Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion
- PMID: 25890096
- PMCID: PMC4334855
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-015-0465-1
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion
Abstract
Background: Bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMSCs) are locally adjacent to the tumor tissues and may interact with tumor cells directly. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of BMSCs on the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells in vitro and the possible mechanism involved.
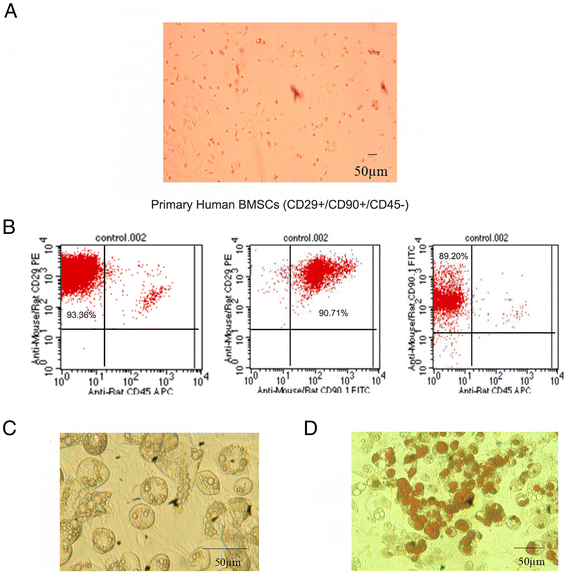
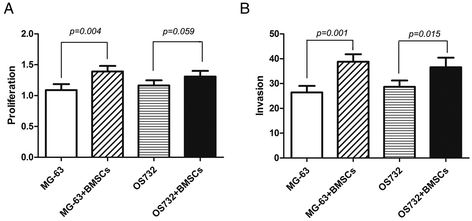
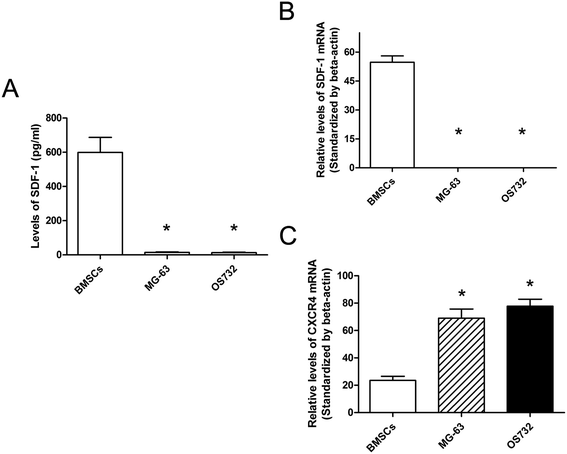
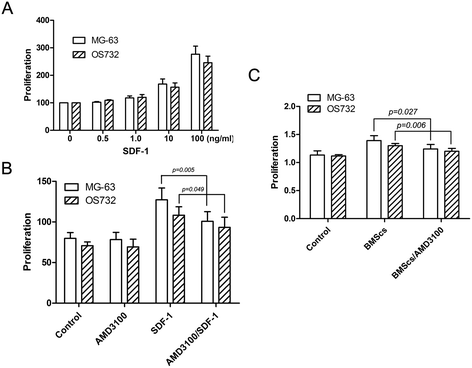
Methods: BMSCs were co-cultured with osteosarcoma cells, and CCK-8 assay was used to measure cell proliferation. The ELISA method was used to determine the concentration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) in the supernatants. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to detect the expression of CXCR4 in osteosarcoma cells and BMSCs. Matrigel invasion assay was performed to measure tumor cell invasion.
Results: SDF-1 was detected in the supernatants of BMSCs, but not in osteosarcoma cells. Higher CXCR4 mRNA levels were detected in the osteosarcoma cell lines compared to BMSCs. In addition, conditioned medium from BMSCs can promote the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells, and AMD3100, an antagonist for CXCR4, can significantly downregulate these growth-promoting effects.
Conclusions: BMSCs can promote the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells, which may involve the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis.
Figures
References
-
- Miyamoto H, Murakami T, Tsuchida K, Sugino H, Miyake H, Tashiro S. Tumor-stroma interaction of human pancreatic cancer: acquired resistance to anticancer drugs and proliferation regulation is dependent on extracellular matrix proteins. Pancreas. 2004;28(1):38–44. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200401000-00006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muerkoster S, Wegehenkel K, Arlt A, Witt M, Sipos B, Kruse ML, et al. Tumor stroma interactions induce chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal carcinoma cells involving increased secretion and paracrine effects of nitric oxide and interleukin-1beta. Cancer Res. 2004;64(4):1331–7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-1860. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

