BLM unfolds G-quadruplexes in different structural environments through different mechanisms
- PMID: 25897130
- PMCID: PMC4482088
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv361
BLM unfolds G-quadruplexes in different structural environments through different mechanisms
Abstract
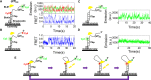
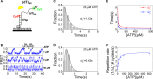
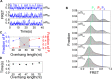
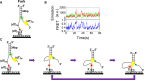
Mutations in the RecQ DNA helicase gene BLM give rise to Bloom's syndrome, which is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by genetic instability and cancer predisposition. BLM helicase is highly active in binding and unwinding G-quadruplexes (G4s), which are physiological targets for BLM, as revealed by genome-wide characterizations of gene expression of cells from BS patients. With smFRET assays, we studied the molecular mechanism of BLM-catalyzed G4 unfolding and showed that ATP is required for G4 unfolding. Surprisingly, depending on the molecular environments of G4, BLM unfolds G4 through different mechanisms: unfolding G4 harboring a 3'-ssDNA tail in three discrete steps with unidirectional translocation, and unfolding G4 connected to dsDNA by ssDNA in a repetitive manner in which BLM remains anchored at the ss/dsDNA junction, and G4 was unfolded by reeling in ssDNA. This indicates that one BLM molecule may unfold G4s in different molecular environments through different mechanisms.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ATP-dependent G-quadruplex unfolding by Bloom helicase exhibits low processivity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 13;43(12):5961-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv531. Epub 2015 May 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25990739 Free PMC article.
-
RecQ-core of BLM unfolds telomeric G-quadruplex in the absence of ATP.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct;42(18):11528-45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku856. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25245947 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insight into the interaction of BLM helicase with intra-strand G-quadruplex structures.Nat Commun. 2014 Nov 24;5:5556. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6556. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25418155 Free PMC article.
-
Helicases FANCJ, RTEL1 and BLM Act on Guanine Quadruplex DNA in Vivo.Genes (Basel). 2019 Oct 31;10(11):870. doi: 10.3390/genes10110870. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31683575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Action and function of helicases on RNA G-quadruplexes.Methods. 2022 Aug;204:110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34509630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition and Unfolding of c-MYC and Telomeric G-Quadruplex DNAs by the RecQ C-Terminal Domain of Human Bloom Syndrome Helicase.ACS Omega. 2020 Jun 11;5(24):14513-14522. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01176. eCollection 2020 Jun 23. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32596589 Free PMC article.
-
A Toolbox for Site-Specific Labeling of RecQ Helicase With a Single Fluorophore Used in the Single-Molecule Assay.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Sep 25;7:586450. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.586450. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33102530 Free PMC article.
-
Branched unwinding mechanism of the Pif1 family of DNA helicases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 3;116(49):24533-24541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1915654116. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31744872 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling the conformational dynamics of I-motif DNA by helicases in ATP-independent mode at acidic environment.iScience. 2021 Dec 6;25(1):103575. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103575. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34988409 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics Studies of DNA with Non-canonical Structure Using NMR Spectroscopy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 11;21(8):2673. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082673. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lohman T.M., Bjornson K.P. Mechanisms of helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:169–214. - PubMed
-
- Cheok C., Bachrati C., Chan K., Ralf C., Wu L., Hickson I. Roles of the Bloom's syndrome helicase in the maintenance of genome stability. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:1456–1459. - PubMed
-
- Goto M. Werner's syndrome: from clinics to genetics. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000;18:760–766. - PubMed
-
- Lindor N.M., Furuichi Y., Kitao S., Shimamoto A., Arndt C., Jalal S. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome due to RECQ4 helicase mutations: report and clinical and molecular comparisons with Bloom syndrome and Werner syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;90:223–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

