Reduction of cardiac and aortic cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic rats fed esters of phytosterol and omega-3 fatty acids
- PMID: 25892771
- PMCID: PMC4397298
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-014-1346-2
Reduction of cardiac and aortic cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic rats fed esters of phytosterol and omega-3 fatty acids
Abstract
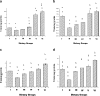
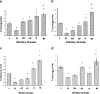
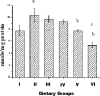
Sterol esters are currently gaining importance because of their recent recognition and application in the food and nutraceutical industries. Phytosterol esters have an advantage over phytosterols, naturally occurring antioxidants, with better fat solubility and compatibility. Antioxidants and hypocholesterolemic agents are known to reduce hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis. The objective of the study was to determine the effects of different sterol esters on cardiac and aortic lipid profile and oxidative stress parameters and on the development of atherosclerosis in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Thirty six rats were divided into six groups: control group, hypercholesterolemic group and four experimental groups fed with EPA-DHA rich sitosterol ester in two different doses, 0.25 g/kg body wt/day and 0.5 g/kg body wt/day, and ALA rich sitosterol ester in two different doses, 0.25 g/kg body wt/day and 0.5 g/kg body wt/day. The sterol esters were gavaged to the rats once daily for 32 days. The cardiac and aortic total cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol and triglyceride level which were elevated in hypercholesterolemia were significantly lowered by both the doses of sterol esters. Antioxidant enzyme activities were significantly decreased and peroxidation product, malondialdehyde was increased in hypercholesterolemia. But administration of both the sterol esters was able to increase enzyme activities and decrease MDA level in the tissues. Histological study of cardiac tissues showed fatty changes in hypercholesterolemic group which was reduced by treatment with sterol esters. The higher doses of sterol-ester caused better effects against hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Hypercholesterolemia; Lipid peroxidation; Phytosterol ester.
Figures


References
-
- Castro SD, Angelantonio ED, Celotto A, Fiorelli M, Passaseo I, Papetti F, Caselli S, Marcantonio A, Cohen A, Pandian N. Short-term evolution (9 months) of aortic atheroma in patients with or without embolic events: a follow-up transoesophageal echocardiographic study. Eur J Echocardio. 2009;10:96–102. doi: 10.1093/ejechocard/jen172. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
