Metabolomic Analysis of Oxidative and Glycolytic Skeletal Muscles by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/IonizationMass Spectrometric Imaging (MALDI MSI)
- PMID: 25893271
- PMCID: PMC4553944
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-015-1133-y
Metabolomic Analysis of Oxidative and Glycolytic Skeletal Muscles by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/IonizationMass Spectrometric Imaging (MALDI MSI)
Abstract
Skeletal muscles are composed of heterogeneous muscle fibers that have different physiological, morphological, biochemical, and histological characteristics. In this work, skeletal muscles extensor digitorum longus, soleus, and whole gastrocnemius were analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry to characterize small molecule metabolites of oxidative and glycolytic muscle fiber types as well as to visualize biomarker localization. Multivariate data analysis such as principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) were performed to extract significant features. Different metabolic fingerprints were observed from oxidative and glycolytic fibers. Higher abundances of biomolecules such as antioxidant anserine as well as acylcarnitines were observed in the glycolytic fibers, whereas taurine and some nucleotides were found to be localized in the oxidative fibers.
Figures

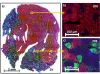


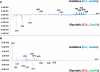

References
-
- Squire JM. Muscle: Design, Diversity, and Disease. The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc.; Menlo Park, California: 1986. pp. 319–322.
-
- Wortmann RL. Diseases of Skeletal Muscle. 8-12. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2000. pp. 208–209.
-
- Schiller J. In: MALDI-MS of Lipids. MALDI MS, editor. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.; KGaA: 2007. pp. 215–243.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

