Knockdown resistance of Anopheles sinensis in Henan province, China
- PMID: 25890038
- PMCID: PMC4381423
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-015-0662-y
Knockdown resistance of Anopheles sinensis in Henan province, China
Abstract
Background: Vivax malaria was historically epidemic in Henan Province of China and Anopheles sinensis was the main vectors and poor farming communities bare the greatest burden of disease. Knockdown resistance in An. sinensis is one of the mechanisms of resistance against pyrethroids. In the present study, the frequency of mutations from An. sinensis was examined in Henan province, China.
Methods: Anopheles was collected from Kaifeng, Tongbai, Tanghe, Pingqiao, Shihe, and Yongcheng counties of Henan province in 2013. Molecular identification of Anopheles species was conducted by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifying the internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2). Part of the IIS6 domain of the para-type sodium channel protein gene was polymerase chain reaction-amplified and directly sequenced. Frequency and geographic difference of kdr gene mutant types were analysed.
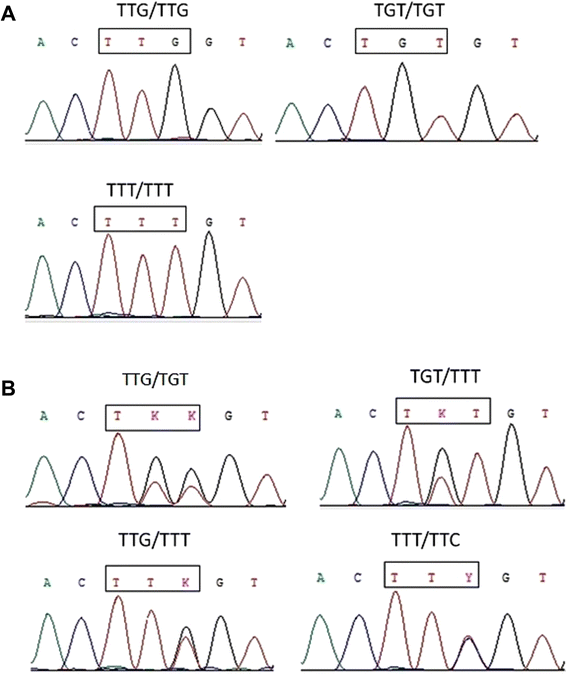
Results: 208 Anopheles were received molecular identification, of which 169 (81.25%) were An. sinensis, 25 (12.02%) were Anopheles yatsushiroensis, and 12 (5.77%) were Anopheles lesteri. A 325 bp fragment of the para-type sodium channel gene including position 1014 was successfully sequenced from 139 Anopheles, of which 125 (89.93%) were An. sinensis, 12 (8.63%) were An. yatsushiroensis, 2 (1.44%) were An. lesteri. The molecular analyses revealed that mutations existed at codon 1014 in An. sinensis but not in An. yatsushiroensis and An. lesteri. Frequency of kdr mutation was 73.60% (92/125) from population of An. sinensis in Henan province, of which L1014F (TTT + TTC) allele frequencies accounted for 46.40% (58/125), and was higher than that of L1014C(TGT) which accounted for 27.20% (34/125) ( χ2 = 55.423, P < 0.001). The frequency of kdr mutation in Kaifeng county was 100% (49/49), and was higher than that of 37.93% (11/29) in Tongbai, 54.55% (6/11) in Pingqiao, 50.00% (3/3) in Shihe, and 62.50% (10/16) in Yongcheng county, respectively (χ2 = 39.538, P < 0.001; χ2 = 24.298, P < 0.001; χ2 = 25.913, P < 0.001; χ2 = 20.244, P < 0.001). While 92.86% (13/14) frequency of kdr mutation was found in Tanghe county, which was higher than that in Tongbai county (χ2 = 11.550, P = 0.0018).
Conclusions: A high frequency of kdr gene mutations from population of An. sinensis in Henan province was found.
Figures
References
-
- Hii J, Rueda LM. Malaria vectors in the Greater Mekong Subregion: overview of malaria vectors and remaining challenges. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2013;44(Suppl 1):73–165. - PubMed
-
- WHO . WHO guidance for countries on combining indoor residual spraying and long-lasting insecticidal nets. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

