Caloric restriction increases ketone bodies metabolism and preserves blood flow in aging brain
- PMID: 25896951
- PMCID: PMC4457572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.03.012
Caloric restriction increases ketone bodies metabolism and preserves blood flow in aging brain
Abstract
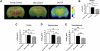
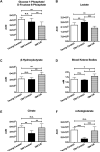
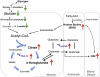
Caloric restriction (CR) has been shown to increase the life span and health span of a broad range of species. However, CR effects on in vivo brain functions are far from explored. In this study, we used multimetric neuroimaging methods to characterize the CR-induced changes of brain metabolic and vascular functions in aging rats. We found that old rats (24 months of age) with CR diet had reduced glucose uptake and lactate concentration, but increased ketone bodies level, compared with the age-matched and young (5 months of age) controls. The shifted metabolism was associated with preserved vascular function: old CR rats also had maintained cerebral blood flow relative to the age-matched controls. When investigating the metabolites in mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle, we found that citrate and α-ketoglutarate were preserved in the old CR rats. We suggest that CR is neuroprotective; ketone bodies, cerebral blood flow, and α-ketoglutarate may play important roles in preserving brain physiology in aging.
Keywords: Aging; Brain metabolism; Cerebral blood flow; Ketone bodies; Mammalian target of rapamycin; Neuroimaging; α-ketoglutarate.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akram M. A focused review of the role of ketone bodies in health and disease. J. Med. Food. 2013;16:965–967. - PubMed
-
- Bentourkia M, Bol A, Ivanoiu A, Labar D, Sibomana M, Coppens A, Michel C, Cosnard G, De Volder AG. Comparison of regional cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in the normal brain: effect of aging. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000;181:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Blazquez C, Woods A, de Ceballos ML, Carling D, Guzman M. The AMP-activated protein kinase is involved in the regulation of ketone body production by astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1999;73:1674–1682. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM, Baltan Tekkok S, Ransom BR. Energy transfer from astrocytes to axons: the role of CNS glycogen. Neurochem. Int. 2004;45:529–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

