Biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: report of 19 cases
- PMID: 25892877
- PMCID: PMC4394088
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4261
Biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: report of 19 cases
Abstract
Aim: To gain a better understanding of biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (BT-IPMN).
Methods: From January 2000 to December 2013, 19 cases of BT-IPMN were retrospectively identified from a total of 343 biliary tract tumors resected in our single institution. Demographic characteristics, clinical data, pathology, surgical strategies, and long-term follow-up were analyzed.
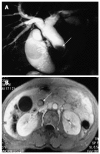
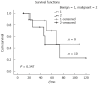
Results: The mean age of the 19 BT-IPMN cases was 53.8 years (range: 25-74 years). The most common symptom was abdominal pain (15/19; 78.9%), followed by jaundice (7/19; 36.8%). Cholangitis was associated with most (16/19; 84.2%) of the BT-IPMN cases. Macroscopically visible mucin was detected in all 19 patients, based on original surgical reports. The most common abnormal preoperative imaging findings for BT-IPMN were bile duct dilation (19/19; 100%) and intraluminal masses (10/19; 52.6%). Thirteen (68.4%) cases involved the intrahepatic bile duct and hilum. We performed left hepatectomy in 11/19 (57.9%), right hepatectomy in 2/19 (10.5%), bile duct resection in 4/19 (21.1%), and pancreatoduodenectomy in 1/19 (5.3%) patients. One (5.3%) patient was biopsied and received a choledochojejunostomy because of multiple tumors involving the right extrahepatic and left intrahepatic bile ducts. Histology showed malignancy in 10/19 (52.6%) patients. The overall median survival was 68 mo. The benign cases showed a non-significant trend towards improved survival compared to malignant cases (68 mo vs 48 mo, P = 0.347). The patient without tumor resection died of liver failure 22 mo after palliative surgery.
Conclusion: BT-IPMN is a rare biliary entity. Complete resection of the tumor is associated with good survival, even in patients with malignant disease.
Keywords: Biliary tract; Cystic tumor; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Mucinous tumor; Papillary tumor.
Figures


References
-
- Sclabas GM, Barton JG, Smyrk TC, Barrett DA, Khan S, Kendrick ML, Reid-Lombardo KM, Donohue JH, Nagorney DM, Que FG. Frequency of subtypes of biliary intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and their MUC1, MUC2, and DPC4 expression patterns differ from pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;214:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Fujii T, Itatsu K, Nakamura K, Minato H, Kasashima S, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Kawashima A, Masuda S, et al. Biliary papillary tumors share pathological features with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Hepatology. 2006;44:1333–1343. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Kim MH, Lee SK, Yoo KS, Park ET, Lim BC, Park HJ, Myung SJ, Seo DW, Min YI. Mucin-hypersecreting bile duct tumor characterized by a striking homology with an intraductal papillary mucinous tumor (IPMT) of the pancreas. Endoscopy. 2000;32:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Oshikiri T, Kashimura N, Katanuma A, Maguchi H, Shinohara T, Shimizu M, Kondo S, Katoh H. Mucin-secreting bile duct adenoma--clinicopathological resemblance to intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas. Dig Surg. 2002;19:324–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

