Strong Correlation Between Concentrations of Tenofovir (TFV) Emtricitabine (FTC) in Hair and TFV Diphosphate and FTC Triphosphate in Dried Blood Spots in the iPrEx Open Label Extension: Implications for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Adherence Monitoring
- PMID: 25895984
- PMCID: PMC4601920
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv239
Strong Correlation Between Concentrations of Tenofovir (TFV) Emtricitabine (FTC) in Hair and TFV Diphosphate and FTC Triphosphate in Dried Blood Spots in the iPrEx Open Label Extension: Implications for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Adherence Monitoring
Abstract
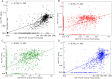
Self-reported adherence to pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has limitations, raising interest in pharmacologic monitoring. Drug concentrations in hair and dried blood spots (DBS) are used to assess long-term-exposure; hair shipment/storage occurs at room temperature. The iPrEx Open Label Extension collected DBS routinely, with opt-in hair collection; concentrations were measured with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. In 806 hair-DBS pairs, tenofovir (TFV) hair levels and TFV diphosphate (DP) in DBS were strongly correlated (Spearman coefficient r = 0.734; P < .001), as were hair TFV/DBS emtricitabine (FTC) triphosphate (TP) (r = 0.781; P < .001); hair FTC/DBS TFV-DP (r = 0.74; P < .001); hair FTC/DBS FTC-TP (r = 0.587; P < .001). Drug detectability was generally concordant by matrix. Hair TFV/FTC concentrations correlate strongly with DBS levels, which are predictive of PrEP outcomes.
Keywords: HIV prevention; PrEP; adherence; dried blood spot (DBS) concentrations; hair concentrations; iPrEx Open Label Extension (OLE); pharmacologic monitoring; pre-exposure prophylaxis; tenofovir/emtricitabine.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

