Randomized Phase III Trial Comparing ABVD Plus Radiotherapy With the Stanford V Regimen in Patients With Stages I or II Locally Extensive, Bulky Mediastinal Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Subset Analysis of the North American Intergroup E2496 Trial
- PMID: 25897153
- PMCID: PMC4451176
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.8138
Randomized Phase III Trial Comparing ABVD Plus Radiotherapy With the Stanford V Regimen in Patients With Stages I or II Locally Extensive, Bulky Mediastinal Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Subset Analysis of the North American Intergroup E2496 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: The phase III North American Intergroup E2496 Trial (Combination Chemotherapy With or Without Radiation Therapy in Treating Patients With Hodgkin's Lymphoma) compared doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) with mechlorethamine, doxorubicin, vincristine, bleomycin, vinblastine, etoposide, and prednisone (Stanford V). We report results of a planned subgroup analysis in patients with stage I or II bulky mediastinal Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
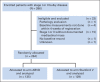
Patients and methods: Patients were randomly assigned to six to eight cycles of ABVD every 28 days or Stanford V once per week for 12 weeks. Two to 3 weeks after completion of chemotherapy, all patients received 36 Gy of modified involved field radiotherapy (IFRT) to the mediastinum, hila, and supraclavicular regions. Patients on the Stanford V arm received IFRT to additional sites ≥ 5 cm at diagnosis. Primary end points were failure-free survival (FFS) and overall survival (OS).
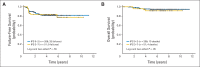
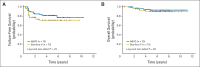
Results: Of 794 eligible patients, 264 had stage I or II bulky disease, 135 received ABVD, and 129 received Stanford V. Patient characteristics were matched. The overall response rate was 83% with ABVD and 88% with Stanford V. At a median follow-up of 6.5 years, the study excluded a difference of more than 21% in 5-year FFS and more than 16% in 5-year OS between ABVD and Stanford V (5-year FFS: 85% v 79%; HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.37 to 1.25; P = .22; 5-year OS: 96% v 92%; HR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.16 to 1.47; P = .19). In-field relapses occurred in < 10% of the patients in each arm.
Conclusion: For patients with stage I or II bulky mediastinal HL, no substantial statistically significant differences were detected between the two regimens, although power was limited. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first prospective trial reporting outcomes specific to this subgroup, and it sets a benchmark for comparison of ongoing and future studies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00003389.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures




References
-
- Hughes-Davies L, Tarbell NJ, Coleman CN, et al. Stage IA-IIB Hodgkin's disease: Management and outcome of extensive thoracic involvement. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;39:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Mauch P, Goodman R, Hellman S. The significance of mediastinal involvement in early stage Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1978;42:1039–1045. - PubMed
-
- Bonfante V, Santoro A, Viviani S, et al. Early stage Hodgkin's disease: Ten-year results of a non-randomised study with radiotherapy alone or combined with MOPP. Eur J Cancer. 1992;29A:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Lister TA, Crowther D, Sutcliffe SB, et al. Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin's disease: Cotswolds meeting. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1630–1636. - PubMed
-
- Bradley AJ, Carrington BM, Lawrance JA, et al. Assessment and significance of mediastinal bulk in Hodgkin's disease: Comparison between computed tomography and chest radiography. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2493–2498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA013650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA017145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA066636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA023318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

