Triptolide abrogates growth of colon cancer and induces cell cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2F
- PMID: 25893635
- PMCID: PMC5001951
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.46
Triptolide abrogates growth of colon cancer and induces cell cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2F
Abstract
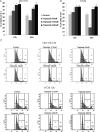
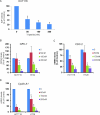
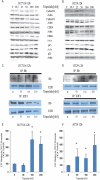
Despite significant progress in diagnostics and therapeutics, over 50 thousand patients die from colorectal cancer annually. Hence, there is urgent need for new lines of treatment. Triptolide, a natural compound isolated from the Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii, is effective against multiple cancers. We have synthesized a water soluble analog of triptolide, named Minnelide, which is currently in phase I trial against pancreatic cancer. The aims of the current study were to evaluate whether triptolide/Minnelide is effective against colorectal cancer and to elucidate the mechanism by which triptolide induces cell death in colorectal cancer. Efficacy of Minnelide was evaluated in subcutaneous xenograft and liver metastasis model of colorectal cancer. For mechanistic studies, colon cancer cell lines HCT116 and HT29 were treated with triptolide and the effect on viability, caspase activation, annexin positivity, lactate dehydrogenase release, and cell cycle progression was evaluated. Effect of triptolide on E2F transcriptional activity, mRNA levels of E2F-dependent genes, E2F1- retinoblastoma protein (Rb) binding, and proteins levels of regulator of G1-S transition was also measured. DNA binding of E2F1 was evaluated by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Triptolide decreased colon cancer cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. Minnelide markedly inhibited the growth of colon cancer in the xenograft and liver metastasis model of colon cancer and more than doubles the median survival of animals with liver metastases from colon cancer. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that at low concentrations triptolide induces apoptotic cell death but at higher concentrations it induces cell cycle arrest. Our data suggest that triptolide is able to induce G1 cell cycle arrest by inhibiting transcriptional activation of E2F1. Our data also show that triptolide downregulates E2F activity by potentially modulating events downstream of DNA binding. Therefore, we conclude that Triptolide and Minnelide are effective against colon cancer in multiple pre-clinical models.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Minnelide Inhibits Androgen Dependent, Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer Growth by Decreasing Expression of Androgen Receptor Full Length and Splice Variants.Prostate. 2017 May;77(6):584-596. doi: 10.1002/pros.23298. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Prostate. 2017. PMID: 28144973 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical evaluation of Minnelide as a therapy for acute myeloid leukemia.J Transl Med. 2019 May 20;17(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1901-8. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31109340 Free PMC article.
-
A preclinical evaluation of Minnelide as a therapeutic agent against pancreatic cancer.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Oct 17;4(156):156ra139. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004334. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23076356 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide and Its Derivatives as Cancer Therapies.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;40(5):327-341. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30975442 Review.
-
Minnelide, a novel drug for pancreatic and liver cancer.Pancreatology. 2015 Jul;15(4 Suppl):S39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2015.05.472. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Pancreatology. 2015. PMID: 26122306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription and Translation Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment.Front Chem. 2020 Apr 21;8:276. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00276. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32373584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notopterol Suppresses IL-17-Induced Proliferation and Invasion of A549 Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Modulation of STAT3, NF-κB, and AP-1 Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 11;24(20):15057. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015057. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894738 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide inhibits proliferation, differentiation and induces apoptosis of osteoblastic MC3T3‑E1 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):7391-7397. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7568. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944904 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide suppresses IL-1β-induced expression of interleukin-8 by inhibiting ROS-Mediated ERK, AP-1, and NF-κB molecules in human gastric cancer AGS cells.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 30;14:1498213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1498213. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39950099 Free PMC article.
-
Co‑treatment with triptolide and RSL3 induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis and ferroptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):202. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13567. Epub 2025 May 16. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40376993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013 Jan;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jul 1;27(19):3109–16. - PubMed
-
- Braun AH, Achterrath W, Wilke H, et al. New systemic frontline treatment for metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 2004 Apr 15;100(8):1558–77. - PubMed
-
- Phillips PA, Dudeja V, McCarroll JA, et al. Triptolide Induces Pancreatic Cancer Cell Death via Inhibition of Heat Shock Protein 70. Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 1;67(19):9407–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

