Systematic comparison of single-chain Fv antibody-fusion toxin constructs containing Pseudomonas Exotoxin A or saporin produced in different microbial expression systems
- PMID: 25889802
- PMCID: PMC4338634
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-015-0202-z
Systematic comparison of single-chain Fv antibody-fusion toxin constructs containing Pseudomonas Exotoxin A or saporin produced in different microbial expression systems
Abstract
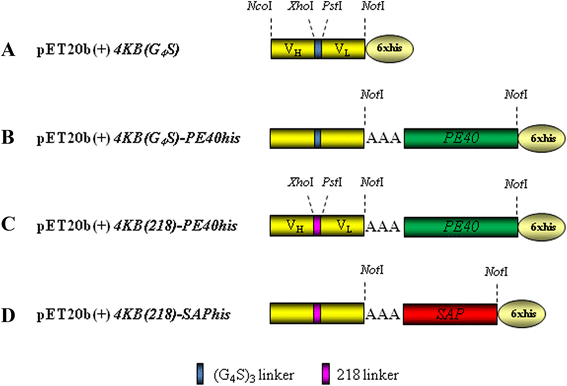
Background: Antibodies raised against selected antigens over-expressed at the cell surface of malignant cells have been chemically conjugated to protein toxin domains to obtain immunotoxins (ITs) able to selectively kill cancer cells. Since latest generation immunotoxins are composed of a toxic domain genetically fused to antibody fragment(s) which confer on the IT target selective specificity, we rescued from the hydridoma 4KB128, a recombinant single-chain variable fragment (scFv) targeting CD22, a marker antigen expressed by B-lineage leukaemias and lymphomas. We constructed several ITs using two enzymatic toxins both able to block protein translation, one of bacterial origin (a truncated version of Pseudomonas exotoxin A, PE40) endowed with EF-2 ADP-ribosylation activity, the other being the plant ribosome-inactivating protein saporin, able to specifically depurinate 23/26/28S ribosomal RNA. PE40 was selected because it has been widely used for the construction of recombinant ITs that have already undergone evaluation in clinical trials. Saporin has also been evaluated clinically and has recently been expressed successfully at high levels in a Pichia pastoris expression system. The aim of the present study was to evaluate optimal microbial expression of various IT formats.
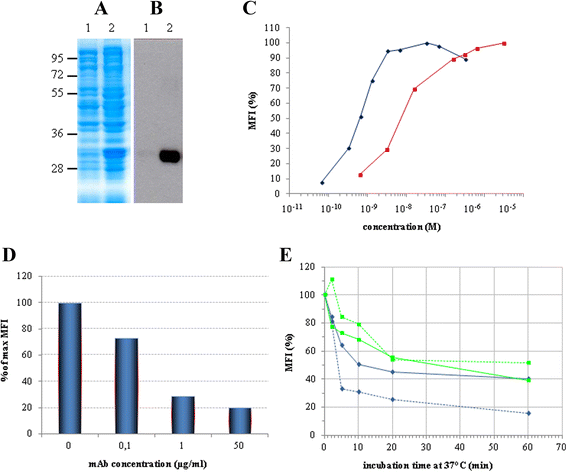
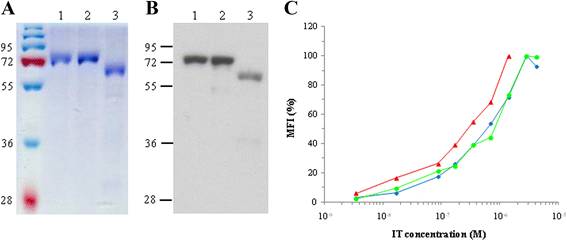
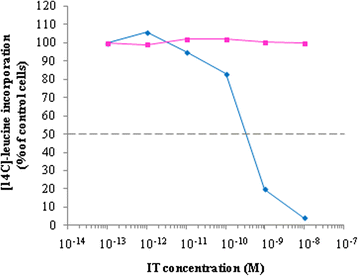
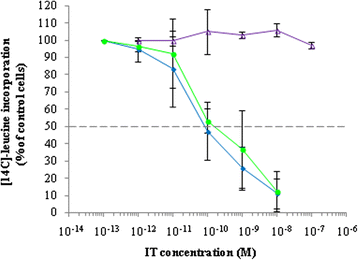
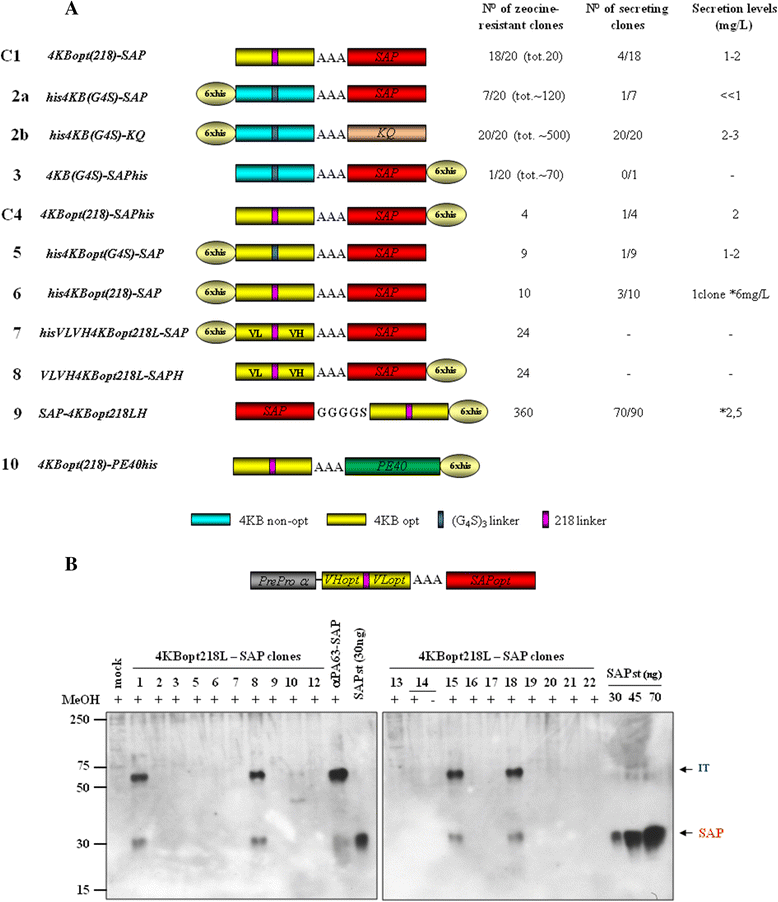
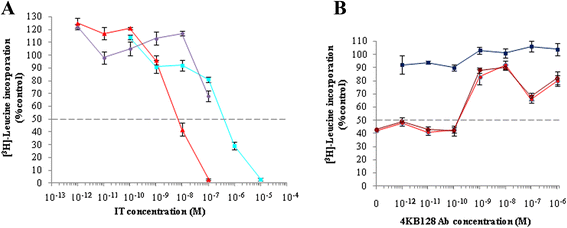
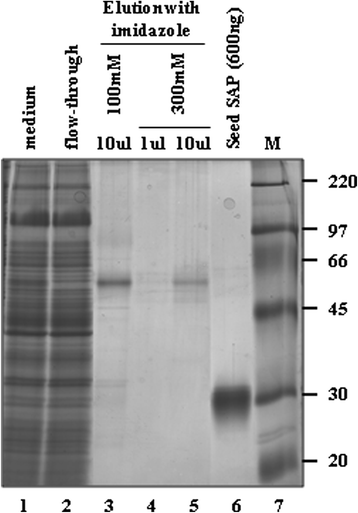
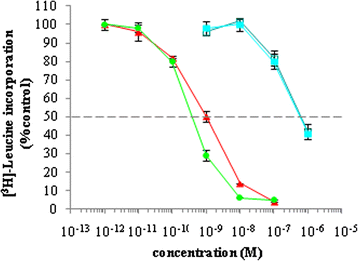
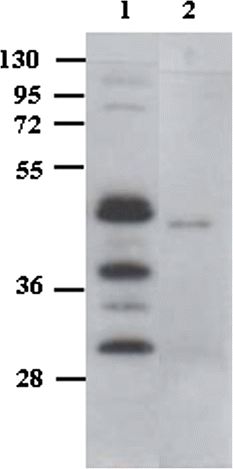
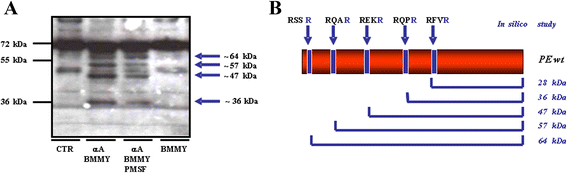
Results: An anti-CD22 scFv termed 4KB was obtained which showed the expected binding activity which was also internalized by CD22+ target cells and was also competed for by the parental monoclonal CD22 antibody. Several fusion constructs were designed and expressed either in E. coli or in Pichia pastoris and the resulting fusion proteins affinity-purified. Protein synthesis inhibition assays were performed on CD22+ human Daudi cells and showed that the selected ITs were active, having IC50 values (concentration inhibiting protein synthesis by 50% relative to controls) in the nanomolar range.
Conclusions: We undertook a systematic comparison between the performance of the different fusion constructs, with respect to yields in E. coli or P. pastoris expression systems and also with regard to each constructs specific killing efficacy. Our results confirm that E. coli is the system of choice for the expression of recombinant fusion toxins of bacterial origin whereas we further demonstrate that saporin-based ITs are best expressed and recovered from P. pastoris cultures after yeast codon-usage optimization.
Figures
References
-
- Vago R, Ippoliti R; Fabbrini, M. S. Current status & Biomedical applications of Ribosome-inactivating proteins. In Antitumor Potential and other Emerging Medicinal Properties of Natural Compounds. Edited by Ng EFFTB: Springer; 2013: 145–179.
-
- Fracasso G, Stirpe F, Colombatti M. Plant toxic proteins, ribosome - inactivating protein - containing conjugates for therapeutic use. Toxic Plant Proteins, Plant Cell Monographs. 2010;18:225–263. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-12176-0_12. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

