The effect of RNA base lesions on mRNA translation
- PMID: 25897124
- PMCID: PMC4482091
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv377
The effect of RNA base lesions on mRNA translation
Abstract
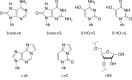
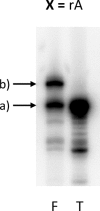
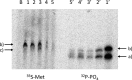
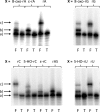
The biological effect of oxidatively damaged RNA, unlike oxidatively damaged DNA, has rarely been investigated, although it poses a threat to any living cell. Here we report on the effect of the commonly known RNA base-lesions 8-oxo-rG, 8-oxo-rA, ε-rC, ε-rA, 5-HO-rC, 5-HO-rU and the RNA abasic site (rAS) on ribosomal translation. To this end we have developed an in vitro translation assay based on the mRNA display methodology. A short synthetic mRNA construct containing the base lesion in a predefined position of the open reading frame was (32)P-labeled at the 5'-end and equipped with a puromycin unit at the 3'-end. Upon in vitro translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates, the encoded peptide chain is transferred to the puromycin unit and the products analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Alternatively, the unlabeled mRNA construct was used and incubated with (35)S-methionine to prove peptide elongation of the message. We find that all base-lesions interfere substantially with ribosomal translation. We identified two classes, the first containing modifications at the base coding edge (ε-rC, ε-rA and rAS) which completely abolish peptide synthesis at the site of modification, and the second consisting of 8-oxo-rG, 8-oxo-rA, 5-HO-rC and 5-HO-rU that significantly retard full-length peptide synthesis, leading to some abortive peptides at the site of modification.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antisense PNA tridecamers targeted to the coding region of Ha-ras mRNA arrest polypeptide chain elongation.J Mol Biol. 1999 Nov 26;294(2):403-16. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3277. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10610767
-
Cell-free translational analysis of messenger ribonucleic acid coding for vitamin D-dependent rat renal calcium-binding protein.Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1652-60. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1652. Endocrinology. 1985. PMID: 2411531
-
Gel shift selection of translation enhancer sequences using messenger RNA display.Anal Biochem. 2011 Feb 1;409(1):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Anal Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20950583
-
Oxidized messenger RNA induces translation errors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 2;104(1):66-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609737104. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17190801 Free PMC article.
-
8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroadenine and 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroadenosine-Chemistry, Structure, and Function in RNA and Their Presence in Natural Products and Potential Drug Derivatives.Chemistry. 2017 May 17;23(28):6706-6716. doi: 10.1002/chem.201605163. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 27960050 Review.
Cited by
-
Abasic and oxidized ribonucleotides embedded in DNA are processed by human APE1 and not by RNase H2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 2;45(19):11193-11212. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx723. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28977421 Free PMC article.
-
Abasic RNA: its formation and potential role in cellular stress response.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):348-358. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2223466. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37322835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endodeoxyribonuclease 1 modulates RNA G-quadruplex folding of miR-92b and controls its expression in cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2317861121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317861121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495925 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of epitranscriptome in shaping stress responses in plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Oct;42(10):1531-1555. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03046-1. Epub 2023 Jul 23. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37481775 Review.
-
Biophysical properties, thermal stability and functional impact of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine on oligonucleotides of RNA-a study of duplex, hairpins and the aptamer for preQ1 as models.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 28;45(4):2099-2111. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw885. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28426093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aas P.A., Otterlei M., Falnes P.O., Vagbo C.B., Skorpen F., Akbari M., Sundheim O., Bjoras M., Slupphaug G., Seeberg E., et al. Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature. 2003;421:859–863. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen H.E., Specht E., Broedbaek K., Henriksen T., Ellervik C., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Tonnesen M., Nielsen P.E., Andersen H.U., Weimann A. RNA modifications by oxidation: a novel disease mechanism. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2012;52:1353–1361. - PubMed
-
- Shan X., Chang Y., Lin C.L. Messenger RNA oxidation is an early event preceding cell death and causes reduced protein expression. FASEB J. 2007;21:2753–2764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

