Artemin Immunotherapy Is Effective in Preventing and Reversing Cystitis-Induced Bladder Hyperalgesia via TRPA1 Regulation
- PMID: 25892657
- PMCID: PMC4489144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.03.014
Artemin Immunotherapy Is Effective in Preventing and Reversing Cystitis-Induced Bladder Hyperalgesia via TRPA1 Regulation
Abstract
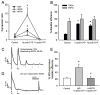
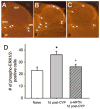
Injury- or disease-induced artemin (ARTN) signaling can sensitize primary afferents and contribute to persistent pain. We demonstrate that administration of an ARTN neutralizing antibody, anti-artemin (α-ARTN), can block the development of, and reverse already established, bladder hyperalgesia associated with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in mice. We further demonstrate that α-ARTN therapy blocks upregulation of TRPA1, an ion channel contributing to persistent bladder pain during cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis, and decreases phospho-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity in regions of the spinal cord receiving bladder afferent input. Thus, α-ARTN is a promising novel therapeutic approach for treatment of bladder hyperalgesia that may be associated with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome, as well as cystitis associated with antitumor or immunosuppressive cyclophosphamide therapy.
Perspective: α-ARTN therapy effectively prevented and reversed ongoing bladder hyperalgesia in an animal model of cystitis, indicating its potential as an efficacious treatment strategy for ongoing bladder pain associated with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome.
Keywords: Bladder; TRPA1; artemin; cystitis; growth factor; pain; visceral.
Copyright © 2015 American Pain Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
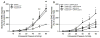
References
-
- Bennett DL, Dmietrieva N, Priestley JV, Clary D, McMahon SB. trkA, CGRP and IB4 expression in retrogradely labelled cutaneous and visceral primary sensory neurones in the rat. Neuroscience letters. 1996;206:33–36. - PubMed
-
- Bielefeldt K, Ozaki N, Gebhart GF. Role of nerve growth factor in modulation of gastric afferent neurons in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G499–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK094593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035790/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS033730/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DKD101681/PHS HHS/United States
- F32 DK094593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS033730/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS0050758/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK101681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA177857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS086749/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050758/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS031826/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK063922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

