98. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.jrpp_73_22. eCollection 2022 Jul-Sep. J Res Pharm Pract. 2023. PMID: 37304222 Free PMC article.
-
Neurologically Potent Molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha; Isolation, Anticholinesterase Inhibition, and Molecular Docking.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 7;8:327. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00327. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28638340 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical investigation and anti-inflammatory potential of Atriplex leucoclada Boiss.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Dec 16;23(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04281-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 38104070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amel OH, Malek BH, Hichem BJ, Ali L, Mahjoub A, Boulbaba S. Antioxidant and anti-acetylcholinesterase activities of extracts from Rapistrum rugosum in Tunisia. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2013;3(5):367–74. doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808(13)60086-9. - DOI
-
- Thatoi H, Patra J, Das S. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant potential of mangrove plants: a review. Acta Physiol Plant. 2014;36(3):561–9. doi: 10.1007/s11738-013-1438-z. - DOI
-
- De Strooper B, Annaert W. Proteolytic processing and cell biological functions of the amyloid precursor protein. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(11):1857–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

