Structure-function analysis and genetic interactions of the Yhc1, SmD3, SmB, and Snp1 subunits of yeast U1 snRNP and genetic interactions of SmD3 with U2 snRNP subunit Lea1
- PMID: 25897024
- PMCID: PMC4436669
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.050583.115
Structure-function analysis and genetic interactions of the Yhc1, SmD3, SmB, and Snp1 subunits of yeast U1 snRNP and genetic interactions of SmD3 with U2 snRNP subunit Lea1
Abstract
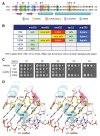
Yhc1 and U1-C are essential subunits of the yeast and human U1 snRNP, respectively, that stabilize the duplex formed by U1 snRNA at the pre-mRNA 5' splice site (5'SS). Mutational analysis of Yhc1, guided by the human U1 snRNP crystal structure, highlighted the importance of Val20 and Ser19 at the RNA interface. Though benign on its own, V20A was lethal in the absence of branchpoint-binding complex subunit Mud2 and caused a severe growth defect in the absence of U1 subunit Nam8. S19A caused a severe defect with mud2▵. Essential DEAD-box ATPase Prp28 was bypassed by mutations of Yhc1 Val20 and Ser19, consistent with destabilization of U1•5'SS interaction. We extended the genetic analysis to SmD3, which interacts with U1-C/Yhc1 in U1 snRNP, and to SmB, its neighbor in the Sm ring. Whereas mutations of the interface of SmD3, SmB, and U1-C/Yhc1 with U1-70K/Snp1, or deletion of the interacting Snp1 N-terminal peptide, had no growth effect, they elicited synthetic defects in the absence of U1 subunit Mud1. Mutagenesis of the RNA-binding triad of SmD3 (Ser-Asn-Arg) and SmB (His-Asn-Arg) provided insights to built-in redundancies of the Sm ring, whereby no individual side-chain was essential, but simultaneous mutations of Asn or Arg residues in SmD3 and SmB were lethal. Asn-to-Ala mutations SmB and SmD3 caused synthetic defects in the absence of Mud1 or Mud2. All three RNA site mutations of SmD3 were lethal in cells lacking the U2 snRNP subunit Lea1. Benign C-terminal truncations of SmD3 were dead in the absence of Mud2 or Lea1 and barely viable in the absence of Nam8 or Mud1. In contrast, SMD3-E35A uniquely suppressed the temperature-sensitivity of lea1▵.
Keywords: 5′; Prp28; Sm proteins; splice site; spliceosome assembly.
© 2015 Schwer and Shuman; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Structure-function analysis of the Yhc1 subunit of yeast U1 snRNP and genetic interactions of Yhc1 with Mud2, Nam8, Mud1, Tgs1, U1 snRNA, SmD3 and Prp28.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4697-711. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku097. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24497193 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis and genetic interactions of the Luc7 subunit of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae U1 snRNP.RNA. 2016 Sep;22(9):1302-10. doi: 10.1261/rna.056911.116. Epub 2016 Jun 27. RNA. 2016. PMID: 27354704 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of the 5' end of yeast U1 snRNA highlights genetic interactions with the Msl5*Mud2 branchpoint-binding complex and other spliceosome assembly factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(15):7485-500. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt490. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23754852 Free PMC article.
-
Branch site recognition by the spliceosome.RNA. 2024 Oct 16;30(11):1397-1407. doi: 10.1261/rna.080198.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39187383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role of U1 snRNP: Splice site selection from a distance.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Jun;1862(6):634-642. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 31042550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
U1 snRNP telescripting: molecular mechanisms and beyond.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov;18(11):1512-1523. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1872963. Epub 2021 Jan 15. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33416026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Will the circle be unbroken: specific mutations in the yeast Sm protein ring expose a requirement for assembly factor Brr1, a homolog of Gemin2.RNA. 2017 Mar;23(3):420-430. doi: 10.1261/rna.059881.116. Epub 2016 Dec 14. RNA. 2017. PMID: 27974620 Free PMC article.
-
Selected humanization of yeast U1 snRNP leads to global suppression of pre-mRNA splicing and mitochondrial dysfunction in the budding yeast.RNA. 2024 Jul 16;30(8):1070-1088. doi: 10.1261/rna.079917.123. RNA. 2024. PMID: 38688558 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics and consequences of spliceosome E complex formation.Elife. 2017 Aug 22;6:e27592. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27592. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28829039 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnections Between RNA-Processing Pathways Revealed by a Sequencing-Based Genetic Screen for Pre-mRNA Splicing Mutants in Fission Yeast.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jun 1;6(6):1513-23. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.027508. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27172183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abovich N, Rosbash M 1997. Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals. Cell 89: 403–412. - PubMed
-
- Abovich N, Liao XC, Rosbash M 1994. The yeast MUD2 protein: An interaction with PRP11 defines a bridge between commitment complexes and U2 snRNP addition. Genes Dev 8: 843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
